Recombinant Mouse Potassium/sodium hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channel 1 (Hcn1), partial
-
中文名称:小鼠Hcn1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP010216MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Hcn1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP010216MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Hcn1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP010216MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Hcn1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP010216MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Hcn1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP010216MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Hcn1; Bcng1; Hac2; Potassium/sodium hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channel 1; Brain cyclic nucleotide-gated channel 1; BCNG-1; Hyperpolarization-activated cation channel 2; HAC-2
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Hyperpolarization-activated ion channel exhibiting weak selectivity for potassium over sodium ions. Contributes to the native pacemaker currents in heart (If) and in neurons (Ih). May mediate responses to sour stimuli.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Study shows that hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channels reduce the rate of exocytosis from a subset of cortical synaptic terminals. PMID: 28071723
- in Hcn1 (-/-) mice, baseline acoustic startle response (ASR)levels were lower, temporal integration was delayed, time constants for ASR depression by noise offset were higher, and their sensitivity to brief gaps and spatial acuity was diminished PMID: 28050647
- Low-voltage-activated K(+) (gKL) and hyperpolarization-activated mixed cation conductances (gh) mediate currents, IKL and Ih, through channels of the Kv1 (KCNA) and HCN families respectively and give auditory neurons the temporal precision required for signaling information about the onset, fine structure, and time of arrival of sounds. PMID: 28065805
- results implicate presynaptic NMDA receptor inhibition followed by reduced activity of presynaptic HCN1 channels, which would result in an increase in glutamate release and postsynaptic glutamate receptor activity, as a mechanism of ketamine action. PMID: 27965425
