-
中文名称:小鼠脂肪酸结合蛋白,脂肪细胞(FABP4)酶联免疫试剂盒
-
货号:CSB-EL007945MO
-
规格:96T/48T
-
价格:¥3600/¥2500
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品描述:小鼠脂肪酸结合蛋白,脂肪细胞(FABP4)酶联免疫试剂盒(CSB-EL007945MO)为双抗夹心法ELISA试剂盒,定量检测血清、血浆、组织匀浆样本中的FABP4含量。FABP4是一种脂肪酸结合蛋白,在脂质代谢、炎症反应等生理过程中发挥重要作用。研究发现它与肥胖、糖尿病、心血管疾病等密切相关。其作用机制涉及调节脂肪酸的摄取、转运和代谢,影响细胞内信号传导,为相关疾病治疗提供了新靶点。试剂盒检测范围为31.25 pg/mL-2000 pg/mL,该产品可广泛应用于基础科研领域,如探究代谢性疾病动物模型中脂肪细胞功能变化、评估药物或基因干预对脂代谢的影响,以及体外细胞实验中FABP4表达调控机制研究等,为代谢相关分子机制探索提供精准检测工具。本品仅用于科研,不用于临床诊断,产品具体参数及操作步骤详见产品说明书。
-
别名:Fabp4 ELISA Kit; Ap2 ELISA Kit; Fatty acid-binding protein ELISA Kit; adipocyte ELISA Kit; 3T3-L1 lipid-binding protein ELISA Kit; Adipocyte lipid-binding protein ELISA Kit; ALBP ELISA Kit; Adipocyte-type fatty acid-binding protein ELISA Kit; A-FABP ELISA Kit; AFABP ELISA Kit; Fatty acid-binding protein 4 ELISA Kit; Myelin P2 protein homolog ELISA Kit; P15 ELISA Kit; P2 adipocyte protein ELISA Kit; Protein 422 ELISA Kit
-
缩写:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
样本类型:serum, plasma, tissue homogenates
-
检测范围:31.25 pg/mL-2000 pg/mL
-
灵敏度:7.81 pg/mL
-
反应时间:1-5h
-
样本体积:50-100ul
-
检测波长:450 nm
-
研究领域:Signal Transduction
-
测定原理:quantitative
-
测定方法:Sandwich
-
精密度:
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): CV%<8%
Three samples of known concentration were tested twenty times on one plate to assess.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): CV%<10%
Three samples of known concentration were tested in twenty assays to assess.
-
线性度:
To assess the linearity of the assay, samples were spiked with high concentrations of mouse FABP4 in various matrices and diluted with the Sample Diluent to produce samples with values within the dynamic range of the assay.
Sample
Serum(n=4)
1:400
Average %
96
Range %
90-100
1:800
Average %
98
Range %
93-103
1:1600
Average %
92
Range %
85-98
1:3200
Average %
103
Range %
98-107
-
回收率:
The recovery of mouse FABP4 spiked to levels throughout the range of the assay in various matrices was evaluated. Samples were diluted prior to assay as directed in the Sample Preparation section.
Sample Type
Average % Recovery
Range
Serum (n=5)
102
98-108
EDTA plasma (n=4)
96
90-102
-
标准曲线:
 These standard curves are provided for demonstration only. A standard curve should be generated for each set of samples assayed.
