Recombinant Mouse E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase CBL-B (Cblb), partial
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase CBL-B(Cblb) ,partial
-
货号:CSB-YP667545MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase CBL-B(Cblb) ,partial
-
货号:CSB-EP667545MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase CBL-B(Cblb) ,partial
-
货号:CSB-EP667545MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase CBL-B(Cblb) ,partial
-
货号:CSB-BP667545MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase CBL-B(Cblb) ,partial
-
货号:CSB-MP667545MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:CblbE3 ubiquitin-protein ligase CBL-B; EC 2.3.2.27; Casitas B-lineage lymphoma proto-oncogene b; RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase CBL-B; SH3-binding protein CBL-B; Signal transduction protein CBL-B
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase which accepts ubiquitin from specific E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes, and transfers it to substrates, generally promoting their degradation by the proteasome. Negatively regulates TCR (T-cell receptor), BCR (B-cell receptor) and FCER1 (high affinity immunoglobulin epsilon receptor) signal transduction pathways. In naive T-cells, inhibits VAV1 activation upon TCR engagement and imposes a requirement for CD28 costimulation for proliferation and IL-2 production. Also acts by promoting PIK3R1/p85 ubiquitination, which impairs its recruitment to the TCR and subsequent activation. In activated T-cells, inhibits PLCG1 activation and calcium mobilization upon restimulation and promotes anergy. In B-cells, acts by ubiquitinating SYK and promoting its proteasomal degradation. Slightly promotes SRC ubiquitination. May be involved in EGFR ubiquitination and internalization. May be functionally coupled with the E2 ubiquitin-protein ligase UB2D3. In association with CBL, required for proper feedback inhibition of ciliary platelet-derived growth factor receptor-alpha (PDGFRA) signaling pathway via ubiquitination and internalization of PDGFRA.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- The establishment of a new model of concurrent tissue-selective CBL/CBL-B deletion should allow a clear assessment of the tumor-intrinsic roles of CBL/CBL-B in non-myeloid malignancies and help test the potential for CBL/CBL-B inactivation in immunotherapy of tumors. PMID: 27276677
- GSK3 catalyzes two previously unreported phosphorylation events at Ser(476) and Ser(480) of Cbl-b. Constitutive activation of PKB in vivo results in a loss of tolerance that is mediated through the downregulation of Cbl-b. The PI3K-PKB-GSK-3 pathway is a novel regulatory axis that is important for controlling the decision between T cell activation and tolerance via Cbl-b. PMID: 29109121
- These studies reveal a novel, cell-autonomous requirement of CBL and CBL-B in epithelial stem cell maintenance during organ development and remodeling through modulation of mTOR signaling. PMID: 28100467
- CBLB directs polyubiquitination of dectin-1 and dectin-2, two key pattern-recognition receptors for sensing Candida albicans, and their downstream kinase SYK, thus inhibiting dectin-1- and dectin-2-mediated innate immune responses. PMID: 27428899
- CBLB controls proximal C-type lectin receptor signaling in macrophages and dendritic cells. CBLB associates with SYK and ubiquitinates SYK, dectin-1, and dectin-2 after fungal recognition. CBLB deficiency results in increased inflammasome activation, enhanced reactive oxygen species production, and increased fungal killing. PMID: 27428901
- study indicates that Cbl-b negatively regulates CLR-mediated antifungal innate immunity PMID: 27432944
- Fasudil, a clinically safe ROCK inhibitor, decreases disease burden in a Cbl/Cbl-b deficiency-driven murine model of myeloproliferative disorders. PMID: 26177294