- HCN channels play a critical role in the separation of overlapping movement responses and allow for successful reaching behaviours. These data provide a novel mechanism for the encoding of multiple movement responses within shared networks of motor cortex. This mechanism supports a viewpoint of primary motor cortex as a site of dynamic integration for behavioural output PMID: 27568501
- The study thus identifies novel candidate QTGs HCN1 that may contribute to variation in emotional learning in mice. PMID: 27277803
- Data show that prostaglandin E2 receptor EP3 subtype (EP3) was expressed in the interstitial cells of Cajal (ICCs) of the bladder and activated hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channels. PMID: 28131828
- Data show that KCNJ15 inward rectifier potassium channel and hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channel currents are changed in Trisomic neuron. PMID: 26501103
- We investigated the effects of an additional genetic deletion of HCN1 on the function and survival of photoreceptors in a mouse model of CNGB1-linked retinitis pigmentosa (RP). PMID: 26740549
- in the absence of HCN1-mediated feedback, the amplitude of rod signals remains at high levels for a prolonged period of time, leading to saturation of the retinal pathways. PMID: 26807953
- Resilience to tinnitus is developed in mice that show a re-emergence of KCNQ2/3 channel activity and a reduction in HCN channel activity. PMID: 26312501
- HCN1, HCN2, and HCN4 subunits may have distinct physiological roles in the developing hippocampus. PMID: 25761792
- Forebrain HCN1 channels contribute to hypnotic and amnestic effects of volatile anesthetics, but do not contribute to immobilizing actions. PMID: 26287296
- This study demonstrated that Increased expression of hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channels in reactive astrocytes following ischemia. PMID: 25042871
- Results suggest that spike-and-wave discharges in an established model of absence epilepsy reduce hippocampal HCN1 expression and function, and that the reduction associates with a spatial learning deficit PMID: 24368169
- Grid fields in HCN1 KO mice display more experience-dependent asymmetry consistent with reports of enhanced long-term potentiation in the absence of HCN1. The loss of HCN1 improves temporal coding via the rate-phase transformation. PMID: 24638961
- We conclude that TRIP8b in the retina is needed to achieve maximal expression of HCN1. PMID: 24409334
