Recombinant Mouse Solute carrier family 12 member 5 (Slc12a5), partial
-
中文名称:小鼠Slc12a5重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP852768MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Slc12a5重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP852768MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Slc12a5重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP852768MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Slc12a5重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP852768MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Slc12a5重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP852768MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:Slc12a5
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Slc12a5; Kcc2; Kiaa1176; Solute carrier family 12 member 5; Electroneutral potassium-chloride cotransporter 2; K-Cl cotransporter 2; mKCC2; Neuronal K-Cl cotransporter
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Mediates electroneutral potassium-chloride cotransport in mature neurons and is required for neuronal Cl(-) homeostasis. As major extruder of intracellular chloride, it establishes the low neuronal Cl(-) levels required for chloride influx after binding of GABA-A and glycine to their receptors, with subsequent hyperpolarization and neuronal inhibition. Involved in the regulation of dendritic spine formation and maturation.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Enhancing GABAAR-mediated inhibition confines KCC2 to the plasma membrane, while antagonizing inhibition reduces KCC2 surface expression by increasing the lateral diffusion and endocytosis of the transporter. PMID: 29176664
- the long-time considered "neuron-specific" KCC2 co-transporter is expressed in pancreatic islet beta-cells where it modulates Ca(2+)-dependent insulin secretion. PMID: 28496181
- increase in KCC2 function mitigated induction of aberrant high-frequency activity during seizures, highlighting depolarizing GABA as a key contributor to the pathological neuronal synchronization seen in epilepsy. PMID: 30224498
- our results demonstrate that local deficits in KCC2 activity within the hippocampus are sufficient to precipitate Mesial temporal lobe epilepsy . PMID: 29884458
- Results demonstrate that KCC2 downregulation preceded convulsant induced epileptiform bursting activities both in vitro and in vivo. Suppression of its membrane expression induced spontaneous epileptiform bursting activities in vitro and Racine III seizure behaviors accompanied by epileptic EEG in vivo. PMID: 28279020
- Disruption of Kcc2-dependent inhibition of olfactory bulb output neurons suggests its importance in odor discrimination. PMID: 27389623
- Study provides evidence for a proconvulsive role of GABAA receptor signaling that depends on the involvement of the KCC2 co-transporter. PMID: 29045814
- This study directly implicates the dephosphorylation and downregulation of KCC2 in the peritumoral brain region in the pathophysiology of tumor-associated epilepsy in disease model mice; proposes that glutamate release from glioma cells mediate the dephosphorylation and downregulation of KCC2, revealing yet another target for the treatment of tumor-associated epilepsies. PMID: 27513374
- Neonatal maternal separation leads to KCC2 expression inhibition persisting until adolescence in hippocampus. PMID: 28962859
- TGF-beta2 is a new regulatory factor for KCC2 functional activation and membrane trafficking. PMID: 27505893
- GluK2-mediated increase in KCC2 recycling to the surface membrane translates to a hyperpolarization of the reversal potential for GABA (EGABA). PMID: 28235805
- these data provide insight into the mechanism regulating Cl(-) homeostasis in immature neurons, and suggest that WNK1-regulated changes in KCC2 phosphorylation contribute to the developmental excitatory-to-inhibitory GABA sequence. PMID: 26126716