These standard curves are provided for demonstration only. A standard curve should be generated for each set of samples assayed. pg/ml
OD1
OD2
Average
Corrected
2000
2.858
2.764
2.811
2.670
1000
2.131
2.067
2.099
1.958
500
1.275
1.328
1.302
1.160
250
0.837
0.829
0.833
0.692
125
0.492
0.511
0.501
0.360
62.5
0.317
0.333
0.325
0.184
31.25
0.238
0.244
0.241
0.100
0
0.137
0.145
0.141
-
数据处理:
-
货期:3-5 working days
引用文献
- Accumulation of advanced oxidation protein products aggravates bone-fat imbalance during skeletal aging YS Huang, JW Gao, RF Ao, XY Liu, DZ Wu,Journal of Orthopaedic Translation,2025
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Lipid transport protein in adipocytes. Binds both long chain fatty acids and retinoic acid. Delivers long-chain fatty acids and retinoic acid to their cognate receptors in the nucleus.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- The findings chart the pathway of FABP4 secretion and provide a potential therapeutic means to control metabolic disorders associated with its dysregulated secretion. PMID: 29212659
- Study in A-FABP knockout mice revealed that A-FABP acts as a physiological stimulator of brown adipose tissue-mediated adaptive thermogenesis. PMID: 28128199
- Fabp4/5 confers protection against metabolic diseases but does not extend lifespan. PMID: 29020626
- Ectopic expression and secretion of FABP4 in vascular endothelial cells contribute to neointima formation after vascular injury. PMID: 28903937
- FABP4 regulates the expression of BLT1R and its downstream signaling via control of oxidative stress in macrophages PMID: 28546450
- Upregulated ROS induced by FABP4 was of significance in activating FoxM1 leading to airway inflammation and epithelial barrier dysfunction. PMID: 29158087
- Collectively, these results demonstrate that C. pneumoniae exploits host FABP4 to facilitate fat mobilization and intracellular replication in adipocytes. This work uncovers a novel strategy used by intracellular pathogens for acquiring energy via hijacking of the host lipid metabolism pathway. PMID: 29108997
- High Fabp4 expression is associated with Acute myeloid leukemia. PMID: 27885273
- These data suggest that the function of SIRT6 in the Fabp4-Cre-expressing cells in addition to mature adipocytes plays a critical role in body weight maintenance and metabolic homeostasis. PMID: 28385723
- This study demonstrating a FABP4-UCP2 axis with the potential to modulate the microglial inflammatory response. PMID: 28214555
- our data establish A-FABP as a new molecular sensor in triggering macrophage-associated sterile inflammation in obesity. PMID: 27920274
- these data offer a novel pathway whereby FABP4/aP2 regulates macrophage redox signaling and inflammasome activation via control of UCP2 expression. PMID: 27795298
- FABP4 locally produced by epicardial/perivascular fat and macrophages in vascular plaques contributes to the development of coronary atherosclerosis. PMID: 27013610
- endothelial PATZ1 thus potently inhibits endothelial function and angiogenesis via inhibition of FABP4 expression, and abnormal induction of endothelial PATZ1 may contribute to multiple aspects of vascular dysfunction in diabetes PMID: 27297106
- These results suggest that the antiinflammatory phenotype of FABP4/aP2 null mice is mediated by increased intracellular monounsaturated fatty acids leading to the increased expression of both uncoupling protein 2 and SirT3. PMID: 26789108
- FABP4 could reverse the activation of the leptin-induced mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation. PMID: 26310911
- FABP4 is a hypoxia inducible gene that sensitizes mice to liver I/R injury. PMID: 26070408
- Data suggest Fabp4 is up-regulated and DNA methylation is down-regulated in aorta in hyperhomocysteinemia induced by high-methionine diet; up-regulation of DNA methyltransferase 1 (Dnmt1) promotes DNA methylation and decreases Fabp4 expression. PMID: 26606905
- Data show that the weight gain was blunted in male, but not female, fatty acid binding protein 4-Cre-driven promoter (FaChOX) mice when placed on either a normal chow diet or an obesogenic Western diet. PMID: 26248218
- Data show that overexpression of cattle adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein (A-FABP)gene promoted fat deposition in the skeletal muscle of transgenic mice. PMID: 25867423
- Data suggest that expression of Fabp4 (fatty acid binding protein 4) in preadipocytes is up-regulated by arachidonic acid during adipogenesis; this up-regulation appears mediated by prostaglandin F2alpha/FP (prostaglandin F2alpha receptor) signaling. PMID: 25325755