- HCN1 channels in cerebellar Purkinje cells reduce the duration of inhibitory synaptic responses. PMID: 24000178
- acute abrogation of HCN1-FLNa interaction in neurons, with the use of decoy peptides that mimic the FLNa-binding domain of HCN1, abolishes the punctate distribution of HCN1 channels in neuronal cell bodies PMID: 24403084
- HCN1 contributes substantially to hyperpolarization-activated current properties in individual cortical plate neurons PMID: 23821600
- HCN1 stabilizes the leading pacemaker region within the sinoatrial node and hence is crucial for stable heart rate and regular beat-to-beat variation. HCN1-deficient mice may be a valuable genetic disease model for human sinus node disease. PMID: 24218458
- Hcn1 ion conductivity was significantly lower in senescence-accelerated mouse prone 8 (SAMP8) compared to that of Japanese fancy mouse 1 (JF1), which may be associated with learning and memory deficiency. PMID: 24125720
- Ther results of this study provided genetic evidence demonstrating the importance of HCN1 to intrinsic persistent firing and the behavioral output of the Prefrontal cortex. PMID: 23966682
- These observations identify Ih as an ionic current that is regulated in a cyclical manner by circulating estradiol within the female brain PMID: 23804103
- Data indicate that the hyperpolarization-activated cation channel HCN1 do not participate directly to the pacemaker activity of periglomerular dopaminergic neurons, but influence their resting membrane potential. PMID: 23418585
- HCN1-containing channels represent a behaviorally relevant molecular target of ketamine. PMID: 23377220
- Leucine zipper motif essential for gating of HCN1 and HCN2. PMID: 23048023
- Data indicate that HCN1 and HCN2 form alternate ternary protein complexes with hair-cell stereociliary proteins. PMID: 22948144
- Loss of KCNE2 leads to downregulation of HCN channel function associated with increased excitability in neurons in the cortico-thalamo-cortical loop. PMID: 22880098
- Suggest that the strongly increased HCN channel activity in hypertrophied myocytes prolongs the repolarization of the ventricular action potential and thereby may increase the arrhythmogenic potential. PMID: 22652004
- Data show that HCN1 and HCN2 channels are expressed at distinct retinal sites and serve different functions. PMID: 22279546
