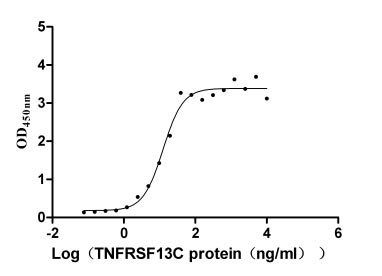
Recombinant Rat Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily A member 1 (Trpa1), partial
-
中文名称:大鼠Trpa1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP764869RA
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:大鼠Trpa1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP764869RA-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:大鼠Trpa1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP764869RA
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:大鼠Trpa1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP764869RA
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:Trpa1
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Trpa1; Anktm1; Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily A member 1; Ankyrin-like with transmembrane domains protein 1; Wasabi receptor
-
种属:Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Receptor-activated non-selective cation channel involved in pain detection and possibly also in cold perception, oxygen concentration perception, cough, itch, and inner ear function. Shows 8-fold preference for divalent over monovalent cations. Has a central role in the pain response to endogenous inflammatory mediators and to a diverse array of irritants, such as allylthiocyanate (AITC) found in mustard oil or wasabi, cinnamaldehyde, diallyl disulfide (DADS) from garlic, and acrolein, an irritant from tears gas and vehicule exhaust fumes. Acts also as an ionotropic cannabinoid receptor by being activated by delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the psychoactive component of marijuana. Is activated by a large variety of structurally unrelated electrophilic and non-electrophilic chemical compounds. Electrophilic ligands activate TRPA1 by interacting with critical N-terminal Cys residues in a covalent manner, whereas mechanisms of non-electrophilic ligands are not well determined. May be a component for the mechanosensitive transduction channel of hair cells in inner ear, thereby participating in the perception of sounds. Probably operated by a phosphatidylinositol second messenger system.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- TRPA1-mediated spontaneous [Ca(2+)]i increase modulates the spontaneous release of peptide hormones from astrocytes. PMID: 29777700
- Upregulated substance P (SP) and TRPA1 in the dorsal root ganglion and stomach and increased serum and gastric mucosa SP levels may contribute to stress-induced acute gastric mucosal lesions. PMID: 29428952
