Recombinant Mouse B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator (Btla), partial
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator(Btla),partial
-
货号:CSB-YP742519MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator(Btla),partial
-
货号:CSB-EP742519MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator(Btla),partial
-
货号:CSB-EP742519MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator(Btla),partial
-
货号:CSB-BP742519MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator(Btla),partial
-
货号:CSB-MP742519MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Btla; B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator; B- and T-lymphocyte-associated protein; CD antigen CD272
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Inhibitory receptor on lymphocytes that negatively regulates antigen receptor signaling via PTPN6/SHP-1 and PTPN11/SHP-2. May interact in cis (on the same cell) or in trans (on other cells) with TNFRSF14. In cis interactions, appears to play an immune regulatory role inhibiting in trans interactions in naive T cells to maintain a resting state. In trans interactions, can predominate during adaptive immune response to provide survival signals to effector T cells.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- these data support a role of BTLA on type I NKT cells in limiting anti-tumor immunity. PMID: 29518903
- these data indicate that HVEM/BTLA interactions are dispensable for the formation of de novo host antidonor isotype-specific antibodies following skin transplantation PMID: 26924526
- The percentage of circulating BTLA+CD4+ lymphocytes was significantly higher in mice with LPS-induced acute lung inflammation. PMID: 28164546
- Dendritic cells require BTLA and HVEM to actively adjust tolerizing T cell responses under steady-state conditions. PMID: 27793593
- these data indicate that CCR7 and BTLA cooverexpression imparts an intermediate immune phenotype in mmature dendritic cells when compared to that in CCR7- or BTLA-expressing counterparts that show a more immunocompetent or immunotolerant phenotype PMID: 28393074
- this study shows that miR-155 is involved in the inhibition of BTLA during CD4+ T cell activation PMID: 27350630
- Our findings indicate that BTLA may be involved in the control of inflammatory responses through increasing Foxp3 expression, rather than attenuating IL-17 production, in dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis. PMID: 25973010
- This study uncovers a BTLA-mediated strategy used by the host that permits Listeria proliferation to enable increasing T cell responses for long-term protection. PMID: 25011109
