Recombinant Mouse Gastric inhibitory polypeptide (Gip), partial
In Stock-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse Gastric inhibitory polypeptide (Gip), partial
-
货号:CSB-YP009434MO
-
规格:¥1656
-
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
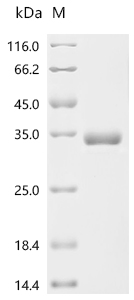
纯度:Greater than 95% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
Greater than 95% as determined by SEC-HPLC. -
生物活性:Not Test
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:GIP;Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
来源:Yeast
-
分子量:31.6 kDa
-
表达区域:44-85aa
-
氨基酸序列YAEGTFISDYSIAMDKIRQQDFVNWLLAQRGKKSDWKHNITQ
Note: The complete sequence including tag sequence, target protein sequence and linker sequence could be provided upon request. -
蛋白标签:N-terminal hFc-tagged
-
产品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
缓冲液:If the delivery form is liquid, the default storage buffer is Tris/PBS-based buffer, 5%-50% glycerol.If the delivery form is lyophilized powder, the buffer before lyophilization is Tris/PBS-based buffer, 6% Trehalose, pH 8.0.
-
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:3-7 business days
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4℃ for up to one week.
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Potent stimulator of insulin secretion and relatively poor inhibitor of gastric acid secretion.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- GIP stimulation induces a switch in GIPR recycling from a rapid endosomal to a slow trans-Golgi network (TGN) pathway. GPCR kinases and b-arrestin2 are required for this switch in recycling. PMID: 27974210
- GIP provides a novel link between the immune system and the gut, with proinflammatory-immune modulatory function but minor glucose regulatory relevance in the context of acute endotoxemia. PMID: 27350651
- our data suggest that the metabolic hormone GIP plays an important role in bone marrow hematopoiesis PMID: 28250160
- It was demonstrated that cardiomyocytes represent a direct target of GIP action in vitro, and that GIP ameliorated AngII-induced cardiac hypertrophy via suppression of cardiomyocyte enlargement, apoptosis, and fibrosis in vivo. PMID: 27375170
- The loss of food-induced GIP response in Roux-limb of intestine likely contributes to the attenuated serum GIP response to feeding. PMID: 26266950
- GIP induces the expression of the proatherogenic cytokine osteopontin (OPN) in mouse arteries via local release of endothelin-1 and activation of CREB. GIPR mRNA is higher in symptomatic carotid endarterectomy patients. PMID: 26395740
- These studies support the hypothesis that a reduction in GIP signaling using a GIP-neutralizing mAb might provide a useful method for the treatment and prevention of obesity and related disorders. PMID: 26487006
- This study provides evidences that GIP acts directly on osteoblasts and is capable of improving collagen maturity and fibril diameter. PMID: 25582623
- There was decrease in GIP gene transcripts and protein in the gut of HNF1a-null mice. PMID: 25979074
- Circulating levels of GIP were significantly decreased in FABP5-deficient mice. PMID: 25268051
- phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase gamma has a role in insulin secretion induced by glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide PMID: 25288806
- The results describe key beneficial immunoregulatory properties for glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide in diet-induced obesity and reveal that its augmentation ameliorates adipose tissue inflammation and improves insulin resistance. PMID: 25217161
- GIP-reduced mice demonstrate that partial reduction of GIP does not extensively alter glucose tolerance, but it alleviates obesity and lessens the degree of insulin resistance under high-fat diet conditions, suggesting a potential therapeutic value. PMID: 24584548
- It was concluded from these observations that GIP, but not glucagon-like peptide-1, directly activates PepT1 activity by a cAMP-dependent signaling pathway in jejunum. PMID: 24072682
- A novel acylated form of (d-Ala(2))GIP with improved antidiabetic potential, lacking effect on body fat stores. PMID: 23518200