- IL-6 synthesis and secretion were connected to acute Peritoneal dialysis fluid exposure, and this response was triggered by TRPA1 receptors, possibly located to non-neuronal cells. PMID: 28698251
- The TRPA1 channel is activated by noxious cold, reactive oxygen species and mechanical stimuli and is expressed in small- and medium-sized nociceptive neurons of the dorsal root, trigeminal, and nodose ganglia. PMID: 28640016
- TRPA1 receptors on nociceptors are active in incised fascia and muscle but this is not evident in incised skin. Even though endogenous TRPA1 agonists like ROS and H2O2 were increased in both incised skin and muscle, those in skin do not contribute to nociceptive behaviors. PMID: 28103292
- Tetracaine facilitated spontaneous l-glutamate release from nerve terminals by activating TRPA1 channels in the substantia gelatinosa (SG), resulting in an increase in the excitability of SG neurons. TRPA1 activation was not specific to amide-type or ester-type local anesthetics (LAs). The facilitatory action of LAs may be involved in pain occurring after recovery from spinal anesthesia. PMID: 28017670
- expression in distal colonic mucosa may be involved restored colonic transit after pelvic nerve denervation PMID: 28032561
- High TRPA1 expression is associated with neuropathic pain. PMID: 28370084
- TRPA1 functions as a sensor that is activated by reactive aldehydes and is modulated when intracellular changes in oxygen levels occur. PMID: 27748654
- data suggest that cardamonin is a selective TRPA1 antagonist, providing novel insight into the target of its anti-nociceptive activity. PMID: 27589700
- Our results indicate that cannabinoids can enhance the mechanosensitivity of TG endings in the inner walls of anterior chambers of rat eye via TRPA1 activation. PMID: 27752892
- TRPA1-channels involvement in the activation of bladder DSM contraction of normal rats and rats with experimental diabetes. Our data show that diabetes affects TRPA1-dependent mechanisms of DSM contractility mainly via an overall inflammatory reaction associated with diabetes, which leads to an enhanced functional coupling between the tachykinin and prostanoid systems. PMID: 26935999
- Spinal TRPA1 may contribute to facilitation of morphine antinociceptive tolerance. PMID: 26922555