- results show that chemical inhibition of lipase activity, genetic deficiency of adipose triglyceride lipase and, to a lesser extent, hormone-sensitive lipase blocked aP2 secretion from adipocytes. PMID: 25535287
- FABP4-/- mice demonstrated a significant decrease in neovessel formation and significant improvement in physiological revascularization. PMID: 24802082
- A-FABP deficiency protects mice against MI/R-induced and/or diabetes-induced cardiac injury at least partially through activation of the eNOS/NO pathway and reduction in superoxide anion production PMID: 26186740
- -). As Cre-loxP-mediated genetic lineage tracing is irreversible and heritable, the genetic labelling (RFP) would inevitably label all descendants of these early FABP4+ embryonic VECs, regardless of whether they express CreER at P7 or not. PMID: 25265869
- FABP4 is expressed in the mouse placental labyrinth, with highest expression at E16.5. FABP4 is dispensable for feto-placental growth and placental lipid accumulation. PMID: 25096952
- The present results demonstrate that deletion of IL-6 driven by a fatty acid binding protein (aP2) promoter-Cre inducible system regulates body weight, body fat and metabolism in a sex-specific fashion. PMID: 24934978
- miR-24 plays an important role in regulating adipocyte differentiation and FABP4 expression. The mechanism involved may be the upregulation of AP-1. PMID: 24301787
- FABP4/5 play an indispensable role in thermogenesis in brown adipose tissue and skeletal muscle. PMID: 24603714
- peripheral uptake of FA via capillary endothelial FABP4/5 is crucial for systemic metabolism and may establish FABP4/5 as potentially novel targets for the modulation of energy homeostasis. PMID: 24244493
- In aP2-Cre/ERalpha(flox/flox) mice, increased serum estrogen levels cause over-stimulation in the uterus. PMID: 24416430
- found that the FABP4 level was higher and PPARgamma level was lower in human visceral fat and mouse epididymal fat compared with their subcutaneous fat PMID: 24319114
- Neutralization of secreted aP2 reduces glucose production. PMID: 23663740
- lower dermis adipose layer development is signalled by expression of FABP4 PMID: 23555789
- Capillary endothelial FABP4/5 are required for (fatty acid)FA transport into FA-consuming tissues that include the heart. PMID: 23968980
- High Fabp4 expression is associated with atherosclerotic lesion. PMID: 23387955
- FABP4 promotes VEGF-induced airway angiogenesis. PMID: 23391391
- FABP4 expression in adipose and hepatic tissues in the settings of obesity and insulin resistance, was analyzed. PMID: 23139800
- fatty acid binding protein 4 (FABP4), commonly known as adipocyte protein 2 (aP2), has been extensively used as a marker for differentiated adipocytes. However, whether aP2 is expressed in adipogenic progenitors is controversial PMID: 23047894
- These findings indicate that FABP4 may have a crucial role in modulating IL-6 and vascular endothelial growth factor as angiogenesis inducers stimulated by the cellular action of thrombin on adipocytes via PAR1. PMID: 23008513
- fatty acid-binding protein (FABP4), an intracellular fatty acid chaperone, in the mouse thymus, and examined its role in the control of cytokine production PMID: 22585040
- In the aP2-Cre mice, the recombinase activity is expressed in the central nervous system of the embryos. PMID: 22150821
- Report statins/dexamethasone synergistically induce FABP4 expression in macrophages. PMID: 22503826
- Unsaturated fatty acids inhibited the basal as well as lipopolysaccharides induced Adipocyte fatty acid binding protein expression. PMID: 21046125
- Fabp4 is highly expressed in mouse decidua. In vitro decidualization is significantly stimulated by Fabp4 overexpression and inhibited by Fabp4 siRNA and FABP4 inhibitor. PMID: 21704217
- Results define a new class of in vivo ligands for aP2 and other fatty acid binding proteins and extend their physiological substrates to include bioactive aldehydes. PMID: 20509169
- The lack of aP2 in donor marrow cells led to the development of smaller (5.5-fold) atherosclerotic lesions in the recipient mice. PMID: 11606480
- data provide support for the portal region hypothesis and suggest dynamic fluctuations in this region regulate cavity access, but not ligand affinity or selectivity PMID: 11827549
- Ap2-deficient mice with advanced atherosclerosis and severe hypercholesterolemia fed a Western diet for 14 weeks have significant reductions in mean atherosclerotic lesion size in the proximal aorta, en face aorta, and innominate/right carotid artery. PMID: 12377750
- A-FABP and E-FABP bind to hormone-sensitive lipase with high affinity PMID: 13129924
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm. Nucleus.
