Recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae Heat shock protein 104 (HSP104), partial
-
中文名称:酿酒酵母HSP104重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP329079SVG
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:酿酒酵母HSP104重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP329079SVG
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:酿酒酵母HSP104重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP329079SVG-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:酿酒酵母HSP104重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP329079SVG
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:酿酒酵母HSP104重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP329079SVG
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:HSP104
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:HSP104; YLL026W; L0948; Heat shock protein 104; Protein aggregation-remodeling factor HSP104
-
种属:Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Required, in concert with Hsp40 (YDJ1) and Hsp70 (SSA1) and small Hsps (HSP26), for the dissociation, resolubilization and refolding of aggregates of damaged proteins after heat or other environmental stresses. Extracts proteins from aggregates by unfolding and threading them in an ATP-dependent process through the axial channel of the protein hexamer, after which they can be refolded by components of the Hsp70/Hsp40 chaperone system. Substrate binding is ATP-dependent, and release of bound polypeptide is triggered by ATP hydrolysis. Also responsible for the maintenance of prions by dissociating prion fibrils into smaller oligomers, thereby producing transmissible seeds that can infect daughter cells during mitosis and meiosis. Loss of HSP104 can cure yeast cells of the prions [PSI+], [URE3] and [PIN+]. Excess HSP104 can also specifically cure cells of [PSI+].
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Our observations suggest that Hsp104 pore loops have non-overlapping functions in protein disaggregation and together coordinate substrate binding, unfolding, and translocation through the Hsp104 hexamer. PMID: 29175998
- The role of Hsp104 protein in protein folding in the ribosome and prion propagation PMID: 27633137
- most yeast prion [PSI(+)] variants arising spontaneously in an hsp104(T160M) strain are cured by restoration of just normal levels of the wild type Hsp104. The curing activity of Hsp104 constitutes an antiprion system, culling many variants of the [PSI+] prion at normal Hsp104 levels. PMID: 28484020