- Mechanistically, NFATc1 induces Nur77 expression at late stage of osteoclast differentiation; in turn, Nur77 transcriptionally up-regulates E3 ubiquitin ligase Cbl-b, which triggers NFATc1 protein degradation. PMID: 26173181
- Silencing Cbl-b significantly enhanced T lymphocyte function and T lymphocyte cytotoxicity activity PMID: 25249301
- mechanisms have therapeutic implications for reducing beta-cell proliferation in insulinomas by inhibiting phospho-HLXB9 or its interaction with Nono and modulating the expression of its direct (Cblb) or indirect (c-Met) targets PMID: 26342078
- SHP-1 regulates Cbl-b-mediated T cell responses by controlling its tyrosine phosphorylation and ubiquitination PMID: 26416283
- Cbl-b(-/-) T cells demonstrate significant lymph node trafficking abnormalities. PMID: 25829233
- These results indicated that NF-kappaB downregulated Cbl-b by binding and suppressing Cbl-b promoter in T cell activation PMID: 25762784
- Cbl-b, together with Stub1, ubiquitinate Foxp3, and regulate tTreg development. PMID: 25560411
- Whereas Cbl-PI3K interaction regulates differentiation and survival, bone resorption is predominantly regulated by Cbl-b in osteoclasts. PMID: 24470255
- Cbl-b is the E3 ubiquitin ligase for Stat6. Cbl-b regulates Th9 in both Stat6-dependent and -independent mechanisms. PMID: 24508458
- The results demonstrate an essential and non-redundant role for Cbl-b in controlling TGFbetaR signaling by directly targeting SMAD7 for degradation during T cell responses in vitro and in vivo. PMID: 23709694
- Cbl-b, by promoting the ubiquitination and degradation of DDR2, functions as a negative regulator in the DDR2 signaling pathway. PMID: 24631539
- genetic deletion of the E3 ubiquitin ligase Cbl-b (casitas B-lineage lymphoma-b) or targeted inactivation of its E3 ligase activity licenses natural killer (NK) cells to spontaneously reject metastatic tumours PMID: 24553136
- Cbl-b plays only a limited role in the induction of antigen-specific T cell responses by murine bone marrow-derived dendritic cells in vitro and in vivo. PMID: 23762309
- study demonstrates that Cbl-b regulates the fate of inducible regulatory T cells via controlling the threshold for T cell activation PMID: 23749633
- Cbl-b inhibits T cell activation by suppressing Pten inactivation independently of its ubiquitin ligase activity. PMID: 22763434
- Data suggest that targeting Cbl-b might serve as a novel 'adjuvant approach', suitable to augment the effectiveness of established anti-cancer immunotherapies. PMID: 21383769
- c-Cbl as well as Cbl-b may play important roles in Hsp90 inhibitor-induced degradation of Flt3-ITD through the ubiquitin proteasome system PMID: 21768087
- Cbl-b is a critical factor in maintaining lung homeostasis upon environmental exposure to aeroallergens. PMID: 20738317
- Interplay between Cblb-dependent T cell anergy and other mechanisms prevents organ-specific islet-cell autoimmunity in transgenic mice. PMID: 21248249
- Selective genetic inactivation of Cbl-b E3 ligase activity phenocopies the T cell responses observed when total Cbl-b is ablated, resulting in T cell hyperactivation, spontaneous autoimmunity, and impaired induction of T cell anergy in vivo. PMID: 21248250
- The resilts of this study suggested that Cbl-b is an important regulatory factor for cytotoxic T-cell infiltration via RANTES production in macrophages. PMID: 21254087
- show that, in contrast to Cbl or Cbl-b single-deficient mice, concurrent loss of Cbl and Cbl-b in the HSC compartment leads to an early-onset lethal myeloproliferative disease in mice PMID: 20805496
- Data show that intrinsic regulation of peripheral T cells by CBL-B serves a uniquely critical role as a failsafe against clinical onset of autoimmune disease in AIRE deficiency. PMID: 20668237
- Data suggest that the regulatory abnormalities in Cbl-b(-/-) mice are related to defects in Teff, not Treg, function. PMID: 20624942