-
蛋白家族:Calycin superfamily, Fatty-acid binding protein (FABP) family
-
数据库链接:
Most popular with customers
-
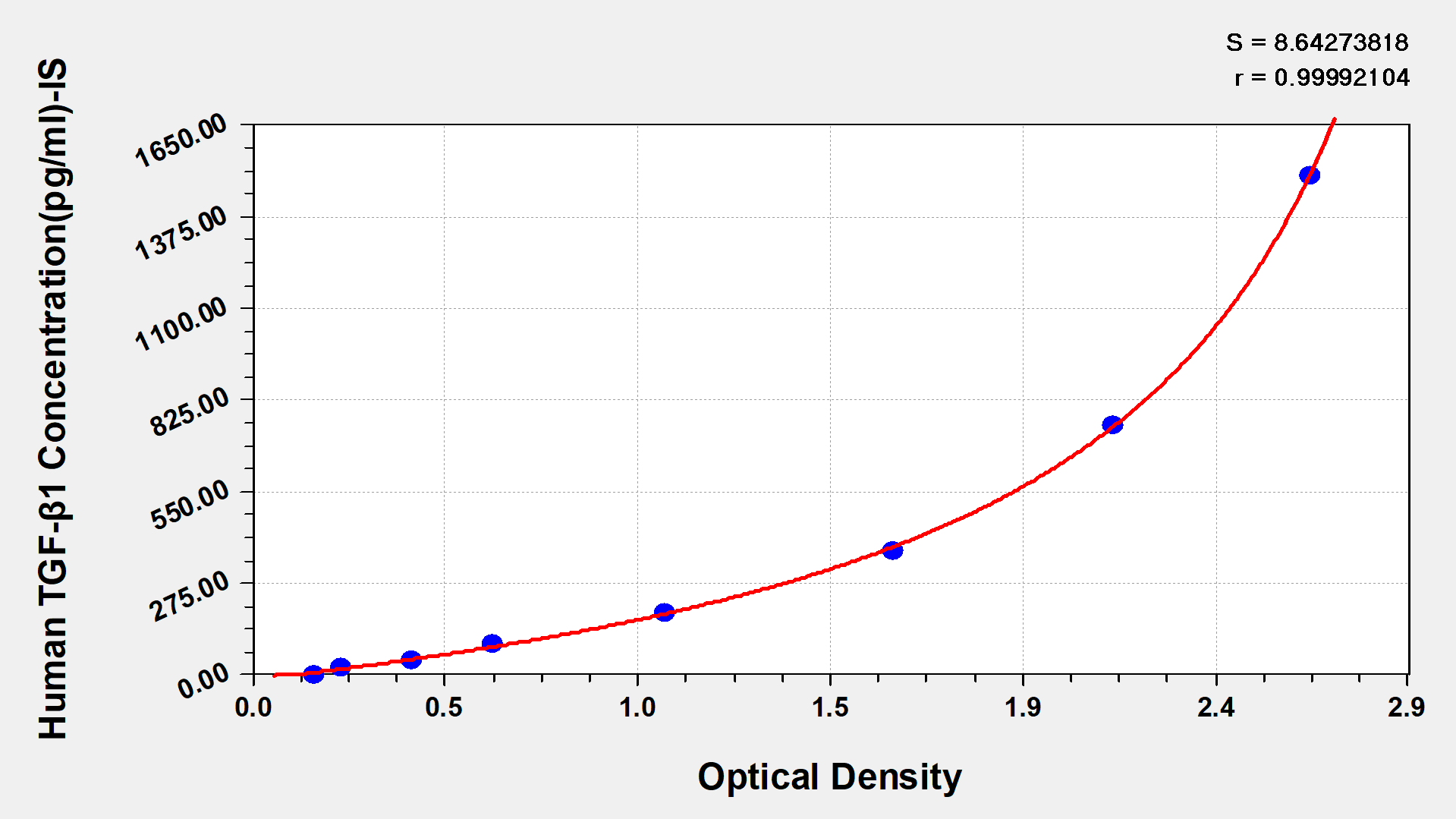
Human Transforming Growth factor β1,TGF-β1 ELISA kit
