Recombinant Mouse Protein FADD (Fadd)
-
中文名称:小鼠Fadd重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP730727MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Fadd重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP730727MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Fadd重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP730727MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Fadd重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP730727MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Fadd重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP730727MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Fadd; Mort1FAS-associated death domain protein; FAS-associating death domain-containing protein; Mediator of receptor induced toxicity; Protein FADD
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:full length protein
-
表达区域:1-205
-
氨基酸序列MDPFLVLLHS LSGSLSGNDL MELKFLCRER VSKRKLERVQ SGLDLFTVLL EQNDLERGHT GLLRELLASL RRHDLLQRLD DFEAGTATAA PPGEADLQVA FDIVCDNVGR DWKRLARELK VSEAKMDGIE EKYPRSLSER VRESLKVWKN AEKKNASVAG LVKALRTCRL NLVADLVEEA QESVSKSENM SPVLRDSTVS SSETP
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Apoptotic adaptor molecule that recruits caspase-8 or caspase-10 to the activated Fas (CD95) or TNFR-1 receptors. The resulting aggregate called the death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) performs caspase-8 proteolytic activation. Active caspase-8 initiates the subsequent cascade of caspases mediating apoptosis. Involved in interferon-mediated antiviral immune response, playing a role in the positive regulation of interferon signaling.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- results show that N-FADD is a more potent apoptotic inducer and VNP20009-mediated targeted expression of N-FADD provides a possible cancer gene therapeutic approach for the treatment of melanoma. PMID: 27767039
- these results demonstrated that RIPK3-mediated signaling in Tie-2 expressing cells was responsible for the embryonic lethality of Fadd-/- with cardiac failure. PMID: 27584790
- The study provides genetic evidence that different RIP1 kinase inactive mutations have distinct impacts on the embryogenesis of Fadd-deficient mice. PMID: 28574501
- Our findings reveal that MLKL and FADD play critical roles in preventing lymphoproliferative disease and activating the NLRP3 inflammasome PMID: 27498868
- miR-7a was a necessary mediator in FADD-regulated FAK expression. In contrast to its classical apoptotic role, FADD interference could reduce the rate of cell migration, which could be rescued by inhibiting miR-7a expression. PMID: 27286445
- In macrophages, ultraviolet radiation induced association of MyD88 with FADD and migration of FADD to the cell membrane PMID: 27676214
- The authors conclude that FADD is a master regulator of glucose and fat metabolism. PMID: 27357657
- Mice deficient in RIPK3 or doubly deficient in MLKL and FADD, but not MLKL alone, are more susceptible to influenza A virus than their wild-type counterparts, revealing an important role for RIPK3-mediated apoptosis in antiviral immunity. PMID: 27321907
- Wild-type cells can execute apoptosis via both, the mitochondrial and the receptor-mediated pathway whereas FADD-deficient cells can only activate the intrinsic pathway. There is a difference in UVC radiation response between two cell lines indicating the role of FADD in the selection of cell death modality. PMID: 27258329
- This study reveals an essential role of SUMOylated FADD in Drp1- and caspase-10-dependent necrosis. PMID: 27799292
- Deletion of FADD in macrophages and granulocytes results in RIP3- and MyD88-dependent systemic inflammation. PMID: 25874713