- this study reports cryo-electron microscopy structures at near-atomic resolution of Hsp104 in different translocation states. PMID: 28619716
- We demonstrate that physiological levels of ADP highly limit Hsp104 activity. This inhibition, however, is moderated by the Hsp70 chaperone, which allows efficient disaggregation by supporting Hsp104 binding to aggregates but not to non-aggregated, disordered protein substrates. PMID: 27223323
- Hsp31 can modulate prion status in cooperation with Hsp104 because it inhibits Sup35 aggregate formation and potentiates [PSI(+)] prion curing upon overexpression of Hsp104 PMID: 27690738
- The cryo-EM structure of wild-type Saccharomyces cerevisiae Hsp104 in the ATP state. PMID: 27478928
- curing by Hsp104 overexpression depends on both the trimming ability of the fungal Hsp104 homolog and the strength of the [PSI(+)] variant: the greater the trimming activity of the Hsp104 homolog and the weaker the variant, the greater the curing. PMID: 28373280
- Study found that Tsa1 and Hsp70 physically interact and that hyperoxidation of Tsa1 by hydrogen peroxide is required for the recruitment of the Hsp70 chaperones and the Hsp104 disaggregase to misfolded and aggregated proteins during aging, but not heat stress. PMID: 27264606
- Kinetics of Formation and Asymmetrical Distribution of Hsp104-Bound Protein Aggregates in Yeast PMID: 27074685
- ATPase activity at NBD1 or NBD2 is sufficient for Hsp104 potentiation. PMID: 26747608
- A latent Hsp104 "holdase" activity is sufficient to delay the higher-order assembly of nascent mutant septins PMID: 25673805
- A key role for Sse1 (Hsp110), in cooperation with Hsp104, in regulating the length and assembly state of [PSI+] prion fibrils in vivo. PMID: 26438827
- Suramin depends upon ATPase events at both NBDs to exert its maximal effect. Suramin could develop into an important mechanistic probe to study Hsp104 structure and function PMID: 25299406
- Our results highlight the importance of feedback regulation in building epigenetic memory and uncover Hsp104 and Dicer as homeostatic controllers PMID: 25543137
- Data indicate that Hsp104-deleted strain resulted in to lower cytotoxicity and increased cell viability. PMID: 25161148
- Hsp70/40 stimulated the association of Hsp104 with aggregates and increased the duration of this association PMID: 25635051
- Data show that Hsp104 N-terminal domain is critical for activity of potentiated Hsp104 variants. PMID: 25620563