Detect Range: 23.5 pg/ml-1500 pg/ml
Sensitivity: 5.8 pg/ml
-
-
-
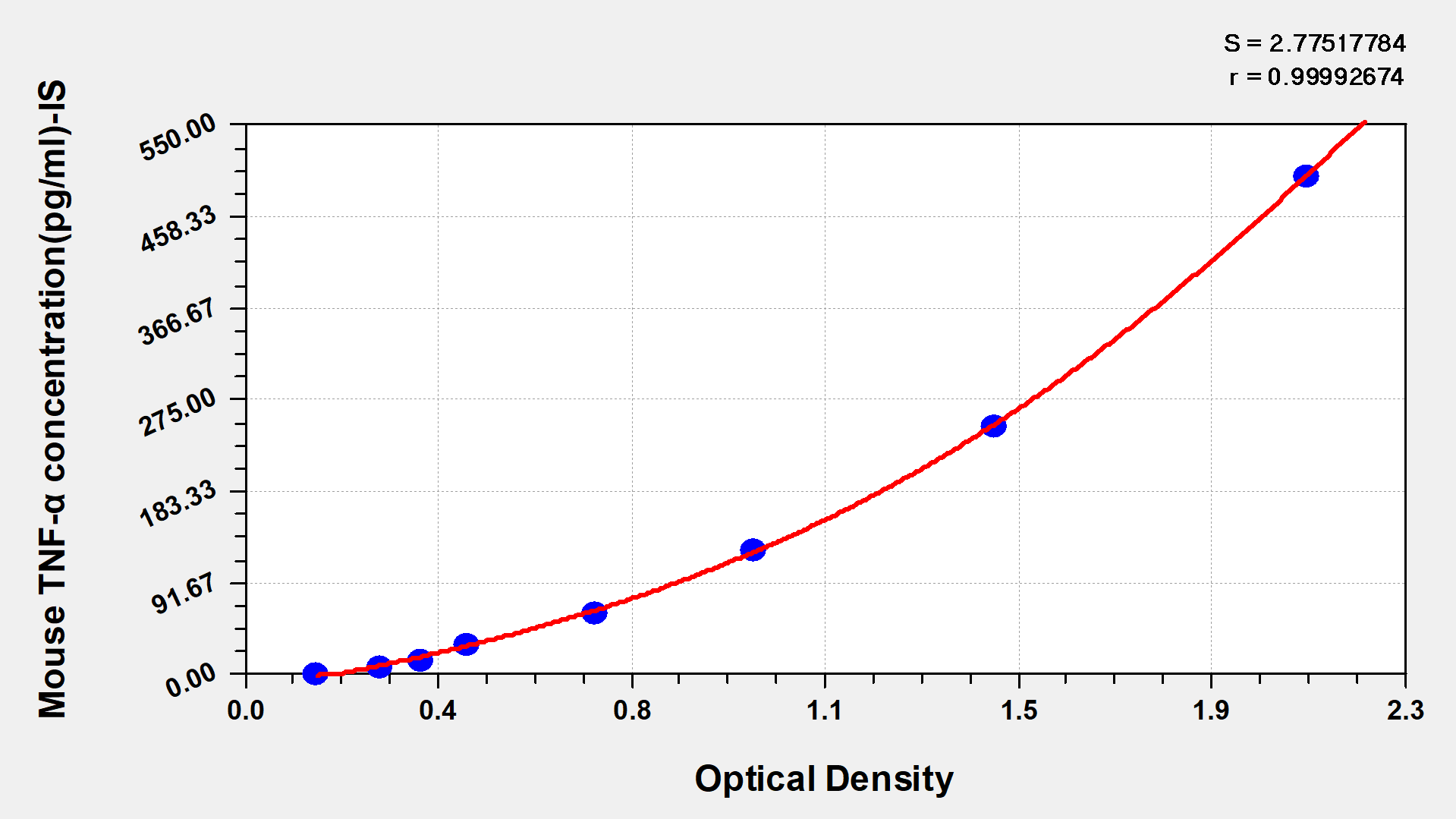
Mouse Tumor necrosis factor α,TNF-α ELISA Kit
Detect Range: 7.8 pg/ml-500 pg/ml
Sensitivity: 1.95 pg/ml
-
-
-
-