- A constitutively phosphoryl-mimicking mutation of Fas-associated death domain (FADD-D) enhances Notch-1 signaling and compromises Wnt signaling in both cultured myoblasts and regenerating muscles. PMID: 26303234
- Beta amyloid-induced upregulation of death receptor 6 accelerates the toxic effect of N-terminal fragment of amyloid precursor protein PMID: 25150572
- Phosphorylation of FADD by the kinase CK1alpha promotes KRASG12D-induced lung cancer. PMID: 25628462
- This study evaluated the role of FADD in pancreatic islets and insulin secretion. PMID: 25641109
- depletion of alphaNAC in multiple types of cancer cells induce typical apoptotic cell death. This anti-apoptotic function is mediated by the FADD/c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway. PMID: 24901053
- These data suggest that as a death receptor, FADD is also required for cell survival in beta-selection as a regulator of Notch1 expression. PMID: 24901044
- using T-cell specific deletion mice, we observed that FADD deficiency in thymocytes led to increased apoptosis and reduced cell numbers, which may be attributed to the reduction of Glut1 expression and correspondingly decreased glucose uptake PMID: 25078620
- FADD deficiency protects against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in a heart failure mouse model. PMID: 24058479
- glycogen synthesis, glycolysis, and gluconeogenesis were dysregulated because of FADD phosphorylation, both in MEFs and liver tissue of the mice bearing phosphorylation-mimicking mutation form of FADD. PMID: 23828893
- FADD regulates the fate determination of cycling satellite cells. PMID: 24375410
- p45 forms a complex with FADD and diminishes Fas-FADD mediated death signaling. PMID: 23935974
- Used proteomics and bioinformatic analysis to study proteins differentially expressed in three cell lines containing FADD and its mutant, FADD-A and FADD-D. PMID: 23744592
- Impaired mitochondrial function and proteolysis may play pivotal roles in the dysfunction associated with FADD deficiency-induced disorders, probably including embryonic lethality. PMID: 23689606
- FADD Protects Cells from IFN-gamma-Activated Necrosis by Preventing Formation of the RIP1-RIP3 Necrosome. PMID: 23898178
- Fas (TNF receptor superfamily member CD95) activates interleukin (IL)-1beta and IL-18 in a caspase-8- and Fas-associated death domain (FADD) protein-dependent and receptor-interacting protein (Rip)3-independent pathway. PMID: 23144495
- show that epidermal keratinocyte-restricted deficiency of the adaptor protein FADD (FADD(E-KO)) induced severe inflammatory skin lesions in mice PMID: 22000287
- RIPK3 and FADD have opposing and complementary roles in promoting T-cell clonal expansion and homeostasis. PMID: 21876153
- tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced necroptosis requires the adaptor proteins FADD and NEMO. PMID: 21746883
- mechanisms preventing RIP3-mediated epithelial cell death are critical for maintenance of intestinal homeostasis and indicate that programmed necrosis of intestinal epithelial cells might be implicated in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease PMID: 21804564
- data demonstrate an unexpected cell-type-specific interplay between FADD and RIP1, which is critical for the regulation of apoptosis and necrosis during embryogenesis and lymphocyte function PMID: 21368761
- specific polymorphisms at Fas, FasL and Fadd genes that differentiate mouse strains exhibiting extreme differences in susceptibility to gamma radiation-induced T-cell lymphomas. PMID: 20889682
- FADD is critical for ODC apoptosis and the development of autoimmune demyelinating disease. PMID: 21068410
- molecular studies led to the discovery of a previously unappreciated HIF-1 binding site in the FADD promoter, which controls repression of FADD during hypoxia. PMID: 20943999