- results support a model whereby BTLA on innate leukocytes is triggered by HVEM and delivers negative signals into BTLA(+) cells, thereby interfering with the protective immune response to this intestinal parasite. PMID: 25595777
- by coordinating expression of BTLA, RORgammat and IL-7 balance suppressive and activation stimuli to regulate gammadelta T cell homeostasis and inflammatory responses PMID: 24315996
- BTLA promotes the pathogenesis of virus-induced fulminant hepatitis by enhancing macrophage viability and function. Targeting BTLA may be a novel strategy for the treatment of FH. PMID: 22637698
- B and T lymphocyte attenuator inhibits LPS-induced endotoxic shock by suppressing Toll-like receptor 4 signaling in innate immune cells. PMID: 23479601
- These findings support role for BTLA and/or HVEM as potential, novel diagnostic markers of innate immune response/status and as therapeutic targets of sepsis. PMID: 22459947
- Combined blockade of BTLA and herpesvirus entry mediator (HVEM) does not inhibit donor T cell infiltration into graft-versus-host reaction organs; instead, it decreases the functional activity of the alloreactive T cells. PMID: 22490863
- During increased resistance to malaria infection, BTLA regulates production of proinflammatory cytokines in a T cell-intrinsic way, while B cells intrinsically regulate the production of nonlethal Plasmodium yoelii 17NL-specific antibodies. PMID: 21998455
- BTLA receptor is a potential immunoregulatory target for the modulation of cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-mediated PMID: 21978997
- dichotomous functions of BTLA in GVHD to serve as a costimulatory ligand of HVEM and to transmit inhibitory signal as a receptor PMID: 21220749
- The effect of the B and T lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA; CD272) on cluster of differentiation (CD)4(+) T cell-mediated corneal immunopathology during murine herpetic stromal keratitis, was investigated. PMID: 21042564
- Targeting of B and T lymphocyte associated (BTLA) prevents graft-versus-host disease without global immunosuppression. PMID: 21078889
- BTLA suppresses IgG2a and IgG2b production in vivo by inhibiting interleukin (IL)-21 production from follicular T helper (Th) cells. PMID: 20660710
- The subcellular localization of BTLA in mouse T cells in a steady state, as well as upon activation, was examined. PMID: 19892849