- Report activation of TRPA1 by o-chlorobenzylidene malononitrile as model of neuropathic pain. PMID: 26046936
- Meningeal blood flow is controlled by H2S-NO crosstalk activating a HNO-TRPA1-CGRP signalling pathway PMID: 25884403
- TRPA1 expression via activation of p38 MAPK in DRG neurons, at least in part, contributes to the development of oxaliplatin-induced acute cold hyperalgesia. PMID: 26567040
- The results of this study showed that TRPA1 in muscle afferents plays an important role in the development of acute mechanical hypersensitivity and in the maintenance of persistent muscle pain and hypersensitivity. PMID: 26393428
- H2S has both inhibitory and excitatory effects by opening KATP and TRPA1 channels, respectively, in RIN14B cells, suggesting potential bidirectional modulation of secretory functions. PMID: 26172081
- The TRPA1 channel mediates the analgesic action of dipyrone and pyrazolone derivatives PMID: 25765567
- TRPA1 appears to be localized not only at presynaptic terminals on SG neurons, enhancing glutamate release PMID: 25896791
- Results suggested that TRPA1 mechanisms play a significant role in the sensitization of ocular-responsive trigeminal brainstem neurons in this model for tear deficient dry eye PMID: 25639234
- TRPA1 is a major mediator of the proinflammatory/proalgesic actions of aromatase inhibitors PMID: 25484020
- TRPA1 channel has a role in activation of mechanosensitive afferent nerve activities of both Adelta- and C-fibers of the rat bladder, although its role in a physiological condition might be small. PMID: 23784920
- TRPA1 activation by H2O2 mediates the entire inflammatory response in an acute gout attack rodent model PMID: 24780252
- The results suggest that TRPA1 channels in rat odontoblastgs are involved in sensing membrane stretching and low-temperature stimulation. PMID: 24358160
- TRPA1 is essential to the in vivo nociceptive effects induced by one of the most important mediators of inflammatory pain, prostaglandin E. PMID: 24607781
- Hydrogen sulfide directly activates TRPA1 and its increment of diffusion into cells may be involved in the potentiation of TRPA1 activation under external acidic conditions. PMID: 23873754
- the actions of cyclooxygenase metabolites are mediated through the functioning of the TRPV1 and TRPA1 receptors PMID: 23832015
- TRPA1 might be involved in the pathophysiological process of ventilator-induced lung injury PMID: 23846257