- The results indicated that ectopic glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide expression in pancreatic beta cells maintains insulin secretion in the absence of proglucagon-derived peptides, revealing a novel mechanism for sustaining incretin action. PMID: 23099862
- Rfx6 increases GIP expression and content in enteroendocrine K-cells and is involved in GIP hypersecretion in high fat diet-induced obesity. PMID: 23192339
- GIP signaling may play a role in early embryonic pancreas differentiation to form insulin-positive cells or beta-cells. PMID: 21270265
- truncated forms of GIP exhibit potent anti-diabetic actions, without pro-obesity effects, and that the C-terminus contributes to the lipogenic actions of GIP PMID: 20231880
- GIP is expressed in and secreted from pancreatic islets and promotes islet glucose competence and also could support islet development and/or survival. PMID: 20138041
- substantial quantities of glycated GIP exist within the intestines of diabetic ob/ob mice, suggesting that this may be a contributing factor to the physiological disarray of this syndrome PMID: 11954659
- a novel pathway of obesity promotion via GIP; GIP directly links overnutrition to obesity PMID: 12068290
- Novel insulin/GIP co-producing cell lines provide unexpected insights into Gut K-cell function in vivo. PMID: 12124779
- Calcium mobilization from intracellular and extracellular sources, independent from K(ATP) channels, regulates secretion from some, but not all, subpopulations of enteroendocrine cells. PMID: 12676650
- GIP is the major insulinotropic factor in the secretion of insulin in response to glucose load in K(ATP) channel-deficient mice. PMID: 15362972
- Transcription factor PDX-1 plays a critical role in the cell-specific expression of the GIP gene. PMID: 15486225
- The physiological importance of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide has been investigated in single and double incretin receptor knockout mice. PMID: 15780432
- PI3K/PKB/Foxo1 signaling mediates GIP suppression of bax gene expression, which is a key pathway by which GIP regulates beta-cell apoptosis in vivo PMID: 15817464
- GIP plays a crucial role in switching from fat oxidation to fat accumulation under the diminished insulin action as a potential target for secondary prevention of insulin resistance PMID: 16105663
- Because GIPR(-/-) mice exhibited an increased plasma calcium concentration after meal ingestion, GIP directly links calcium contained in meal to calcium deposition on bone. PMID: 16469773
- Prohormone convertase 1/3 is essential for processing of the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide precursor PMID: 16476726
- protein kinase B, LKB1, and AMP-activated protein kinase have roles in activation of lipoprotein lipase by glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide in adipocytes PMID: 17244606
- Glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide inhibits bone resorption and stimulates bone formation PMID: 17321229
- First characterization of the anatomical distribution of GIP-immunoreactive cells in the rat brain providing an anatomical framework for future investigations regarding the functions of GIP in the central nervous system. PMID: 17510976
- Administration of resistin to adipocytes mimicked the effects of GIP on the PKB/LKB1/AMPK/LPL pathway: increasing phosphorylation of PKB, reducing levels of phosphorylated LKB1 and AMPK, and increasing LPL activity. PMID: 17890220
- genetic inactivation of GIP signaling can prevent the development of aging-associated insulin resistance through body composition changes PMID: 17937928
- GATA-4 may function to augment or enhance GIP expression rather than act as an initiator of GIP transcription. PMID: 18343025
- Gpr40 modulates FFA-stimulated insulin secretion from beta-cells not only directly but also indirectly via regulation of incretin(GIP and GLP-1) secretion PMID: 18519800
- The GIP-induced increase in glucose transport appears to be mediated, at least in part, by SGLT-1. PMID: 18719661
- These results indicate that inhibition of GIP signaling increases adiponectin levels, resulting in increased fat oxidation in peripheral tissues under high-fat diet. PMID: 18723001
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Secreted.