- Hsp104 overexpression cures [PSI(+)] by dissolution of the prion seeds in a two-step process. PMID: 24632242
- Trehalose led to Hsp104 overexpression in mutant human-huntingtin-expressing cells, and resulted in rescue of the endocytotic defect in the yeast cell. PMID: 24248470
- Regulation of the M-domain of Hsp104 is critical for efficient prion propagation. PMID: 24466354
- Both mutants Hsp104-G254D and Hsp104-G730D impair weak SUP36 propagation, but are capable of propagating the less stable strong SUP36 variant to some extent. PMID: 24064980
- this study investigated the interaction between Hsp104 and Sup35 in the lysates of [PSI(+)] cells using fluorescence cross-correlation spectroscopy (FCCS), which can analyze the codiffusion events of different fluorophores. PMID: 24216111
- we were able to identify the functions of Hsp104 and the osmoprotectant trehalose in solubilising mutant huntingtin. PMID: 24412307
- Identify soluble, more SDS-sensitive oligomers of Sup35 as prion propagons and show that Hsp104 plays a role in their maintenance. PMID: 24145167
- full-length Hsp70 on its own could activate the Hsp104 hexamer by promoting intersubunit coordination, suggesting that Hsp70 is an activator of the Hsp104 motor. PMID: 23650362
- ATPase-deficient Hsp104 mutants did not restore mobility, suggesting that, rather than preventing aggregation, Hsp104 disaggregates mutant SOD1 after it has aggregated PMID: 23583391
- Hsp104 remodels the distinct intermolecular contacts of different synthetic Sup35 prion strains in a way that selectively amplifies prions encoding strong [PSI(+)] and simultaneously eliminates prions encoding weak [PSI(+)]. PMID: 23177195
- establish that Hsp104 hexamers adapt different mechanisms of intersubunit collaboration to disaggregate stress-induced aggregates versus amyloid. PMID: 23141537
- Study investigated the interaction between Hsp104 and Sup35, the priongenic protein in yeast that forms the [PSI ] prion; found that a 20-amino acid segment within the highly-charged, unstructured middle domain of Sup35 contributes to the physical interaction between the middle domain and Hsp104. PMID: 22561166
- findings point to crucial roles of Hsp70, Sti1, and Hsp90 for efficient curing by overexpressed Hsp104 and provide evidence supporting the earlier suggestion that destruction of prions by protein disaggregation does not adequately explain the curing PMID: 20479121