- Cold activates rat and mouse TRPA1 but not human or rhesus monkey TRPA1. A single residue within the S5 transmembrane domain (G878 in rodent but V875 in primate) accounts for the difference in cold sensitivity. PMID: 24071625
- Reactive oxygen species enhance synaptic transmission in dorsal horn cells through TRPA1 (and TRPV1) channel activation. PMID: 23707800
- Data suggest spinal TRPA1 channels in posterior horn cells are involved in mechanical pain hypersensitivity, in increased cutaneous blood flow due to antidromic activation of nociceptive nerves, and in pronociceptive action of dynorphin A. PMID: 23959730
- Monosodium urate injection increases tissue H2 O2 , thereby stimulating TRPA-1 on sensory nerve endings to produce inflammation and nociception. PMID: 23918657
- H2S induces a nonspecific sensitizing effect on capsaicin-sensitive lung vagal fibers to both chemical and mechanical stimulation in rat lungs, which appears mediated through an action on the TRPA1 receptors. PMID: 23842678
- Gene silencing of TRPA1 completely prevents carrageenan-induced hyperalgesia and significantly reduces TRPA1 expression in dorsal root ganglia cells. PMID: 23098993
- The results of this study demonstrated that TRPA1 mediates some of the key inflammatory mechanisms, suggesting a key role of this receptor in pain and inflammation. PMID: 23521647
- Factors that stimulate TRPA1 channels expand Ca2+ signal-effector coupling at discrete sites along the endothelium to evoke graded cerebral artery vasodilation. PMID: 22928941
- TRPA1 channel in the skin contributes to sustained as well noxious mechanical stimulus-evoked postoperative pain PMID: 22588108
- Hydrogen sulfide activates TRPA1 receptors causing CGRP release from sensory nerves of rat tracheae. PMID: 22721614
- TRPA1 is functionally expressed primarily by IB4-binding, non-peptidergic mouse and rat sensory neurons PMID: 23133534
- Trpa1 expression in female Wistar rats varied with postnatal age, tissue (urothelium, detrusor, or whole bladder), and duration (4-h, 48-h, or chronic) of cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis. PMID: 22865090
- TRPA1 contributes to cold-induced contractions of the rat colon smooth muscle, and the mechanism involves the PLC/IP(3)/Ca(2+) pathway. PMID: 20717636
- TRPA1 is expressed on a substantial fraction of dural afferents, and activation of meningeal TRPA1 produces behaviors consistent with those observed in patients during migraine attacks. PMID: 22809691