-
蛋白家族:Glucagon family
-
数据库链接:
Most popular with customers
-
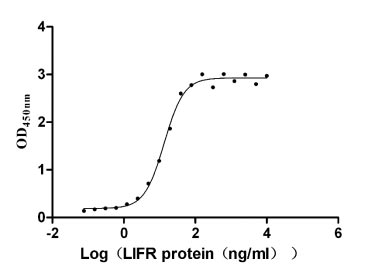
Recombinant Human Leukemia inhibitory factor receptor (LIFR), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
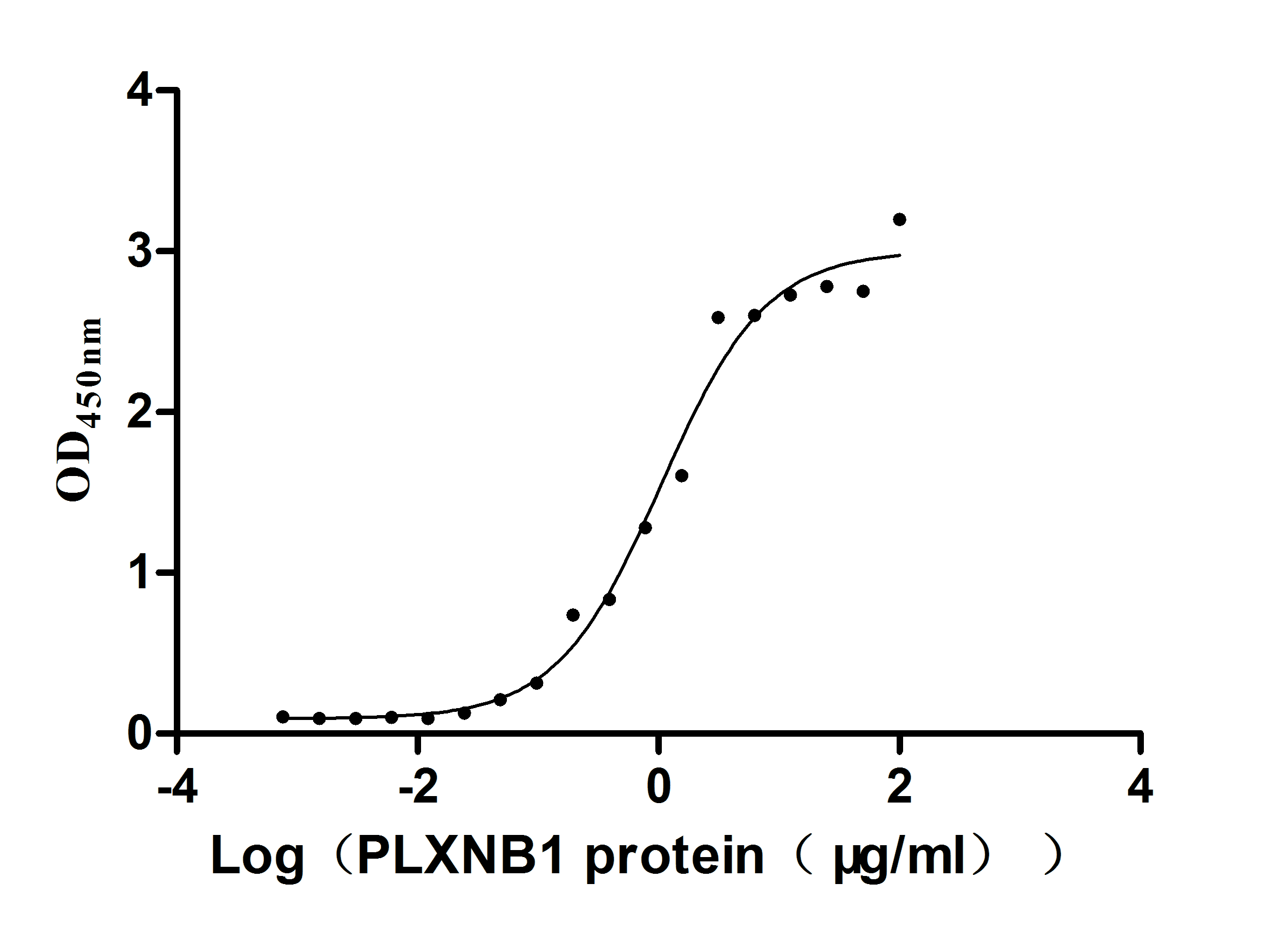