- TRIP8b isoforms are important regulators of HCN1 trafficking in entorhinal neurons. PMID: 22363812
- Data show that proper cone vision under mesopic conditions requires rapid adaptational feedback modulation of rod output via hyperpolarization-activated and cyclic nucleotide-gated channels 1. PMID: 22068599
- blockade and activation of HCN channel activity in vitro bidirectionally altered the membrane excitability of the STN neurons. PMID: 22013231
- Shortening and shaping of light responses by activation of HCN1 is an important step at least in the scotopic pathways. PMID: 22183410
- HCN1 represents the isoform which is selectively expressed in most parts of the conduction system suggesting a substantial contribution of HCN1 to pacemaking. PMID: 21945247
- Although the dorsal-ventral gradient of the grid pattern was preserved in HCN1 knockout mice, the size and spacing of the grid fields, as well as the period of the accompanying theta modulation, was expanded at all dorsal-ventral levels. PMID: 22100643
- The results of this study suggested that that HCN1 contributes to vestibular hair cell function and the sense of balance. PMID: 22090507
- HCN1 is strongly expressed in neurons and in entorhinal cortex grid cells, which provide spatial information to the CA1 and CA3 regions of the hippocampus. PMID: 22099465
- we demonstrate in vivo and in vitro that the interplay of a negative chloride reversal potential, a strong inhibition and a powerful IH results in a temporally precise, duration-sensitive offset response in the superior paraolivary nucleus. PMID: 21903083
- increasing cAMP levels in cells antagonized the up-regulation of HCN1 channels mediated by a TRIP8b construct binding the CNBD exclusively. PMID: 21504900
- hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) ion channel function was reduced in MitoPark DA neurons, although HCN messenger RNA was unchanged. PMID: 21233488
- HCN1 channel inhibits glutamate synaptic release by suppressing the activity of low-threshold voltage-gated T-type Cav3.2 calcium channel signaling. PMID: 21358644
- This study suggested that the outgrowth and coalescence of olfactory sensory neurons axons is, at least in part, subject to activity-dependent mechanisms mediated via HCN channels. PMID: 21147989
- Down-regulation of HCN1 associated with rodent models of epilepsy may be a contributing factor in seizure behavior. PMID: 20384728
