Recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae [PIN+] prion protein RNQ1 (RNQ1)
-
中文名称:酿酒酵母RNQ1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP340693SVG
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:酿酒酵母RNQ1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP340693SVG
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:酿酒酵母RNQ1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP340693SVG-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:酿酒酵母RNQ1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP340693SVG
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:酿酒酵母RNQ1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP340693SVG
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:RNQ1
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:RNQ1; YCL028W; YCL181; YCL28W; [PIN+] prion protein RNQ1; Rich in asparagine and glutamine protein 1
-
种属:Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast)
-
蛋白长度:full length protein
-
表达区域:1-405
-
氨基酸序列MDTDKLISEA ESHFSQGNHA EAVAKLTSAA QSNPNDEQMS TIESLIQKIA GYVMDNRSGG SDASQDRAAG GGSSFMNTLM ADSKGSSQTQ LGKLALLATV MTHSSNKGSS NRGFDVGTVM SMLSGSGGGS QSMGASGLAA LASQFFKSGN NSQGQGQGQG QGQGQGQGQG QGSFTALASL ASSFMNSNNN NQQGQNQSSG GSSFGALASM ASSFMHSNNN QNSNNSQQGY NQSYQNGNQN SQGYNNQQYQ GGNGGYQQQQ GQSGGAFSSL ASMAQSYLGG GQTQSNQQQY NQQGQNNQQQ YQQQGQNYQH QQQGQQQQQG HSSSFSALAS MASSYLGNNS NSNSSYGGQQ QANEYGRPQQ NGQQQSNEYG RPQYGGNQNS NGQHESFNFS GNFSQQNNNG NQNRY
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Transferable epigenetic modifier which forms a prion responsible for the non-Mendelian trait [PIN+]. The native function of the soluble protein is unknown.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- concluded that slow decoding of particular codons induces defects in protein homeostasis that interfere with key steps in cytokinesis and nuclear segregation PMID: 28281930
- results show that the presence of Rnq1p in the cell significantly decreases the loss of [PSI;(+)] prion, which is caused by a double mutation in SUP35 (Q61K, Q62K substitutions in the Sup35 protein). PMID: 28537243
- Taking into account the earlier reports of the beneficial effect of expression of N-wt-Htt on the aggregation of mutant huntingtin, the function of wild-type huntingtin as an inhibitor of protein aggregation in the cell needs to be explored. PMID: 26628321
