Recombinant Mouse Tight junction protein ZO-1 (Tjp1), partial
-
中文名称:小鼠Tjp1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP023573MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Tjp1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP023573MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Tjp1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP023573MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Tjp1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP023573MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Tjp1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP023573MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Tjp1; Zo1; Tight junction protein ZO-1; Tight junction protein 1; Zona occludens protein 1; Zonula occludens protein 1
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Tjp1, TjpP2, and Tjp3 are closely related scaffolding proteins that link tight junction (TJ) transmembrane proteins such as claudins, junctional adhesion molecules, and occludin to the actin cytoskeleton. The tight junction acts to limit movement of substances through the paracellular space and as a boundary between the compositionally distinct apical and basolateral plasma membrane domains of epithelial and endothelial cells. Necessary for lumenogenesis, and particularly efficient epithelial polarization and barrier formation. Plays a role in the regulation of cell migration by targeting Cdc42bpb to the leading edge of migrating cells. Plays an important role in podosome formation and associated function, thus regulating cell adhesion and matrix remodeling. With Tjp2 and TJjp3, participates in the junctional retention and stability of the transcription factor Dbpa, but is not involved in its shuttling to the nucleus.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Podocyte-specific deletion of the ZO-2 gene did not cause overt defects; however, double knockout of ZO-1 and ZO-2 genes accelerated the defects observed in ZO-1 knockout mice. These results suggest that ZO-2 plays supportive roles in the ZO-1-dependent regulation of podocyte filtration barrier. PMID: 29845705
- the endothelial barrier was preserved in respiratory epithelium isolated from MCU-/- mice after exposure to IL-13. In the ovalbumin-model of allergic airway disease, MCU deficiency resulted in decreased apoptosis within the large airway epithelial cells. Concordantly, expression of the tight junction protein ZO-1 was preserved, indicative of maintenance of epithelial barrier function PMID: 29225050
- Busulfan treatment down-regulated the epididymal expression of vimentin and zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1). PMID: 29101242
- At 3days after the first tamoxifen injection, Akt1(-/-)/iAkt2 KO hearts showed decreased expression of connexin43 (Cx43) and connexin-interacting protein zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1). Furthermore, Akt1/2 silencing significantly decreased both Cx43 and ZO-1 expression PMID: 29378301