- The differences in evolution and fucntion of HCN1 and HCN2 are reported. PMID: 20130205
- The expression pattern of HCN isoforms in the olfactory bulb of mice, is described. PMID: 20140458
- This study indicated that upregulation of alpha5 subunit-mediated GABA(A) receptor tonic current compensates quantitatively for loss of dendritic I(h) in cortical pyramidal neurons from HCN1 knock-out mice to maintain normal synaptic summation. PMID: 20164346
- determination that S5-P Cys(318) of HCN1 is externally accessible and that the external pore vestibule and activation gating of HCN channels are allosterically coupled PMID: 12351622
- Major contributions of HCN1 and HCN2 channel isoforms to hyperpolarization-activated, non-selective cation current. HL-1 cells display a hyperpolarization-activated current which might contribute to spontaneous contractile activity of these cells. PMID: 12433951
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:Potassium channel HCN family
-
组织特异性:Predominantly expressed in brain. Highly expressed in apical dendrites of pyramidal neurons in the cortex, in the layer corresponding to the stratum lacunosum-moleculare in the hippocampus and in axons of basket cells in the cerebellum. Expressed in a sub
-
数据库链接:
Most popular with customers
-
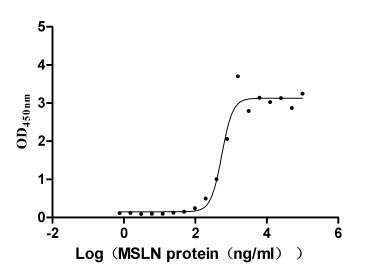
Recombinant Human Mucin-16 (MUC16), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
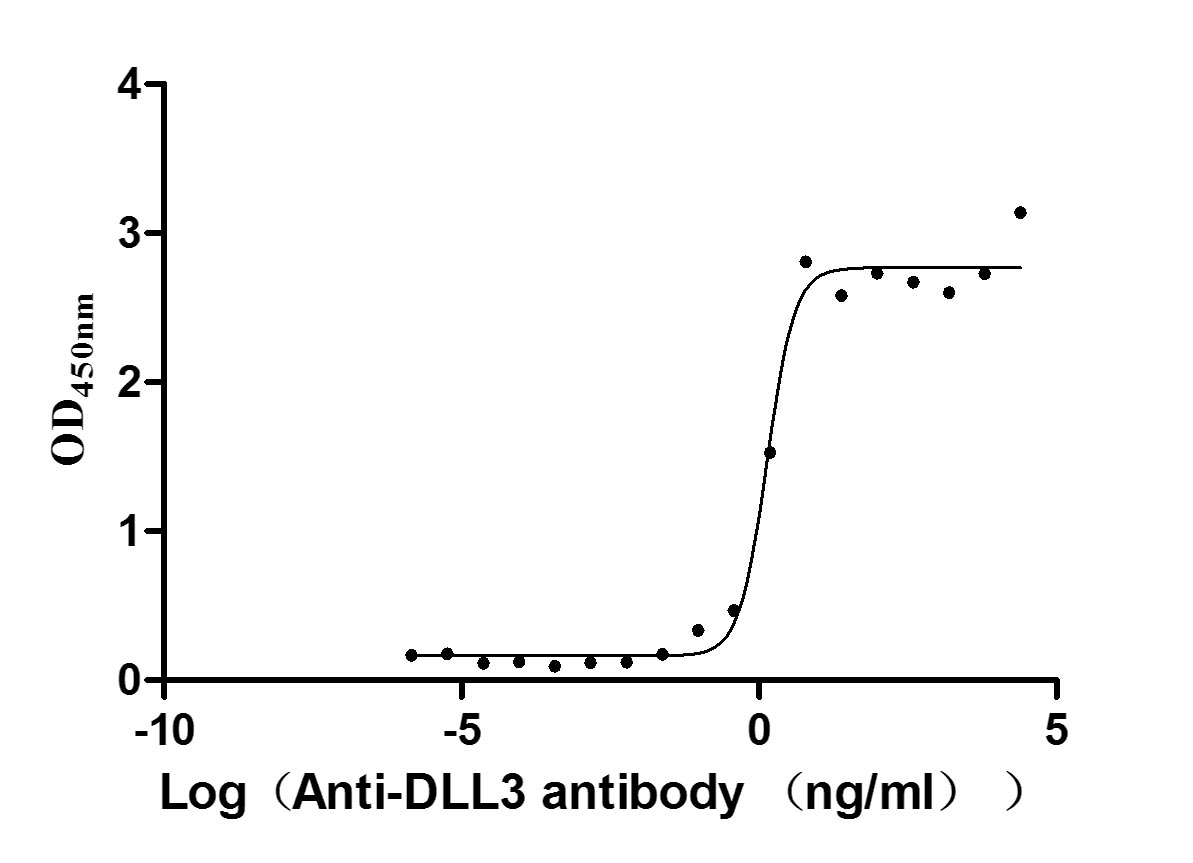
Recombinant Human Delta-like protein 3 (DLL3), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Neuropilin-1 (NRP1) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
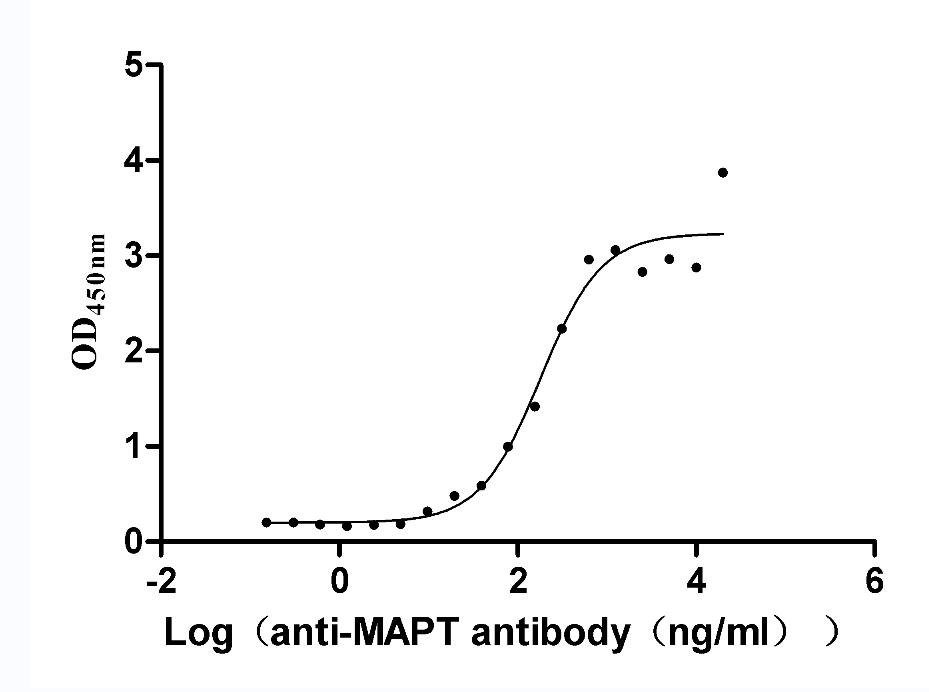
Recombinant Rat Microtubule-associated protein tau (Mapt) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
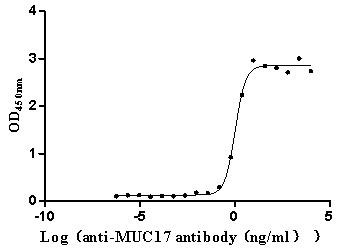
Recombinant Human Mucin-17 (MUC17), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
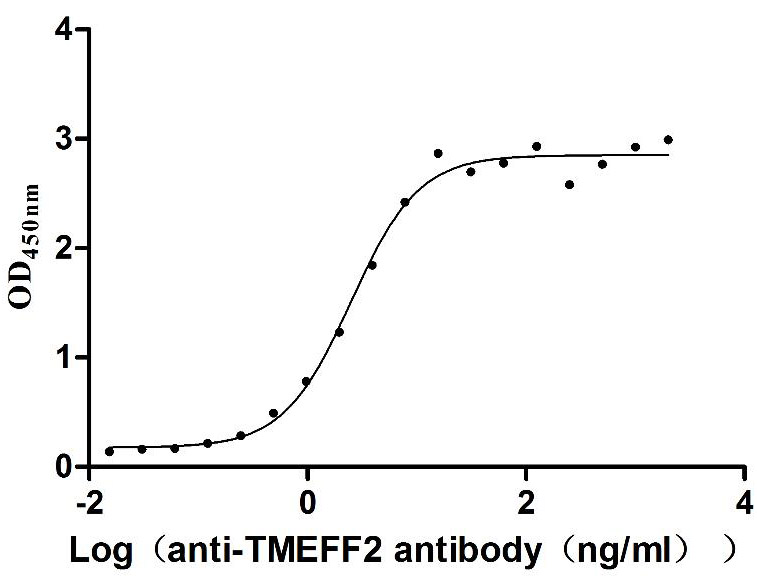
Recombinant Human Tomoregulin-2 (TMEFF2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
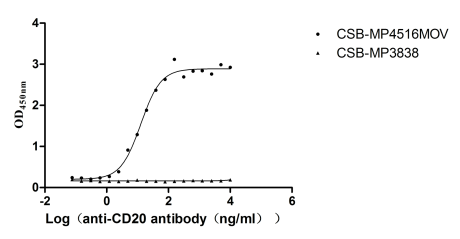
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Membrane spanning 4-domains A1 (MS4A1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
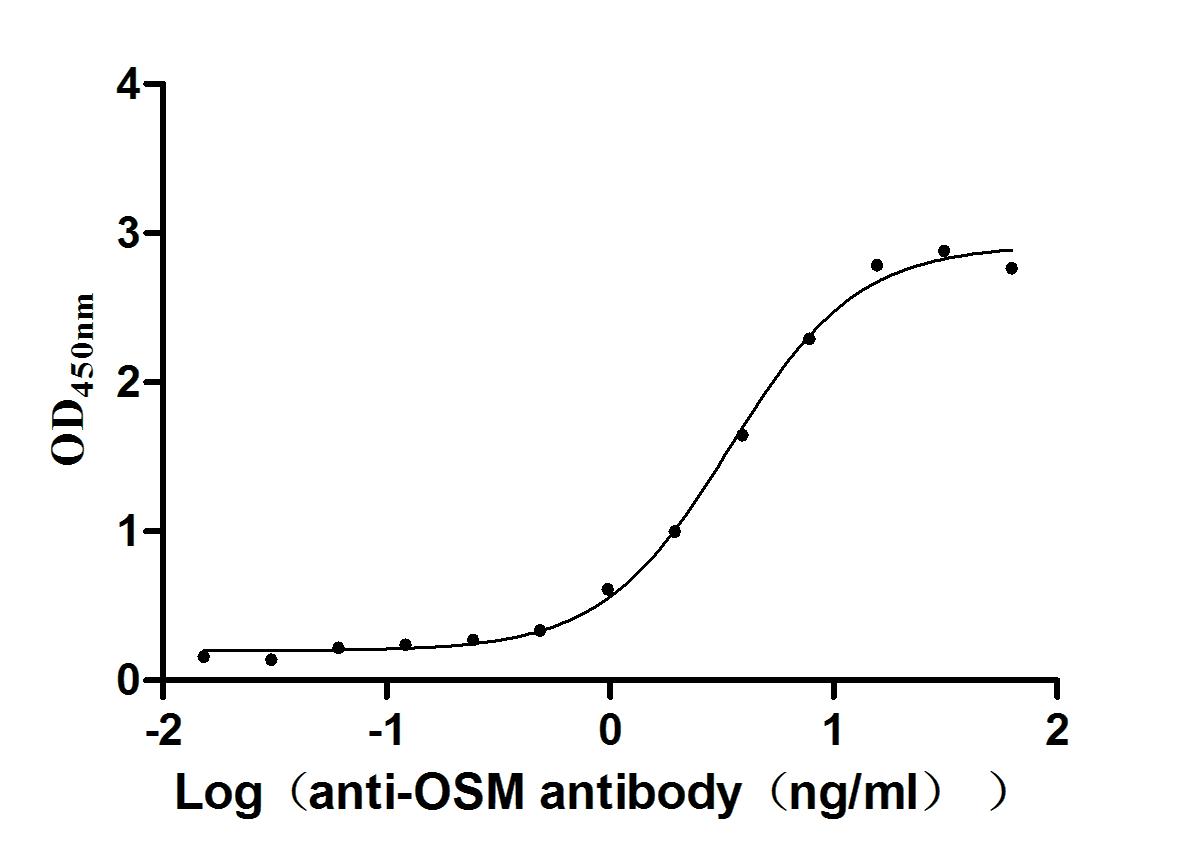
Recombinant Human Oncostatin-M (OSM), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)