- fitted structures confirm that the subunit arrangement of Hsp104 is similar to other AAA+ machines, and place the M-domains on the Hsp104 exterior, where they can potentially interact with large, aggregated proteins. PMID: 20404203
- Neither Sti1 nor Cpr7 is necessary for prion propagation but the authors show that deletion of the STI1 and CPR7 genes leads to a significant reduction in the generation of [psi(-)] cells by Hsp104 overexpression. PMID: 20014008
- Hsp104-dependent degradation of mutant ataxin-1 may account for the ability of this chaperone to reduce toxicity caused by polyQ-repeat proteins. PMID: 19995551
- the direct effects of Hsp104 concentration on the different conformational states of NM, the prion domain of Sup35 were defined PMID: 15155912
- Hsp104 plus other factor(s) in the yeast cytosol are required for severing Sup35 prion fiber. PMID: 15448141
- Hsp104 is essential to dissociate substrate proteins from aggregates with incorporated small heat shock proteins PMID: 15843375
- Hsp104 facilitates disaggregation and reactivates aggregated proteins with assistance from Hsp70 (Ssa1) and Hsp40 (Ydj1) PMID: 15845535
- upon association with a polypeptide, a conformational change occurs within Hsp104 that strongly reduces the dynamics of nucleotide exchange and commits the bound polypeptide to ATP hydrolysis PMID: 16135516
- Yeast hsp104 overexpressed in transgenic mice that express the first 171 residues of mutant human huntingtin reduces polyglutamine aggregation and increases survival of Huntington's disease (HD) model mice by 20%. PMID: 16204350
- Despite retention of [PSI(+)], excess Hsp104 decreases toxicity of overproduced Sup35 in [PSI(+)] strains. PMID: 16307272
- Hsp104 mutants defective in threading peptides through the hexamer pore had reduced ability to support [PSI(+)] in proportion to protein resolubilization defects PMID: 16582428
- Hsp104 catalyzes de novo prion nucleation from soluble, native protein. PMID: 16885031
- HSP104 molecules undergoing quality control in THO/sub2 mutants fall into two populations: One that is quickly degraded after transcription induction and another that escapes rapid decay and accumulates in foci associated with HSP104 transcription site. PMID: 17410208
- First report of the crystallization of a eukaryotic member of the Hsp100 family of molecular chaperones PMID: 17768355