Recombinant Human Plexin-B1 (PLXNB1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
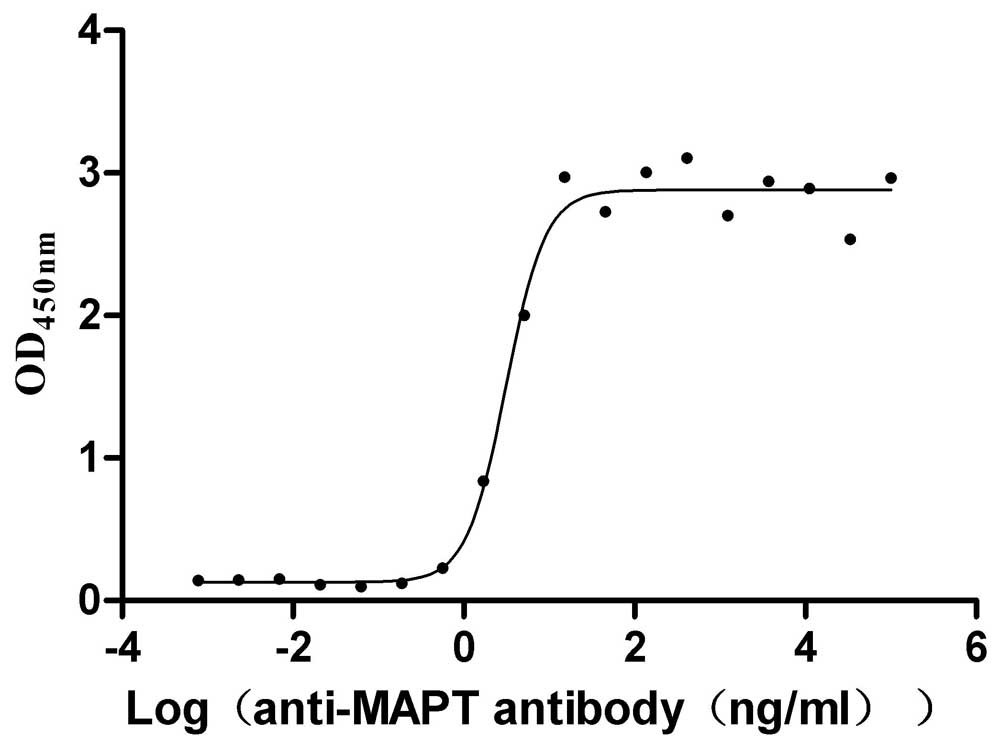
Recombinant Macaca mulatta Microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca mulatta (Rhesus macaque)
-