- The extracellular domain of BTLA binds herpesvirus entry mediator (HVEM), blocks BTLA-HVEM interactions and significantly improves antitumor immunity in cervical cancer when combined with heat shock protein (HSP)70 vaccine. PMID: 19923459
- BTLA is a third inhibitory receptor on T lymphocytes with similarities to cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (CTLA-4) and programmed death 1 (PD-1). PMID: 12796776
- BTLA is expressed by all mature lymphocytes, splenic macrophages, and mature, but not immature bone marrow-derived dendritic cells. BTLA is implicated as a negative regulator of the activation and/or function of various hemopoietic cell types. PMID: 15128774
- Binding of HVEM to BTLA attenuates T cell activation, identifying HVEM/BTLA as a coinhibitory receptor pair. PMID: 15647361
- existence of three distinct BTLA alleles among 23 murine strains, differing both in Ig domain structure and cellular distribution of expression on lymphoid subsets PMID: 15749870
- BTLA adds to the growing list of cell surface proteins that are potential targets to down-modulate T cell function. PMID: 16272294
- these receptors are critical determinants of the duration of allergic airway inflammation PMID: 16547224
- BTLA had a regulatory effect on the expression of B7 on dendritic cells. PMID: 16805995
- mice deficient in full-length BTLA or its ligand, herpesvirus entry mediator, had increased number of memory CD8(+) T cells PMID: 17206146
- BTLA inhibits antigen-induced eosinophil recruitment into the airways by preventing IL-5 production from Th2 cells. PMID: 17541277
- These results suggest that BTLA functions to regulate T-cell signaling by controlling the phosphorylated form of TCRzeta accumulation in the lipid raft. PMID: 17607320
- BTLA-herpesvirus entry mediator (HVEM) interactions are functionally involved in T cell regulation during Plasmodium berghei strain ANKA blood-stage malaria and regulate sequestration of T cells in brain capillaries. PMID: 17785848
- The LTbetaR and HVEM-BTLA pathways form an integrated signaling network regulating DC homeostasis. PMID: 18097025
- BTLA employs a conserved binding mode for herpesvirus entry mediator recognition. PMID: 18178834
- HVEM triggers inhibitory signals by acting as a ligand that binds to B and T lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA), an immunoglobulin super family member. PMID: 18519647
- BTLA plays an important role in the maintenance of immune tolerance and the prevention of autoimmune diseases. PMID: 18668554
- role of BTLA on the proliferation, recruitment, and survival of T cells in response to inhaled allergen PMID: 18713967