- the presence of [SWI+] can affect the interactions between Sup35 and Rnq1 during [PSI+] initiation and maturation process PMID: 24727082
- Study describes a spectrum of prion variants occurring naturally in wild yeast. all of the [RNQ+] variants characterized were efficient inducers of [PSI+], but differed in the subset of [PSI+] variants that formed and [RNQ+] structures can be modified after inducing, or interacting with, [PSI+] and in some cases, this interaction resulted in the loss of [RNQ+]. PMID: 24673812
- Polymorphism of RNQ1 was selected to protect cells from detrimental effects of the [PIN+] prion. PMID: 22949655
- Data indicate that the majority of mutated residues are mapped to the surface, and on one side, of contiguous alpha-helices of the nonprion domain of Rnq1, suggesting its involvement in interactions with a prion or a factor necessary for prion developmentt PMID: 21453425
- Data suggest that transient Hsp104 overproduction enhances prion generation through persistent effects on Rnq1 amyloid, as well as by disassembly of amorphous Ure2 aggregates, driving the aggregation toward the amyloid pathway. PMID: 21467567
- polyglutamine tracts are potent inducers of spontaneous Sup35 and Rnq1 amyloidogenesis PMID: 20224794
- Differences exist in the ability of the [RNQ(+)] prion variants to faithfully propagate themselves and to template the aggregation of other proteins. PMID: 20442412
- These findings indicate that the N-terminal non-prion domain of Rnq1 harbors a potent activity to regulate the maintenance of the [PIN(+)] prion. PMID: 20009538
- The [RNQ1Delta100(+)] prion demonstrates selfish activity to eliminate a heterologous prion in S. cerevisiae, showing the first instance of a selfish prion variant in living organisms. PMID: 19371377
- Rnq1 encompasses multiple prion determinants that can independently drive amyloid formation in vitro. PMID: 20107602
- Data show that increasing heat-shock protein 40 chaperone Sis1 activity before Rnq1-GFP expression, shifted Rnq1-GFP aggregation from the cytosol to the nucleus. PMID: 19656852
- We report that a null rnq1 mutation in the yeast RNQ1 (YCL028w) prion-like gene of so far unknown function produces the doubling of spores in the asci. PMID: 16356475