- Decreasing [Cl(-)]i levels caused by increasing KCC2 levels in the 12 N could play important roles in regulating the frequency of respiration-related rhythmic activity during development. PMID: 25596421
- Results showed that the fast functional up-regulation of KCC2 in the mouse hippocampus following neonatal status epilepticus is dependent on BDNF PMID: 25229715
- In these neurons, the plasmalemmal expression of KCC2, which establishes the low [Cl(-) ]i required for GABAA R-mediated inhibition PMID: 25066727
- Decreased KCC2 protein expression, serine 940 dephosphorylation in motoneurons was found in mice with post-stroke spasticity. PMID: 25546454
- study demonstrates that the level of KCC2 function sets the strength of postsynaptic inhibition. PMID: 25834055
- Phosphorylation of S940 plays a critical role in potentiating KCC2 activity to limit the development of status epilepticus. PMID: 25733865
- Results reveal KARs as regulators of KCC2, significantly advancing our growing understanding of the tight interplay between excitation and inhibition. PMID: 24910435
- KCC2a and KCC2b isoforms have overlapping roles in neonatal neurons. PMID: 24639001
- NO-mediated suppression of KCC2 can modulate synaptic inhibition in the superior paraolivary nucleus. PMID: 24987336
- Suppressed expression of PRIPs induces an elevated expression of KCC2 in the spinal cord, resulting in inhibition of nociception and amelioration of neuropathic pain in DKO mice. PMID: 23639135
- NL2 also regulates KCC2 to modulate GABA functional switch. PMID: 23663753
- BPA can disrupt Kcc2 gene expression through epigenetic mechanisms PMID: 23440186
- Loss of the Neto2:KCC2 interaction reduced KCC2-mediated Cl(-) extrusion, resulting in decreased synaptic inhibition in hippocampal neurons. PMID: 23401525
- impaired Cl- extrusion capacity resulting from decreased KCC2 activity reduces the analgesic efficacy of certain GABAA receptor agonists and allosteric modulators. PMID: 22537560
- ISO domain of KCC2 is required for neuronal chloride regulation PMID: 22723714
- Ablation of Kcc2 from granule cells impaired consolidation of long-term phase learning of the vestibulo-ocular reflex, whereas baseline performance, short-term gain-decrease learning and gain consolidation remained intact. PMID: 22252133
- KCC2 gene regulation plays a crucial role in the development of immature neurons via Egr4 downstream of the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway PMID: 21837281
- Data show that neuronal networks within the spinal cord are more excitable in KCC2 mutant mice, which suggests that KCC2 strongly modulates the excitability of spinal cord networks. PMID: 21255132
- Egr4 is an important component in the mechanism of BDNF-dependent KCC2 gene regulation via the ERK1/2 pathway in immature neurons. PMID: 21228173
- These results point to a role of KCC2 in neuronal differentiation and migration during early development mediated by its direct structural interactions with the neuronal cytoskeleton. PMID: 20529123
- Tyrosine phosphorylation of KCC2 is thus likely to play a key role in regulating the degradation of KCC2, a process that may be responsible for pathological losses of KCC2 function that are evident in status epilepticus and other forms of epilepsy. PMID: 20600929
- These results suggest that absence of KCC2 preserves the depolarizing action of GABA in CR cells and support the notion that KCC2 is a key factor controlling Cl- homeostasis and preventing hyperexcitability. PMID: 18789906
- chromosome 5 mapping PMID: 11701957
- Hyperexcitability and epilepsy associated with disruption of the mouse neuronal-specific K-Cl cotransporter gene. PMID: 12000122
- KCC2 was localized to approximately 34% of GnRH neurons. PMID: 12810559