- Methylglyoxal activates nociceptors through transient receptor potential channel A1 (TRPA1): a possible mechanism of metabolic neuropathies. PMID: 22740698
- Study propose that endogenous and exogenous ligands of TRPA1 cause Ca(2) influx and induce basal insulin release and that TRPA1-mediated depolarization acts synergistically with K(ATP) channel blockade to facilitate insulin release. PMID: 22701540
- The results indicate that warmth suppresses and desensitizes damage-sensing ion channel TRPA1. PMID: 22458587
- TRPA1 channel exerts an important role in the pathogenesis of peripheral diabetic neuropathy. Blocking the TRPA1 channel provides a selective disease-modifying treatment of PDN. PMID: 22133672
- The electrophysiological characteristics of TRPA1 suggest that it might play a unique role in nociception. PMID: 21653898
- These findings that a short-term application of artemin inhibits the TRPA1 channel's activity and the sequential pain behaviors suggest a role of artemin in regulation of sensory neurons. PMID: 21619614
- Data show that the TRPA1 activation and upregulation seem to exert an important role in overactive bladder following spinal cord injury. PMID: 21367919
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:Transient receptor (TC 1.A.4) family
-
组织特异性:Specifically expressed in a subset of nociceptive neurons. Expressed in dorsal root ganglia.
-
数据库链接:
Most popular with customers
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human HLA class II histocompatibility antigen gamma chain (CD74), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
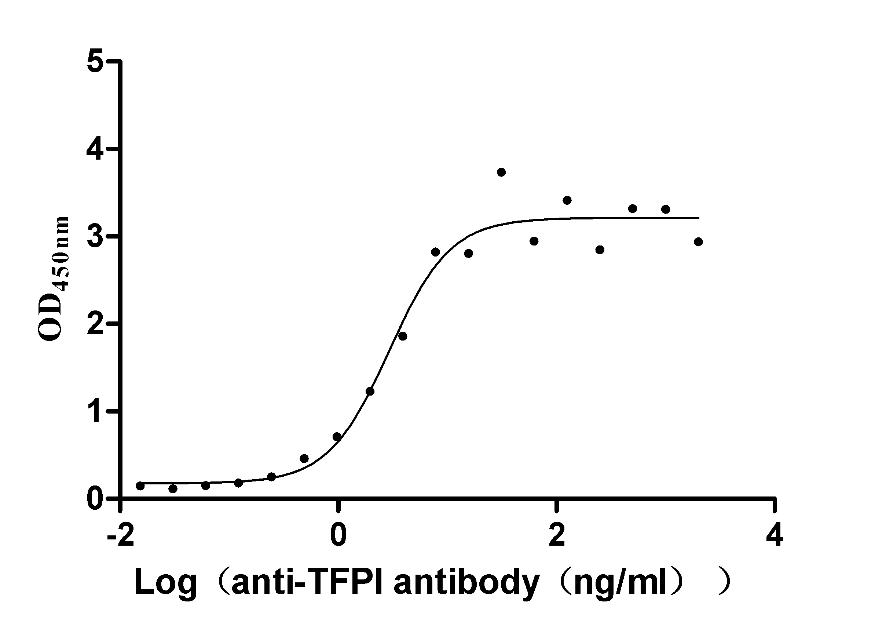
Recombinant Rabbit Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Oryctolagus cuniculus (Rabbit)
-
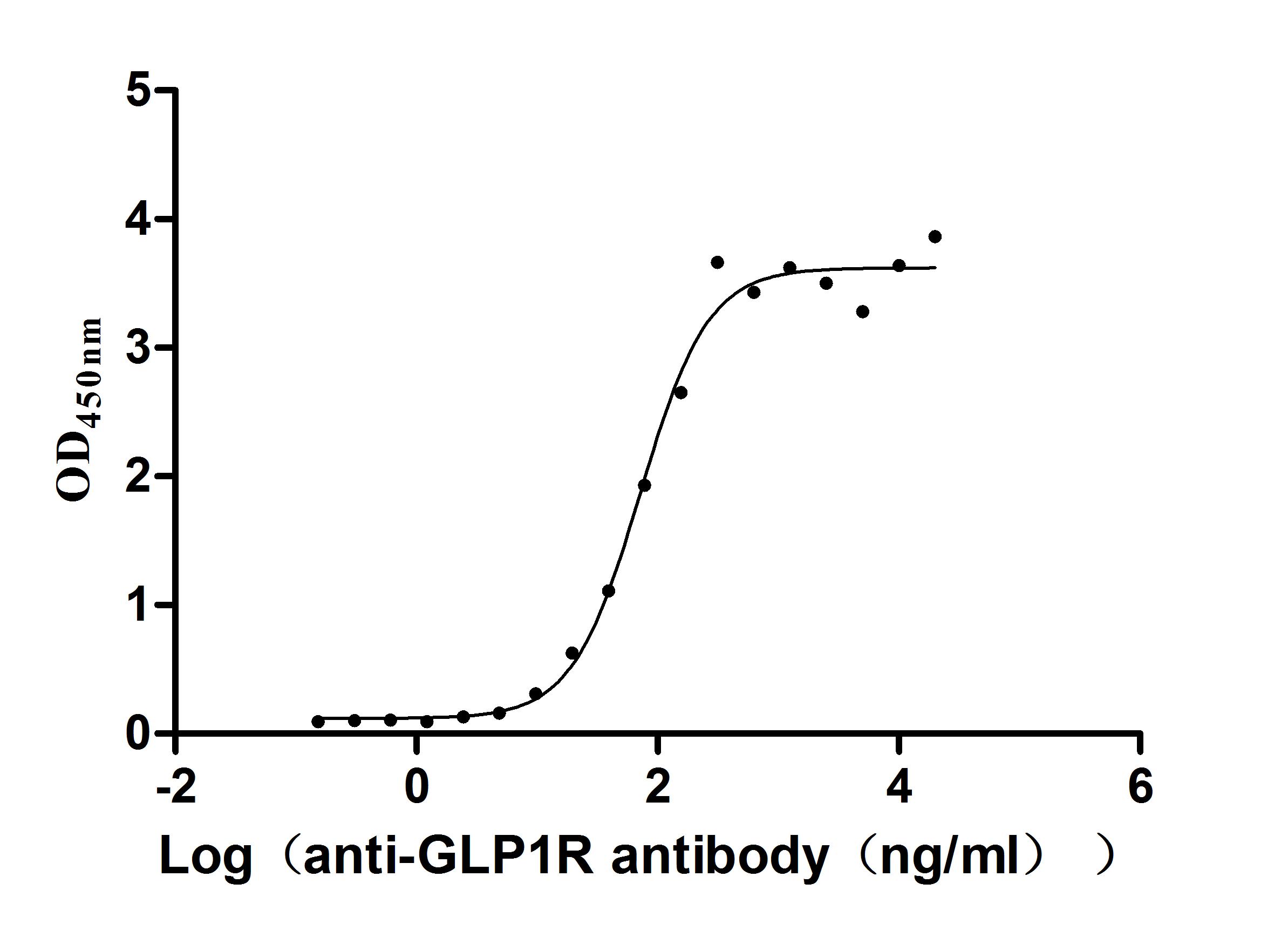
Recombinant Human Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (GLP1R), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
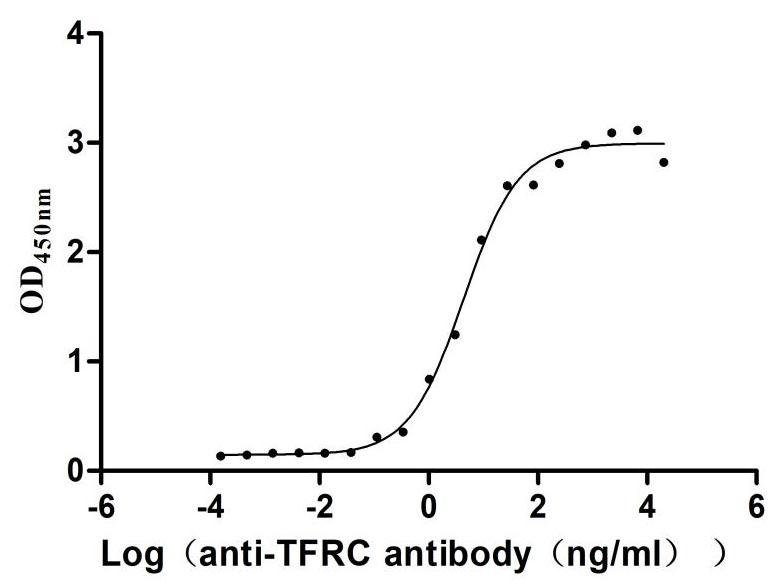
Recombinant Human Transferrin receptor protein 1 (TFRC), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
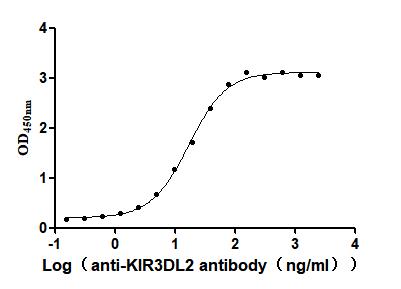
Recombinant Human Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 3DL2 (KIR3DL2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
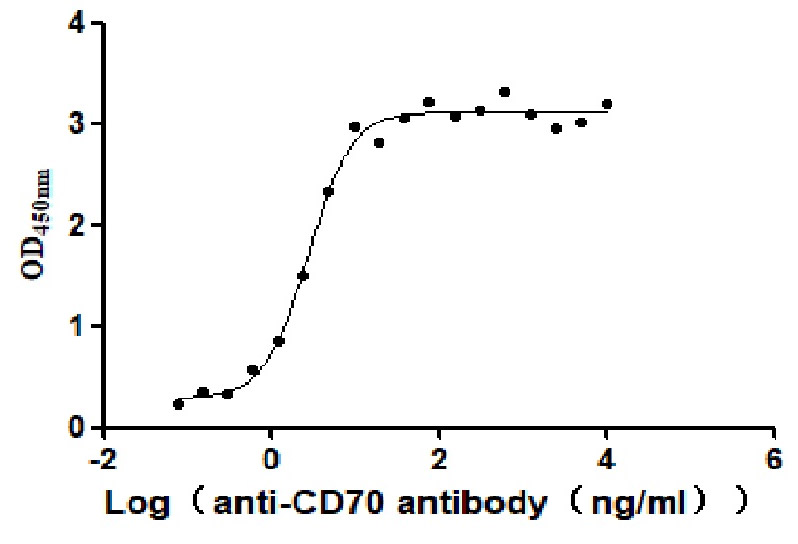
Recombinant Human CD70 antigen (CD70), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)