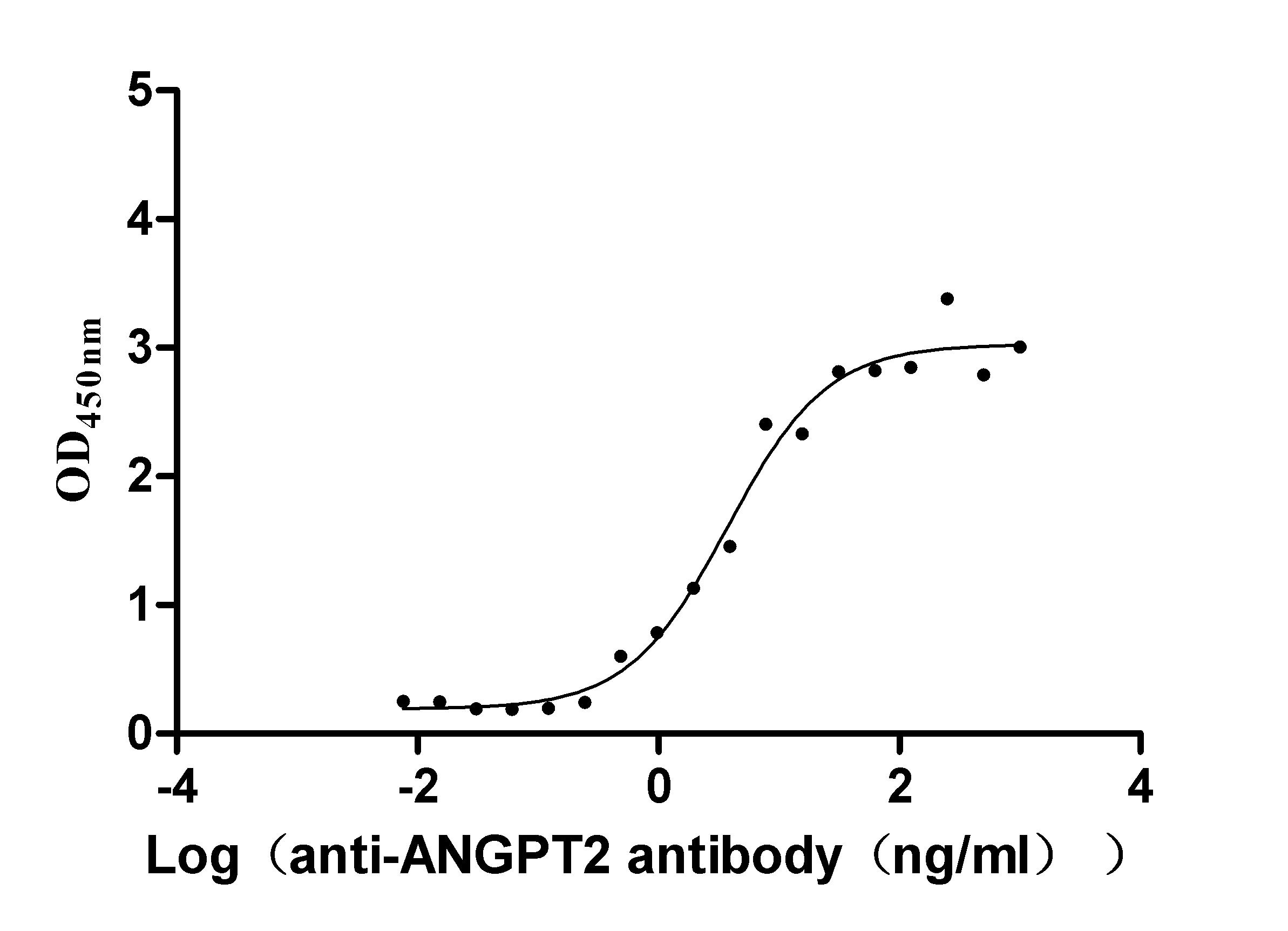
Recombinant Dog Angiopoietin-2 (ANGPT2) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris)
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
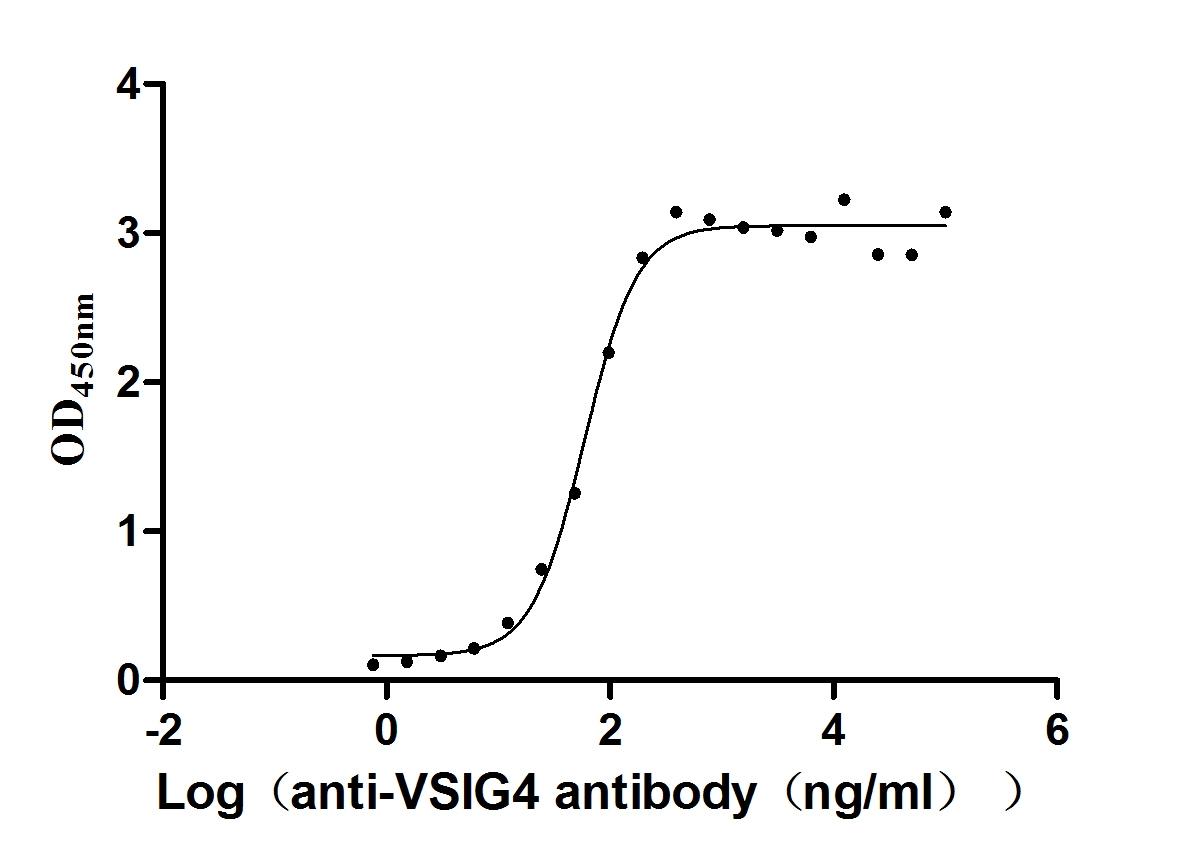