- Overexpression of SHANK3 enhanced ZO-1 expression, and knockdown of SHANK3 resulted in decreased expression of ZO-1. Regulation of ZO-1 expression by SHANK3 seems to be mediated through a PKCepsilon-dependent pathway. The expression level of SHANK3 affects ZO-1 expression and the barrier function in intestinal epithelial cells in mice. PMID: 28906292
- Endothelial cellsTLR4 strongly regulates retinal vessel permeability by reducing expression of occludin and zonula occludens 1. PMID: 29136627
- Cx43 tethers the F-actin cytoskeleton through a ZO-1 linker and supports cell spreading and exploration during locomotion in cerebral endothelial cells. PMID: 26289751
- Expression of Podocalyxin, which positively regulates the formation of microvilli and the apical membrane, is repressed in embryoid bodies lacking both ZO-1 and ZO-2 and this correlates with an aberrant submembranous localization of Ezrin. PMID: 24905925
- Zonula occludens-1, occludin and E-cadherin expression and organization in salivary glands PMID: 25248927
- Tjp1 expression was decreased in glomerular diseases in human and animal models, our results indicate that the suppression of Tjp1 could directly aggravate glomerular disorders, highlights Tjp1 as a potential therapeutic target. PMID: 25184792
- Arecoline increases the production of TNF-alpha and induces protein redistribution of ZO-1. PMID: 25200553
- Vcl plays a crucial role in stabilizing gap junctions and myocyte integrity through direct interactions with ZO-1 and stabilization of CX43. PMID: 24413171
- Activation of RhoA/ROCK1 by high glucose in diabetic nephropathy disrupts the expression and translocation of occludin/ZO-1, which can be corrected by simvastatin. PMID: 24244596
- Vascular endothelial tight junctions and barrier function are disrupted by 15(S)-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid partly via protein kinase C epsilon-mediated zona occludens-1 phosphorylation at threonine 770/772. PMID: 24338688
- The JAM-A and ZO-1 genes were highly expressed in all the tested tissues. PMID: 23568966
- The results establish that ZO-1 acts as a true scaffolding protein and that the coordinated activity of multiple domains is required for normal TJ structure and function. PMID: 23418357
- Findings reveal novel roles for ZO-1 in mESC self-renewal, pluripotency, and differentiation by influencing several signaling networks that regulate these processes. PMID: 22782886
- results suggest that ARHGEF11 mediates RhoA-myosin light chain signaling pathways at cell-cell junctions, functioning in cooperation with ZO-1. PMID: 22665792
- CPEB-mediated zonal occludens-1 mRNA localization is essential for tight-junction assembly and mammary epithelial cell polarity PMID: 22334078
- Data indicate that Zo-1 is a response protein to inner medullary tonicity and that extracellular stressors can promote Zo-1 protein expression, tyrosine phosphorylation and cytoskeleton association. PMID: 21734410
- Here we report the (15)N, (13)C, and (1)H chemical shift assignments of the first PDZ domain of mouse ZO-1. PMID: 21431884
- ZO-1 redistribution is the earliest cellular event yet identified as a herald of physiological cell shedding, and redistribution of tight junction function along the lateral plasma membrane sustains epithelial barrier during cell shedding. PMID: 21346149