- FADD constitutes a mechanism to keep TCR-induced programmed necrotic signaling in check during early phases of T-cell clonal expansion. PMID: 20615958
- Importance in signaling in serum deprivation and hypoxia-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis PMID: 12063258
- inhibition of FADD function blocks proliferation but not MAP kinase-activation and interleukin-2-production during primary stimulation of T cells PMID: 12115619
- MORT1/FADD is indispensable for Fas and TNF-mediated hepatic injury PMID: 12500197
- FADD acquired a domain during evolution, rendering it a "proliferation-apoptosis coupler" that balances cell proliferation and apoptosis. PMID: 12705854
- Loss of this protein's expression results in a biased Fas-signaling pathway and correlates with the development of tumoral status in thyroid follicular cells. PMID: 12743602
- In a highly regulated fashion, FADD can transduce either a signal for survival or one that leads directly to apoptosis; the balance between these opposing outcomes is crucial to adaptive immunity. PMID: 12817005
- RIP, TRAF2, and FADD are crucial in mediating ROS accumulation in TNF-induced necrotic cell death PMID: 14701813
- Modifications and intracellular trafficking of Mort1 after T-lymphocyte activation was studied. PMID: 15017386
- binding of Fas-associated death domain (FADD) to the tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand receptor DR5 is regulated by the death effector domain of FADD PMID: 15173180
- FasL induces NF-kappaB activation and IL-8 production by a novel mechanism, distinct from that of TNF-alpha and FADD had a dominant-negative effect on the FasL-induced NF-{kappa}B activation. PMID: 15337758
- Data suggest that the loss of FADD/caspase-8 function during development and/or in mature T cells selectively impacts on some but not other pathways of T-cell activation and maturation. PMID: 15376191
- mammalian cells lacking the death-domain-containing protein FADD are defective in intracellular dsRNA-activated gene expression, including production of type I (alpha/beta) interferons, and are thus very susceptible to viral infection PMID: 15549108
- A site is identified in the death domain of FADD that is essential for signal-specific binding to Fas and TRADD and for mediating apoptosis. PMID: 16009710
- Casein kinase Ialpha (CKIalpha) phosphorylates FADD at Ser194 both in vitro and in vivo. Phosphorylation of FADD by CKI is a crucial event during mitosis. PMID: 16061179
- FADD plays a dispensable role during thymocyte development, but is essential in maintaining peripheral T cell homeostasis. and regulating both apoptotic and proliferation signals. PMID: 16116191
显示更多
收起更多
-
数据库链接:
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus Spike glycoprotein (S), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Human SARS coronavirus (SARS-CoV) (Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus)
-
Recombinant Human E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase ZNRF3 (ZNRF3), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human B-lymphocyte antigen CD20 (MS4A1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Intestinal-type alkaline phosphatase (ALPI) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Mouse Retinol-binding protein 4 (Rbp4) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
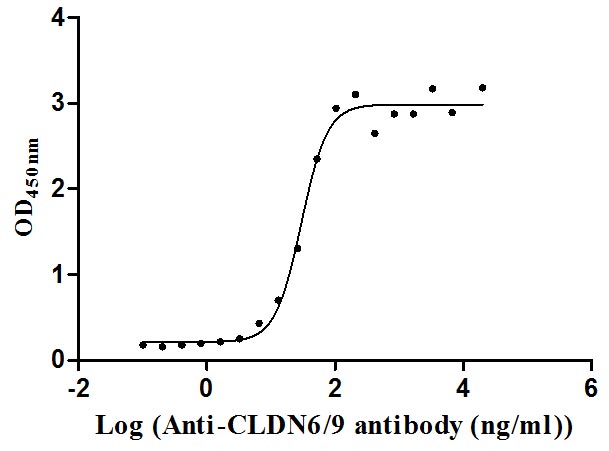
Recombinant Human Claudin-9 (CLDN9)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
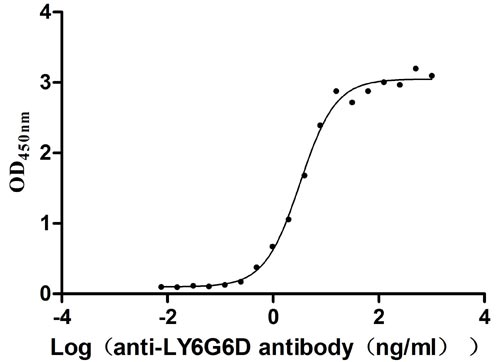
Recombinant Human Lymphocyte antigen 6 complex locus protein G6d (LY6G6D) (Active)
Express system: Yeast
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
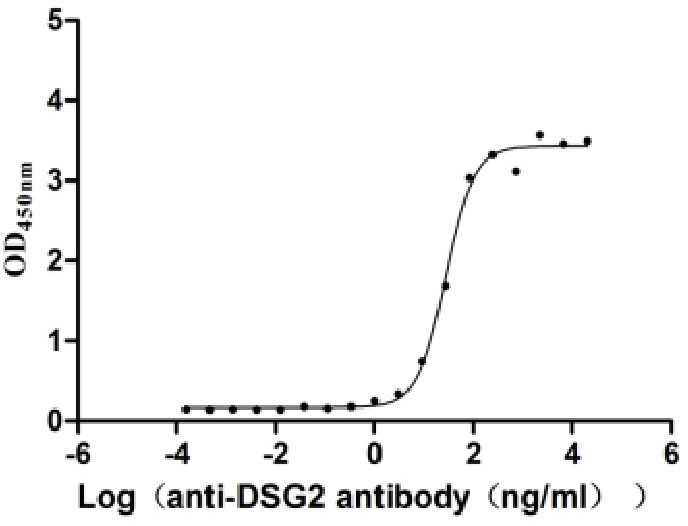
Recombinant Human Desmoglein-2 (DSG2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)