- tyrosine-phosphorylation seems to be less important in the emergence of low intracellular chloride than the transcriptional upregulation of KCC2 PMID: 14648690
- Neither neuronal spiking nor ionotropic glutamatergic and GABAergic transmission are required for the developmental expression of KCC2 in mouse hippocampal neurons in vitro. PMID: 14686894
- Cortical neurons lacking KCC2, not only fail to show a developmental decrease in [Cl-]i, but also are unable to regulate [Cl-]i on Cl- loading or maintain [Cl]i during membrane depolarization. PMID: 15469961
- We propose a model for functional coupling between the Na+, K+-ATPase alpha2 subunit and KCC2, which excludes Cl- from the cytosol in respiratory center neurons. PMID: 15564586
- the functional activity of KCC2 in vivo parallels the developmental expression of the protein, whereas cultured neurons require an additional activation step (mimicked by staurosporine) for KCC2 to become functional. PMID: 15787696
- Almost all KCC2-positive dendrites (more than 98%) attached to and formed synapses with mossy fiber terminals. As development proceeded, the number of KCC2-positive granule cells increased, and all granule cells became positive by P21. PMID: 17008020
- The KCC2 was first detected within the Purkinje cells in the Purkinje cell layer of the hemisphere at embryonic day 15 (E15) and the vermis at E17, but the ventricular and intermediate zones were negative. PMID: 17134779
- Analysis of KCC2 potassium-chloride cotransporter (Slc12a5) promoter and proximal intron-1 regions reveals 10 candidate transcription factor binding sites that are highly conserved in mammalian KCC2 genes. PMID: 17192429
- The novel KCC2a isoform differs from the only previously known KCC2 isoform (now termed KCC2b) by 40 unique N-terminal amino acid residues, including a putative Ste20-related proline alanine-rich kinase-binding site. PMID: 17715129
- KCC2 interacts with the dendritic cytoskeleton to promote spine development. PMID: 18093524
- a reduction of KCC2 expression by half results in increased susceptibility to seizure PMID: 18394864
- Deregulation of KCC2 expression may break the balance of intracellular and extracellular chloride concentration which contributes to the mechanism of hyperexcitability leading to seizures. PMID: 18550034
- Injured neurons reverse their response to BDNF by switching the BDNF-induced downregulation of KCC2 to upregulation. PMID: 18596173
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell projection, dendrite. Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Note=Detected on dendrites, but not on axons of spinal cord neurons and at GPHN-positive inhibitory synapses.
-
蛋白家族:SLC12A transporter family
-
组织特异性:Isoform 2 expressed in brainstem and spinal cord, isoform 1 expressed in brainstem, spinal cord and olfactory bulb of 17 dpc embryos. Isoforms 1 and 2 expressed in all parts of the brain and spinal cord in postnatal day 14 mice.
-
数据库链接:
Most popular with customers
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Glypican-3 (GPC3) (G537R), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
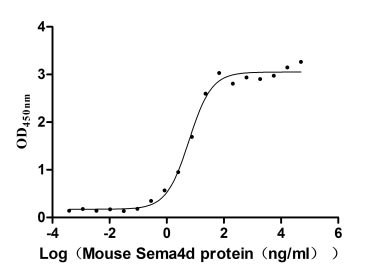
Recombinant Mouse Semaphorin-4D (Sema4d), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human R-spondin-1 (RSPO1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Mouse Transthyretin (Ttr) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human Trophoblast glycoprotein (TPBG), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
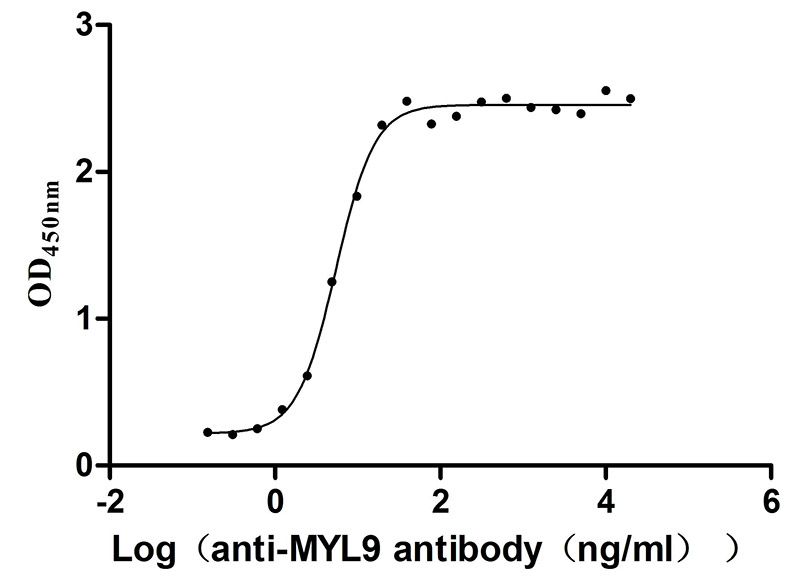
Recombinant Human Myosin regulatory light polypeptide 9 (MYL9) (Active)
Express system: Yeast
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Cytotoxic and regulatory T-cell molecule (CRTAM), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)