Recombinant Human V-set and immunoglobulin domain-containing protein 4 (VSIG4), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
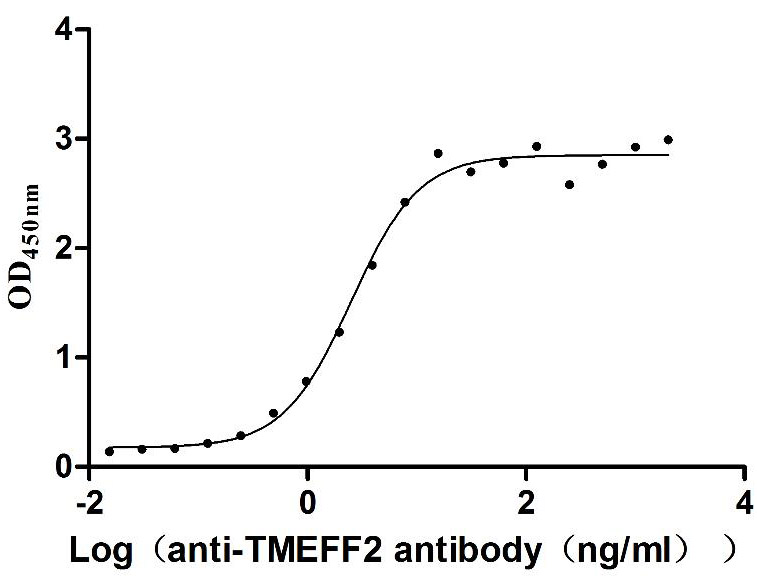
Recombinant Human Tomoregulin-2 (TMEFF2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)



-AC1.jpg)