- RNQ1 deletion reduced expression from the divergently transcribed BIK1, allowing the identification of genetic interactors with bik1. PMID: 16972090
- analysis of the Rnq1 prion domain cross-seeding interactions with Sup35NM PMID: 17121829
- Data report that, upon depletion of Sis1, as well as upon inactivation of Hsp104, Rnq1 aggregates increased in size. PMID: 17673909
- use of NMR methods to examine amyloid formed in vitro from recombinant Rnq1 prion domain (residues 153-405) labeled with Tyr-1-(13)C (14 residues), Leu-1-(13)C (7 residues), or Ala-3-(13)C (13 residues) PMID: 18268327
- the nonprion domain of Rnq1 plays a crucial role in self-regulation of the highly reactive QN-rich prion domain of Rnq1 PMID: 18332119
- the J-protein Sis1, the Hsp70 Ssa, and the AAA+ ATPase Hsp104, act sequentially in the fragmentation of yeast prions [PSI(+)], [RNQ(+)], and [URE3], but the threshold of Sis1 activity required for each prion varies PMID: 18955697
- These data are consistent with a model of [PSI+] induction caused by physical interactions between Rnq1p and Sup35p. PMID: 19324054
- This study supports the occurrence of in vivo cross-seeding between Sup35 and Rnq1 and provides a new tool that can be used to dissect the mechanism of the de novo appearance of prions. PMID: 19411620
- Results for fibrils formed by the prion protein Rnq1 support an in-register parallel beta-sheet structure, with one Rnq1 molecule per 0.47-nm beta-sheet repeat spacing. PMID: 19706519
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm. Nucleus.
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: sce:YCL028W
STRING: 4932.YCL028W
Most popular with customers
-
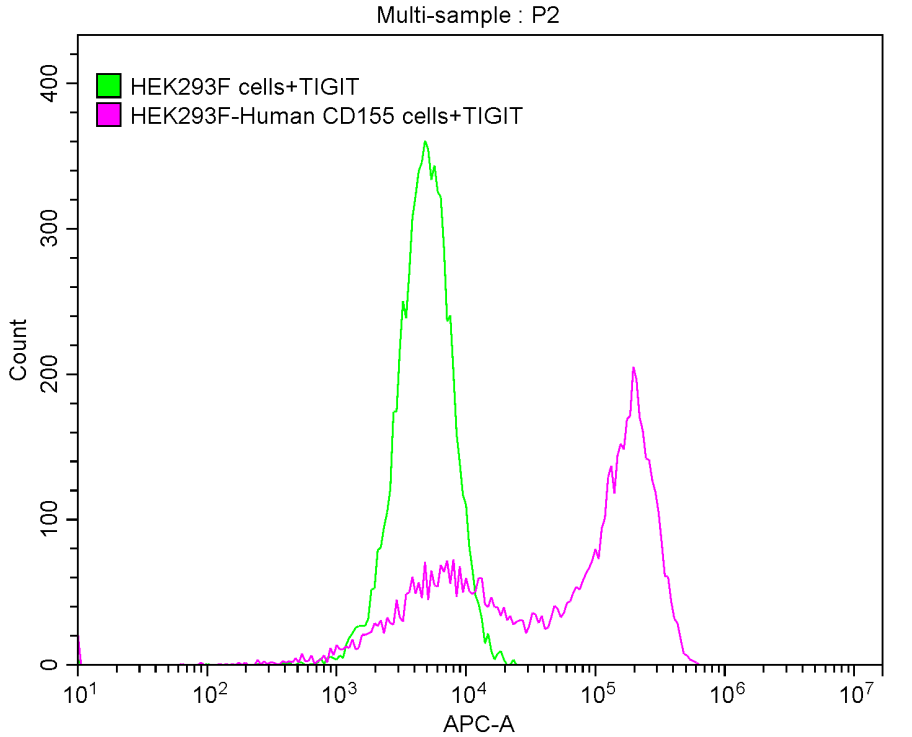
Recombinant Human T-cell immunoreceptor with Ig and ITIM domains (TIGIT), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Poliovirus receptor (PVR) (I340M), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
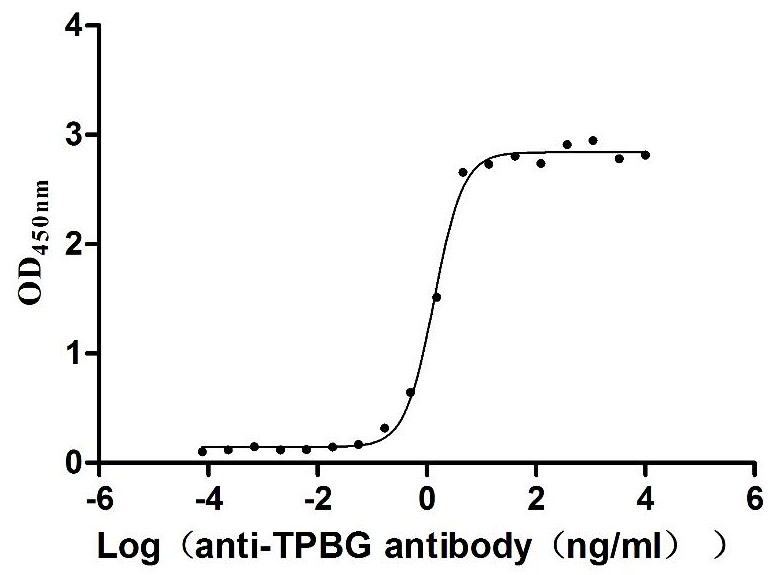
Recombinant Human Trophoblast glycoprotein (TPBG), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
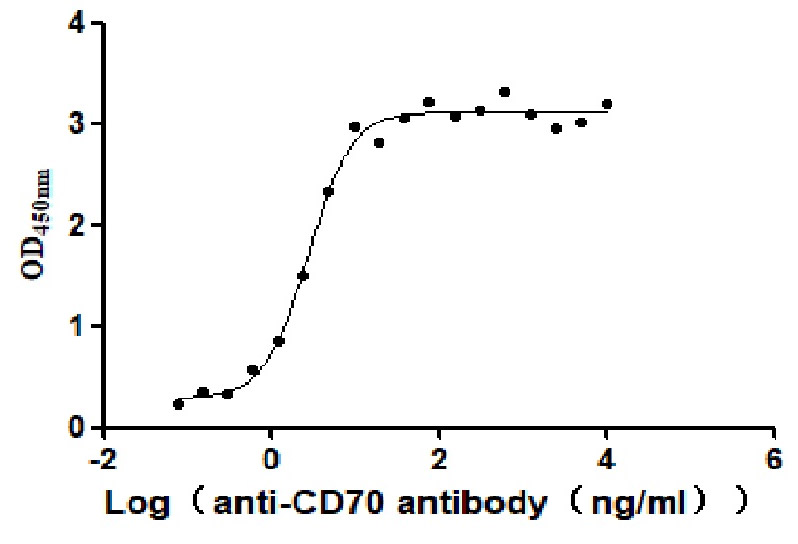
Recombinant Human CD70 antigen (CD70), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)