- ZO-1 and ZONAB are critical for differentiation and homeostasis of the RPE monolayer and may be involved in RPE disorders such as proliferative vitroretinopathy and atrophic age-related macular degeneration PMID: 21209887
- ZO-1, which is the central structural protein of the tight junction, is the binding partner of the cytoplasmic domain of mouse VSIG1 PMID: 20957455
- PLEKHA7 is a cytoplasmic component of the epithelial adherens junction belt, distinct from ZO-1 and E-cadherin PMID: 20808826
- suggest that MLCK-dependent ZO-1 exchange is essential to this mechanism of barrier regulation. PMID: 20404178
- Surface plasmon resonance study of interaction of occludin with ZO-1 PMID: 11700038
- Data show that a high level of ZO-1 is expressed in the mouse lens, and lens connexins were shown to co-immunoprecipitate with ZO-1. PMID: 12064591
- colocalizes with nectin and afadin at the puncta adhaerentia junctions between the mossy fiber terminals and the dendrites of the pyramidal cells in the CA3 hippocampal area PMID: 12717711
- Demonstration of a ZO-1/Cx35 association suggests a regulatory and/or scaffolding role of ZO-1 at gap junctions that form electrical synapses between neurons in mammalian brain. PMID: 15090040
- ZO-1 and ZO-2 function redundantly to some extent in junction formation/epithelial polarization but they are not functionally identical PMID: 15292177
- common molecular mechanism of forming a helical bundle between the hinge region/GuK domain of ZO-1 and alpha-catenin and occludin is identified as a general molecular principle organizing the association of ZO-1 at adherens and tight junctions. PMID: 15548514
- Tat decreased mRNA levels of ZO-1 and marked disruption of ZO-1 continuity and induced oxidative stress, affecting the integrity of the blood-brain barrier through the ERK 1/2 pathway. PMID: 15829913
- ZO-1-mediated delivery of Cx43 from a lipid raft domain to gap junctional plaques. PMID: 15855237
- focal VEGF and angiopoietin-2 hyperstimulation in the mouse brain increases MMP-9 activity and decreases ZO-1 protein PMID: 15947259
- The results of this study extend the CNS cell types that express the ZO-1, demonstrate an additional connexin (Cx30) that directly interacts with ZO-1, and show the association of a MsY3 with ZO-1 localized to oligodendrocyte and astrocyte gap junctions. PMID: 16045494
- Analysis showed increased ZO-1 membrane assembly in VEGF-treated RPE cells. Thus, VEGF has a dual capability with respect to the regulation of the expression of some TJ proteins at the transcriptional and post-translational levels depending on cell type. PMID: 16163490
- Alterations in the content and localization of ZO-1 may be relevant to the pathogenesis of proteinuria in diabetes. PMID: 16567508
- These findings indicate that ZO-1 and ZO-2 can independently determine whether and where claudins are polymerized. PMID: 16923393