- Carbonylated proteins are associated with Hsp104p-containing protein aggregates and these aggregates, like oxidized proteins, are retained in the progenitor cell during cytokinesis by a Sir2p-dependent proces. PMID: 17908928
- elimination of the whole C-terminal extension results in an Hsp104 molecule which is unable to assemble and becomes aggregation prone at high temperature, highlighting a novel structural role for this region PMID: 18197703
- Data show that Hsp104 variant that harbour a reduced threading activity were affected in both protein disaggregation and prion propagation, demonstrating that substrate threading represents the common mechanism for processing both substrate classes. PMID: 18312264
- Hsp104 regulates the gene expression on the posttranscriptional level. PMID: 18389629
- analysis of chromatin reassembly at HSP104 PMID: 18445041
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Note=Shuttles between the cytoplasm and the nucleus in an importin KAP95- and KAP121-dependent and an exportin XPO1-dependent manner. Accumulation in the nucleus is enhanced by severe heat shock. In the cytoplasm, concentrates on a perivacuolar compartment, the 'insoluble protein deposit' (IPOD), in which terminally aggregated proteins are sequestered. It is also found, to a lesser extent, at a 'juxtanuclear quality control' (JUNQ) compartment, where soluble ubiquitinated misfolded proteins accumulate.
-
蛋白家族:ClpA/ClpB family
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: sce:YLL026W
STRING: 4932.YLL026W
Most popular with customers
-
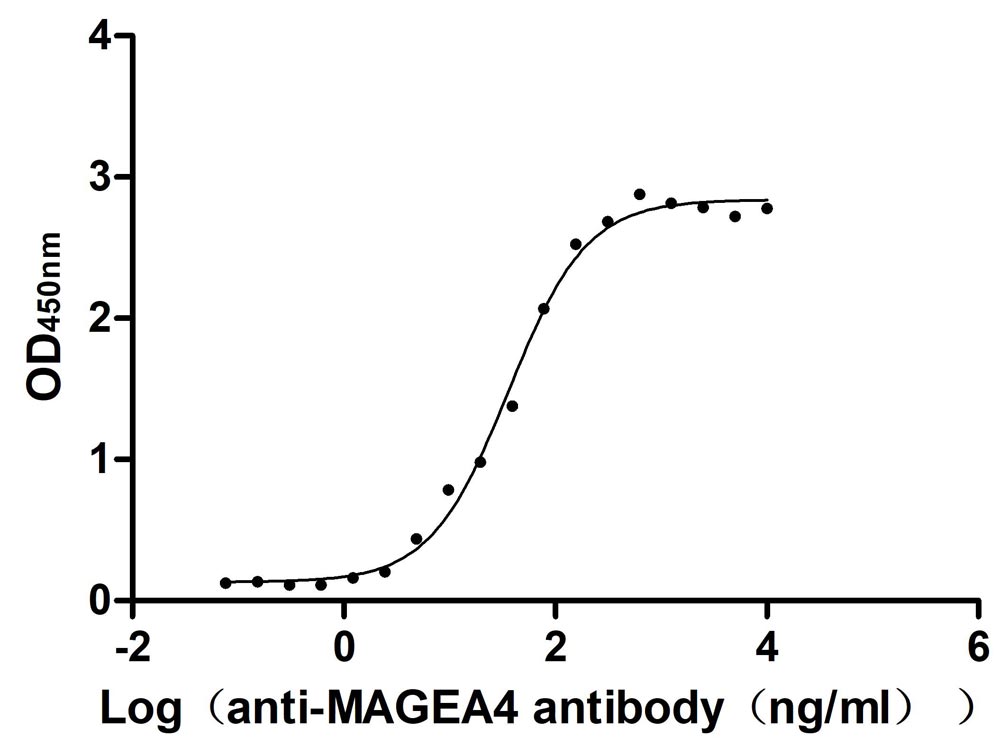
Recombinant Human Melanoma-associated antigen 4 (MAGEA4) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
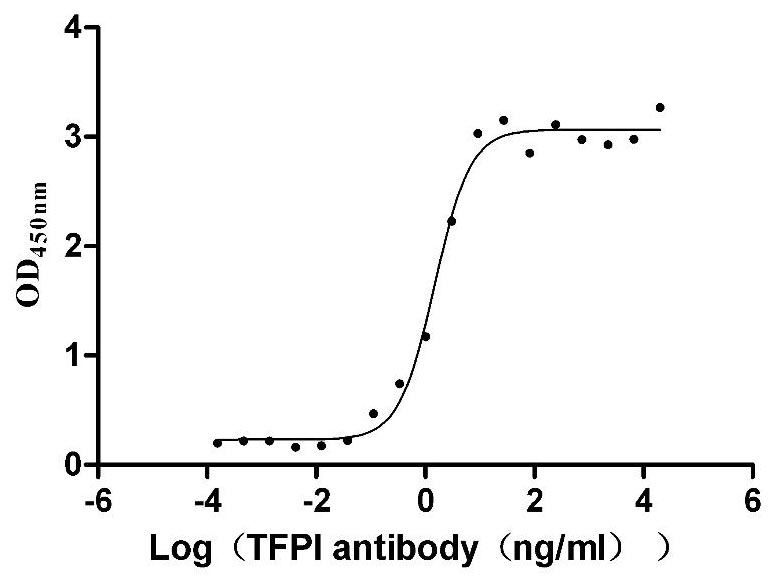
Recombinant Human Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Rat Intestinal-type alkaline phosphatase 1 (Alpi) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
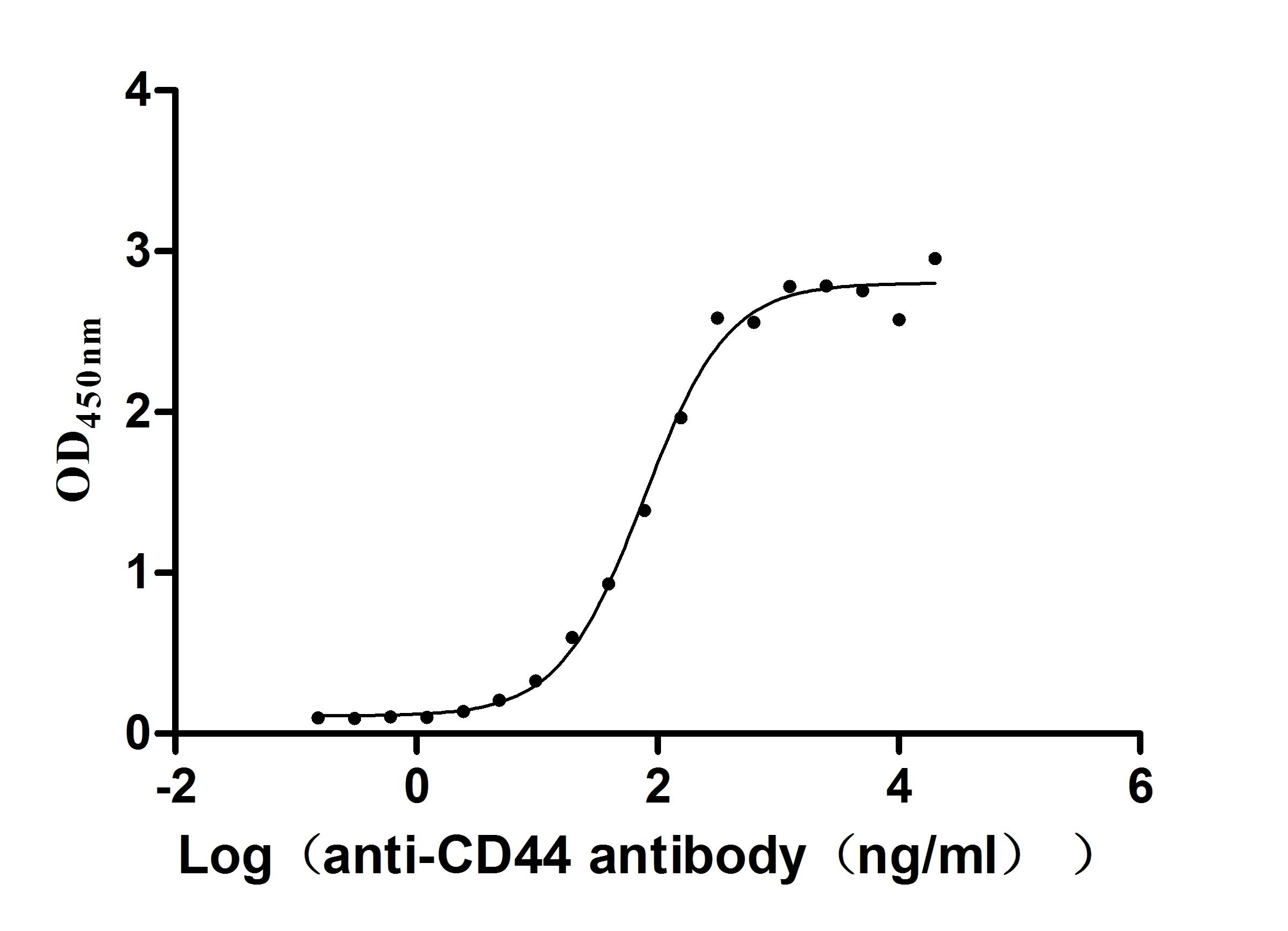
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis CD44 antigen (CD44), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
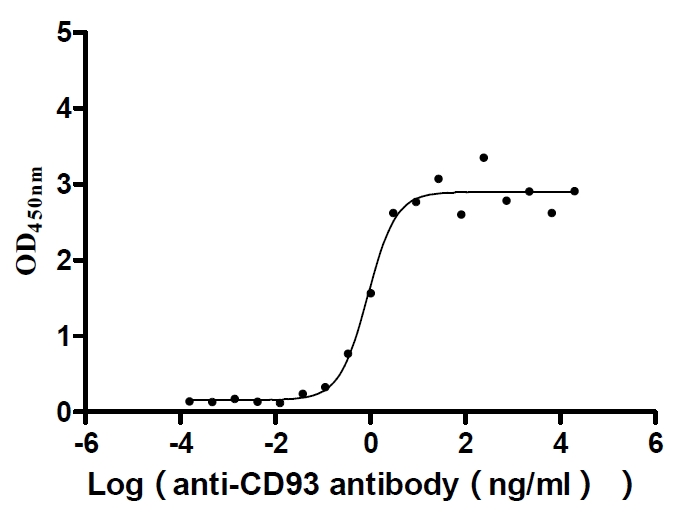
Recombinant Human Complement component C1q receptor (CD93), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis lymphocyte antigen 6 family member G6D (LY6G6D) (Active)
Express system: Yeast
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Human Interleukin-2 (IL2) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Serotransferrin(TF) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)