- demonstrate an important role for BTLA in the induction of peripheral tolerance of both CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells in vivo PMID: 19342624
- B and T lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA) coinhibitory signaling of natural killer T (NKT) cells is required to temper early inflammation in a model of acute hepatitis. PMID: 19535622
- role in down-modulating immune responses[REVIEW] PMID: 19567411
- engagement of the newly discovered coinhibitory receptor B and T lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA) by herpesvirus entry mediator (HVEM) is critical for negatively regulating early host immunity against intracellular bacteria. PMID: 19587015
- the HVEM-BTLA cis-complex competitively inhibits HVEM activation by ligands expressed in the surrounding microenvironment, thus helping maintain T cells in the naive state. PMID: 19915044
- BTLA functions as the inhibitory coreceptor of NKT cells PMID: 19949073
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein.
-
组织特异性:Expressed in splenic T- and B-cells as well as lymph node tissues but very weakly in somatic tissues. Also expressed in macrophages, NK cells and dendritic cells. A polymorphic tissue distribution between several strains is seen.
-
数据库链接:
Most popular with customers
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
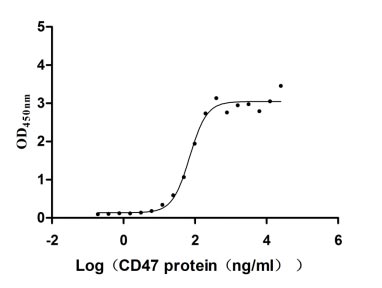
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
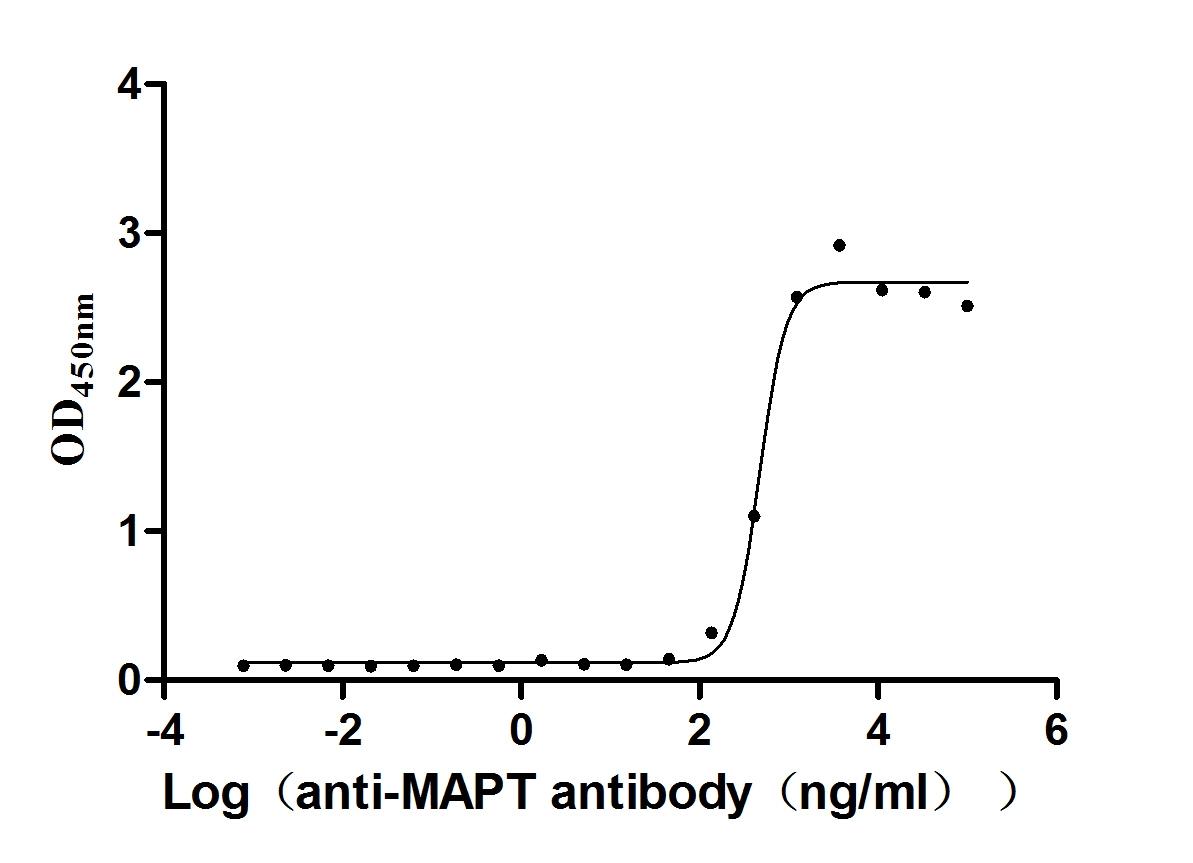
Recombinant Mouse Microtubule-associated protein tau (Mapt) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
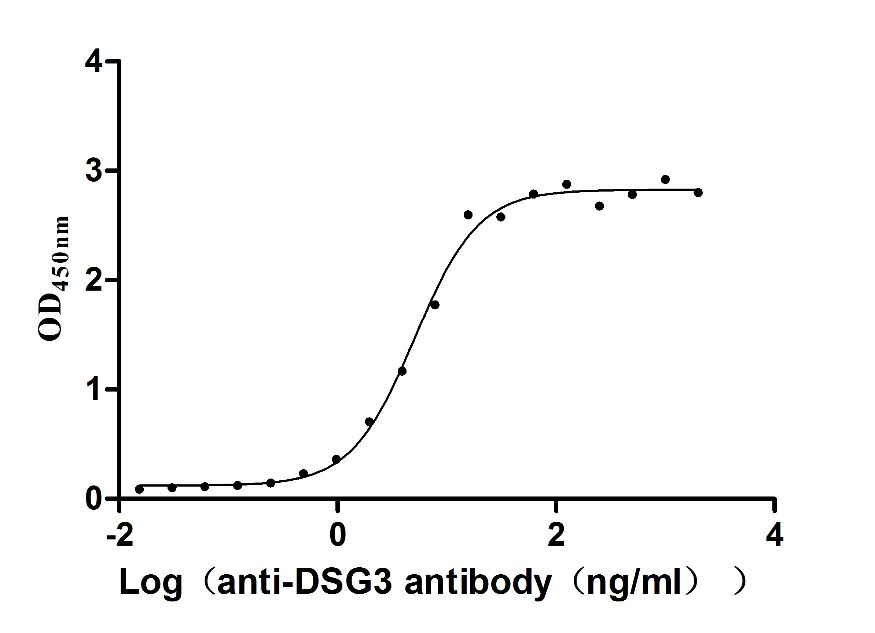
Recombinant Human Desmoglein-3 (DSG3), partial (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
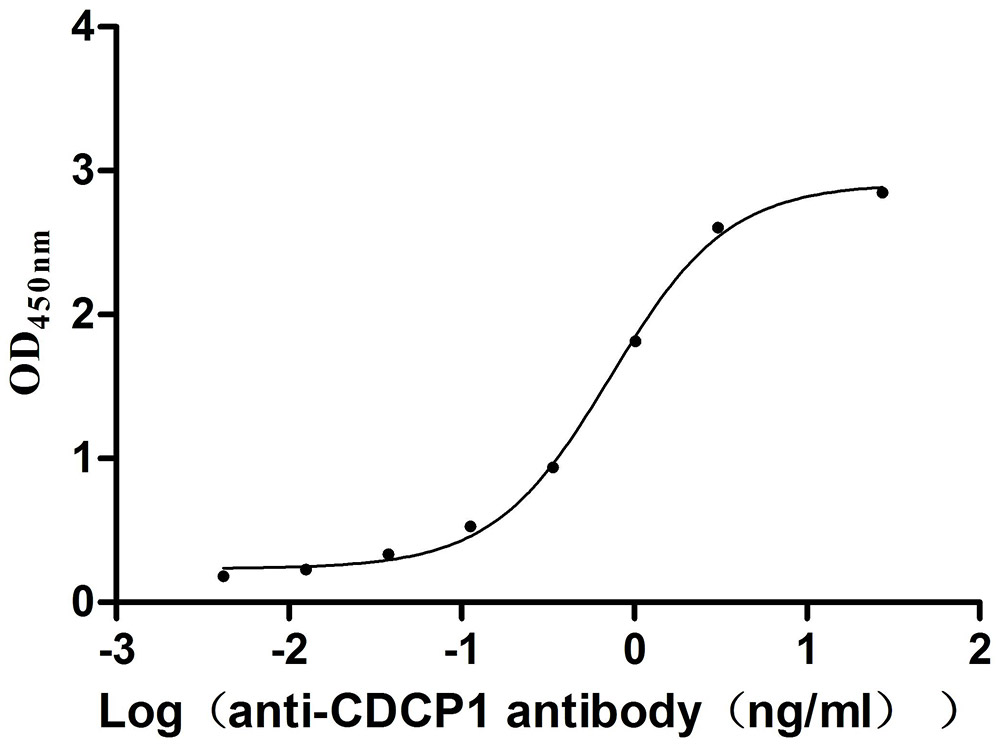
Recombinant Mouse CUB domain-containing protein 1 (Cdcp1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
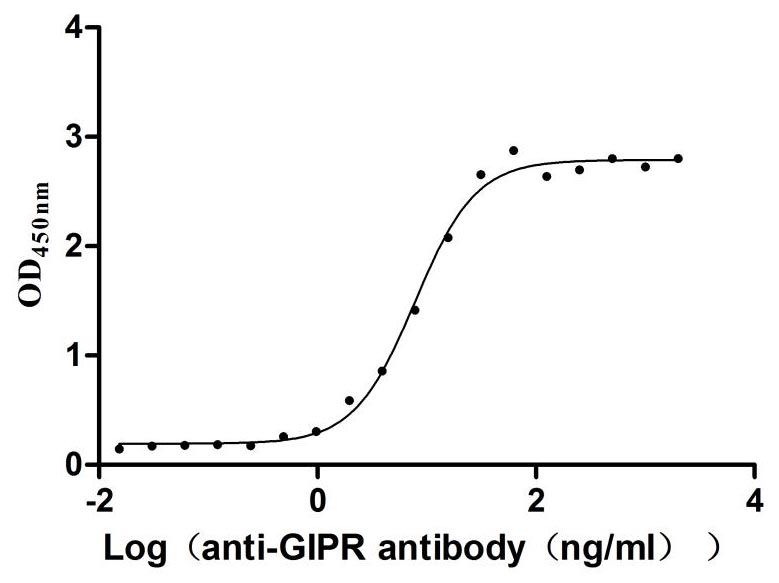
Recombinant Rat Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor (Gipr), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
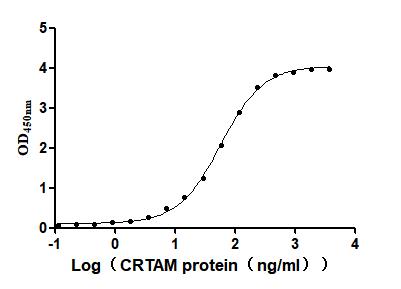
Recombinant Mouse Cytotoxic and regulatory T-cell molecule (Crtam), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
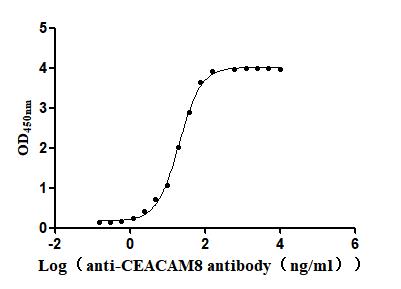
Recombinant Human Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 8(CEACAM8) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
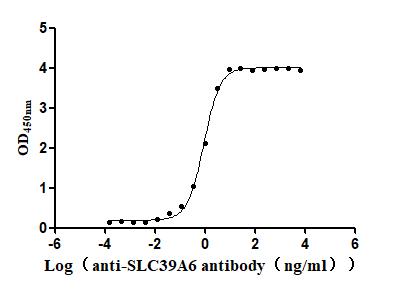
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Zinc transporter ZIP6 isoform X1(SLC39A6),partial (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)