- ZO-1 plays crucial roles not only in TJ formation, but also in the conversion from "fibroblastic" AJs to belt-like "polarized epithelial" AJs through Rac1 activation. PMID: 17353356
- loss of ZO-1 and increased permeability preceded the development of significant intestinal inflammation suggesting that in colitis alterations in the tight junction complex occur before the intestinal inflammation PMID: 17418867
- Shroom2 and ZO-1 form a tight-junction-associated scaffolding complex, possibly linked to myosin VIIa, that bridges the junctional membrane to the underlying cytoskeleton, thereby contributing to the stabilization of these junctions. PMID: 17666436
- These results suggest zonula occludens-1 interaction with connexin36 but not with Cx57 in the outer plexiform layer, and an absence of connexin57/connexin36 heterotypic gap junctional coupling in mouse retina. PMID: 17681699
- Activation of HIF-1alpha in the brain of dystrophic mice coupled with VEGF and VEGFR-2 up-regulation and ZO-1 and claudin-1 rearrangement might contribute to both blood-brain barrier opening and increased angiogenesis. PMID: 17784876
- These results suggest novel roles for ZO proteins as Src/Csk scaffolds potentially involved in the regulation of Src transformation. PMID: 18086565
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-linked superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1) mutants with different biochemical characteristics disrupted the blood-spinal cord barrier in mice by reducing the levels of the tight junction protein ZO-1. PMID: 18344992
- ZO-1 may be functionally important for cell remodeling and tissue organization in both the embryonic and extraembryonic regions, thus playing an essential role in embryonic development. PMID: 18353970
- These results provide the first evidence that ZO-1 is involved in blastocyst formation from the morula by regulating accumulation of fluid and differentiation of nonpolar blastomeres to polar trophoblast cells. PMID: 18423437
- analysis of ZO-1- and ZO-2-dependent integration of myosin-2 to epithelial zonula PMID: 18596233
- ZO-1 knockdown, or combined ZO-1 and ZO-2 knockdown, generated a more severe inhibition of blastocoel formation indicating distinct roles for ZO proteins in blastocyst morphogenesis. PMID: 18817772
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Peripheral membrane protein; Cytoplasmic side. Cell junction, tight junction. Cell junction, gap junction. Cytoplasm, myofibril, sarcomere, I band.
-
蛋白家族:MAGUK family
-
数据库链接:
Most popular with customers
-
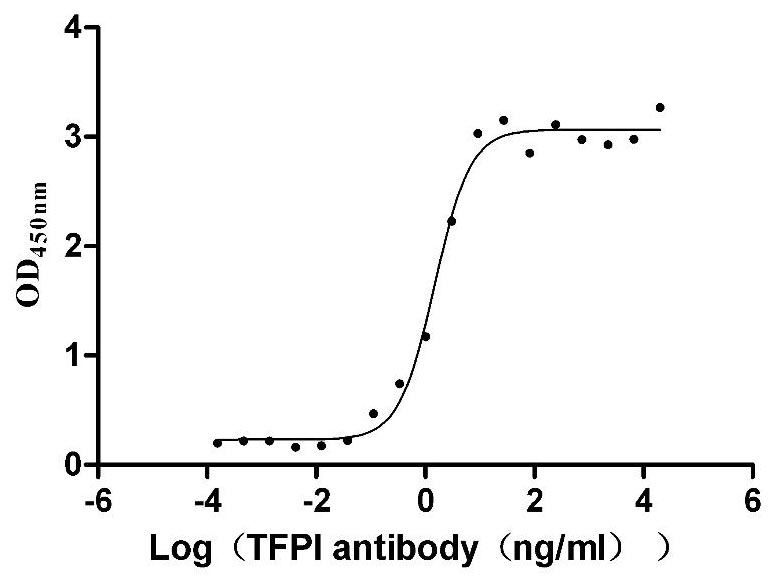
Recombinant Human Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Interleukin-17A (IL17A) (T26A) (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
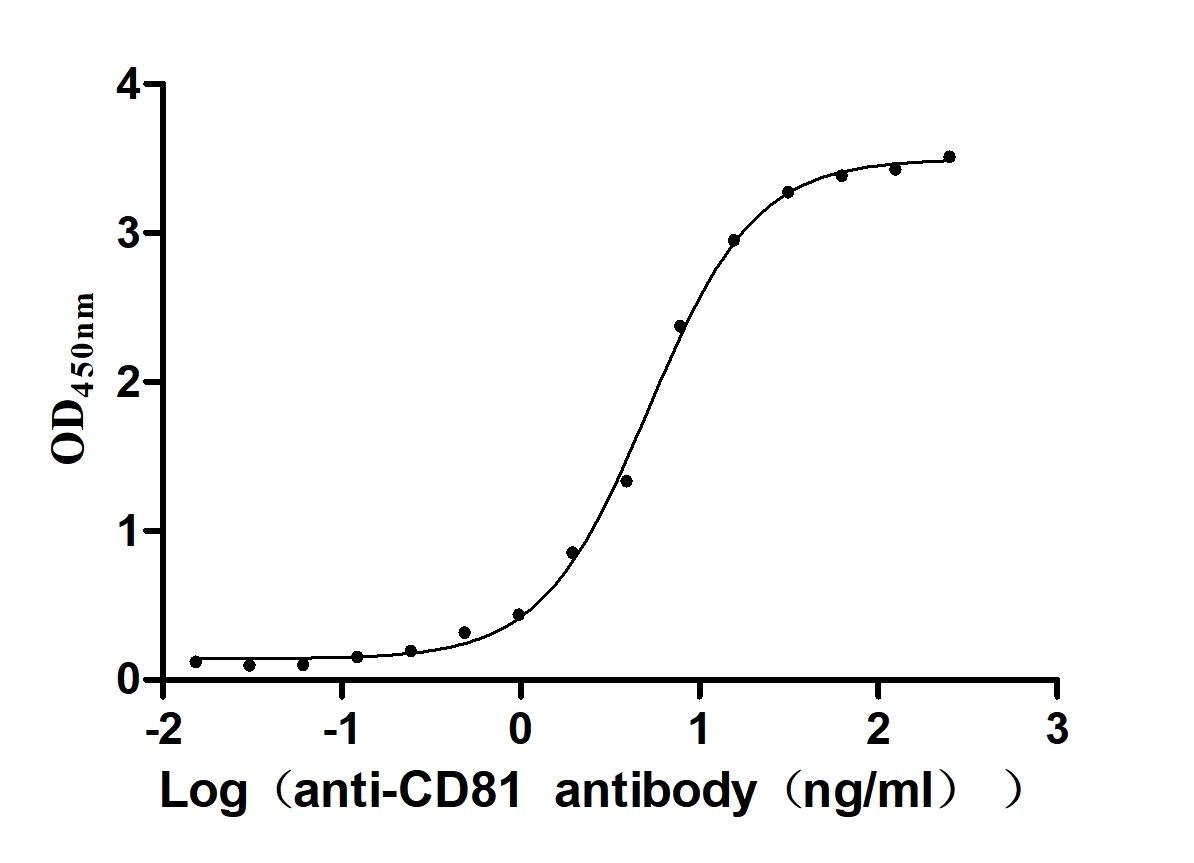
Recombinant Human CD81 antigen (CD81), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
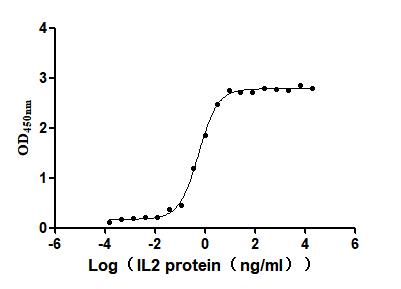
Recombinant Human Interleukin-2 (IL2) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
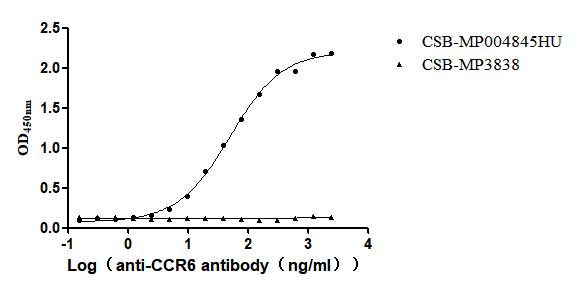
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 6(CCR6)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)
-AC1.jpg)