- gene deletion of both Cbl-b and Itch leads to augmented T cell activation and spontaneous autoimmunity PMID: 20637659
- Results indicate that Cbl-b controls Runx2 expression at the post-translational level. PMID: 20578243
- This study reveals that Foxo factors promote transcription of the Foxp3 gene in induced T reg cells, and thus provides new mechanistic insight into Foxo-mediated T cell regulation. PMID: 20439537
- Cbl-b plays a positive modulatory role in GPVI-dependent platelet signaling, which translates to an important regulatory role in hemostasis and thrombosis in vivo PMID: 20400514
- Cbl-b and itch are key regulators of peripheral T-cell tolerance [review] PMID: 20395198
- NFATc1 interacts endogenously with c-Src, c-Cbl, and Cbl-b in osteoclasts. PMID: 20037154
- novel E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase; role in regulation of immune response - review PMID: 11826757
- Cbl-b negatively regulates BCR signaling by targeting Syk for ubiquitination. PMID: 12771181
- both c-Cbl and Cbl-b can initiate a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B-independent signaling pathway critical to insulin-stimulated GLUT4 translocation PMID: 12842890
- Cbl-b and c-Cbl have divergent effects on Fc epsilon RI signal transduction and that Cbl-b, but not c-Cbl, functions as a negative regulator of Fc epsilon RI-induced degranulation. PMID: 15265912
- activated KIT in turn induces phosphorylation and activation of Cbl proteins PMID: 15315962
- Study provides a molecular framework for Cbl-b/Vav1-dependent and Cbl-b/Vav1-independent CD28 activation pathways essential for the organization of secondary lymphoid tissues and in vivo immunity to viral infection. PMID: 15661906
- E3 ubiquitin ligase Cbl-b plays an integral role in T cell TGF-beta signaling; its absence results in multifunctional TGF-beta-related defects that have important disease-related implications. PMID: 16424156
- cbl-b is a negative regulator of long-term memory, and its neuronal mechanism regulates synaptic transmission in the hippocampus PMID: 16549761
- results suggest that Cbl-b induces resistance of osteoblasts to IGF-I during denervation by increasing IRS-1 degradation and that Cbl-b-mediated modification of IGF-I signaling may contribute to decreased bone formation during denervation PMID: 16734387
- Cbl proteins play a critical role in establishing the MHC-dependent CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cell development programs. PMID: 17045823
- Cbl-b functions as a potent negative regulator of cytokines that promote allergic and inflammatory reactions. PMID: 17056522
- Ablation of Cbl-b can be an efficient strategy for eliciting immune responses against both inoculated and spontaneous tumors. PMID: 17364027
- identify Cbl-b as a key signaling molecule that controls spontaneous antitumor activity of cytotoxic T cells in different cancer models PMID: 17403934
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm. Note=In adipocytes, translocates to the plasma membrane upon insulin stimulation.
-
数据库链接:
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase ZNRF3 (ZNRF3), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Claudin-6 (CLDN6)-VLPs, Fluorescent (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (GLP1R), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Dickkopf-related protein 1 (DKK1) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
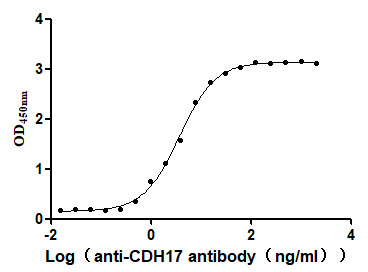
Recombinant Human Cadherin-17 (CDH17), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
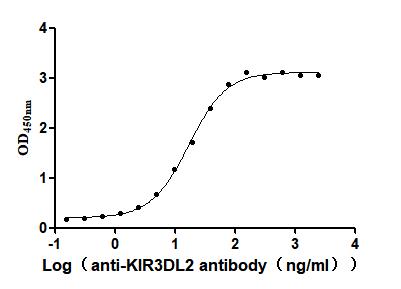
Recombinant Human Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 3DL2 (KIR3DL2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
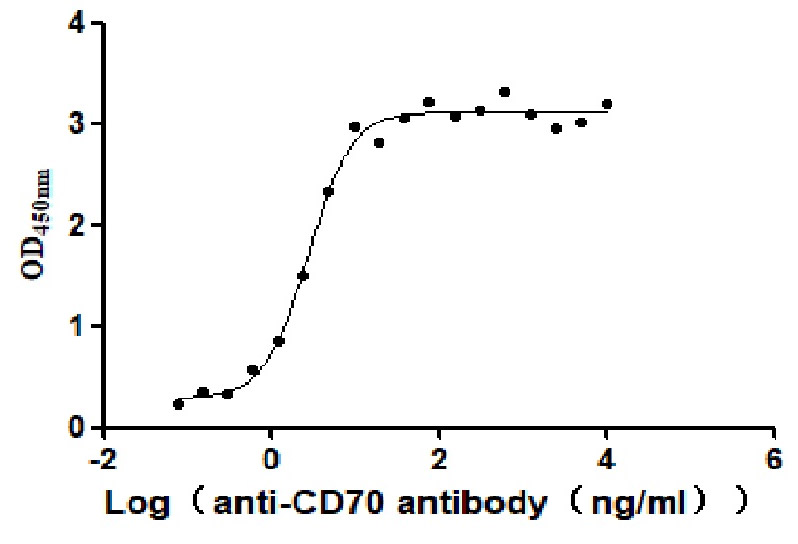
Recombinant Human CD70 antigen (CD70), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


f4-AC1.jpg)
-AC1.jpg)