Recombinant Mouse Microtubule-associated protein 1B (Map1b), partial
-
中文名称:小鼠Map1b重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP013401MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Map1b重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP013401MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Map1b重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP013401MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Map1b重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP013401MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Map1b重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP013401MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:Map1b
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Map1b; Mtap1b; Mtap5Microtubule-associated protein 1B; MAP-1B; MAP1(X); MAP1.2) [Cleaved into: MAP1B heavy chain; MAP1 light chain LC1]
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Phosphorylated MAP1B may play a role in the cytoskeletal changes that accompany neurite extension. Possibly MAP1B binds to at least two tubulin subunits in the polymer, and this bridging of subunits might be involved in nucleating microtubule polymerization and in stabilizing microtubules. Acts as a positive cofactor in DAPK1-mediated autophagic vesicle formation and membrane blebbing. Facilitates tyrosination of alpha-tubulin in neuronal microtubules. Required for synaptic maturation.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Data show that loss of MAP1B function affects general cognitive ability through a profound, brain-wide WM deficit with likely disordered or compromised axons. PMID: 30150678
- MAP1B knockout neurons display a decrease in the density of presynaptic and postsynaptic terminals, which involves a reduction in the density of synaptic contacts, and an increased proportion of orphan presynaptic terminals. MAP1B knockout neurons present altered synaptic vesicle fusion events, and a decrease in the density of both synaptic vesicles and dense core vesicles at presynaptic terminals. PMID: 27425640
- MAP1B restricts the access of AMPARs to dendritic spines and the postsynaptic membrane, contributing to downregulating synaptic transmission PMID: 28904092
- MAP1B confers increased stability to tyrosinated and acetylated, but not detyrosinated microtubules. PMID: 26773468
- Both FMRP deficiency in Fmr1(I304N) mice and Fmr1 knockdown impeded the axonal delivery of miR-181d, Map1b, and Calm1 and reduced the protein levels of MAP1B and calmodulin in axons. PMID: 26711345
- MAP1B is a specific marker protein of the podocyte microtubular cytoskeleton. PMID: 26448484
- The morphology, phenotype, regional distribution, proliferative dynamics, and stage-specific marker expression of Map5 cells in the rabbit and mouse central nervous system, were characterized. PMID: 23667595
- The MAP1B-Tiam1-Rac1 relay is essential for spine structural plasticity and removal of AMPA receptors from synapses during long-term depression. PMID: 23881099
- MAP1B interacts directly with EB1 and EB3 (EBs), two core 'microtubule plus-end tracking proteins' ( TIPs), and sequesters them in the cytosol of developing neuronal cells. PMID: 23572079
- MKK7 is specifically phosphorylated in the neurite shaft which triggers Map1b phosphorylation to regulate microtubule bundling leading to neurite elongation. PMID: 23226105
- Mutation of the Map1b binding site of Na(v)1.6 prevented generation of sodium current in transfected cells. The data indicate that Map1b facilitates trafficking of Na(v)1.6 to the neuronal cell surface PMID: 22474336
- Microtubule associated protein 1B, a microtubule stabilizing protein, and clathrin heavy chain, the major component of the clathrin triskelion, were identified as interaction partners for dystonin-a PMID: 21936565
- important role for MAP1B in the formation and maturation of dendritic spines PMID: 21984824
- HuD simultaneously binds both RNA and MAP1B-light chain 1 (MAP1B-LC1) in vitro and that it tightly associates with microtubules in cells in an LC1-dependent manner PMID: 21288476
- MAP1S and MAP1B both are involved in regulating trafficking of NR3A-containing NMDAR. PMID: 20304030
- Participation of structural microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs) in the development of neuronal polarity. PMID: 11891784
- developmentally programmed FMRP expression represses the translation of microtubule associated protein 1B (MAP1B) and is required for the accelerated decline of MAP1B during active synaptogenesis in neonatal brain development PMID: 15475576
- Through MAP1B function, Reelin could modify the neuronal cytoskeleton of migration neurons PMID: 15590913
- GSK-3beta phosphorylation of MAP1B at Ser1260 and Thr1265 is spatially restricted to growing axons PMID: 15731007
- The interactions of MAP1B with LIS1 in hippocampal neurons, and the association of LIS1 with dynein are reported. PMID: 15762842
- Mice homozygous for a deletion of the MAP1B gene demonstrate impaired locomotor activity most likely correlated to a lack of physical endurance. Electroretinography indicated a reduction of the a-wave amplitude in response to a flash of white light. PMID: 16102853
- MAP1B is associated with the regulation of retrograde axonal transport of mitochondria PMID: 16536727
- The 3'UTR of MAP1B mRNA interacts with QKI, and oligodendroglia-specific QKI-deficiency in the quakingviable mutant mice resulted in reduced MAP1B mRNA expression. PMID: 16855020
- We conclude, that the MAP1B heavy chain has a microtubule-stabilization effect, and contains an actin-binding site that may play a role in the crosslinking of actin and microtubules, a function that may be important in neurite elongation. PMID: 17292804
- Mtap1b-Light chain 1 has the potential to repress cell proliferation by modulating the nucleolar levels of Pes1 PMID: 17308336
- GAPDH may be essential in the local energy provision of cytoskeletal structures and MAP1B may help to keep this key enzyme close to the cytoskeleton. PMID: 17521179
- These results reveal an S-nitrosylation-dependent signal-transduction pathway that is involved in regulation of the axonal cytoskeleton and identify MAP1B as a major component of this pathway. PMID: 17704770
- MAP1B is required for microtubule backfolding, thereby unravelling an important molecular mechanism implicated in coupling the movements of actin and microtubules during process retraction of neural cells. PMID: 17764972
- MAP1B regulates tyrosination of alpha-tubulin in neuronal microtubules. This regulation may be important for general processes involved in nervous system development such as axonal guidance and neuronal migration. PMID: 18075266
- Nonprimed and DYRK1A-primed GSK3 beta-phosphorylation sites on MAP1B regulate microtubule dynamics in growing axons. PMID: 19549690
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton. Cytoplasm. Cell junction, synapse. Cell projection, dendritic spine.; [MAP1 light chain LC1]: Cytoplasm.
-
蛋白家族:MAP1 family
-
数据库链接:
Most popular with customers
-
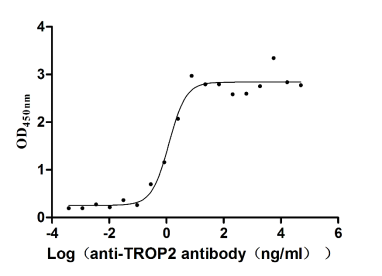
Recombinant Human Tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 2 (TACSTD2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
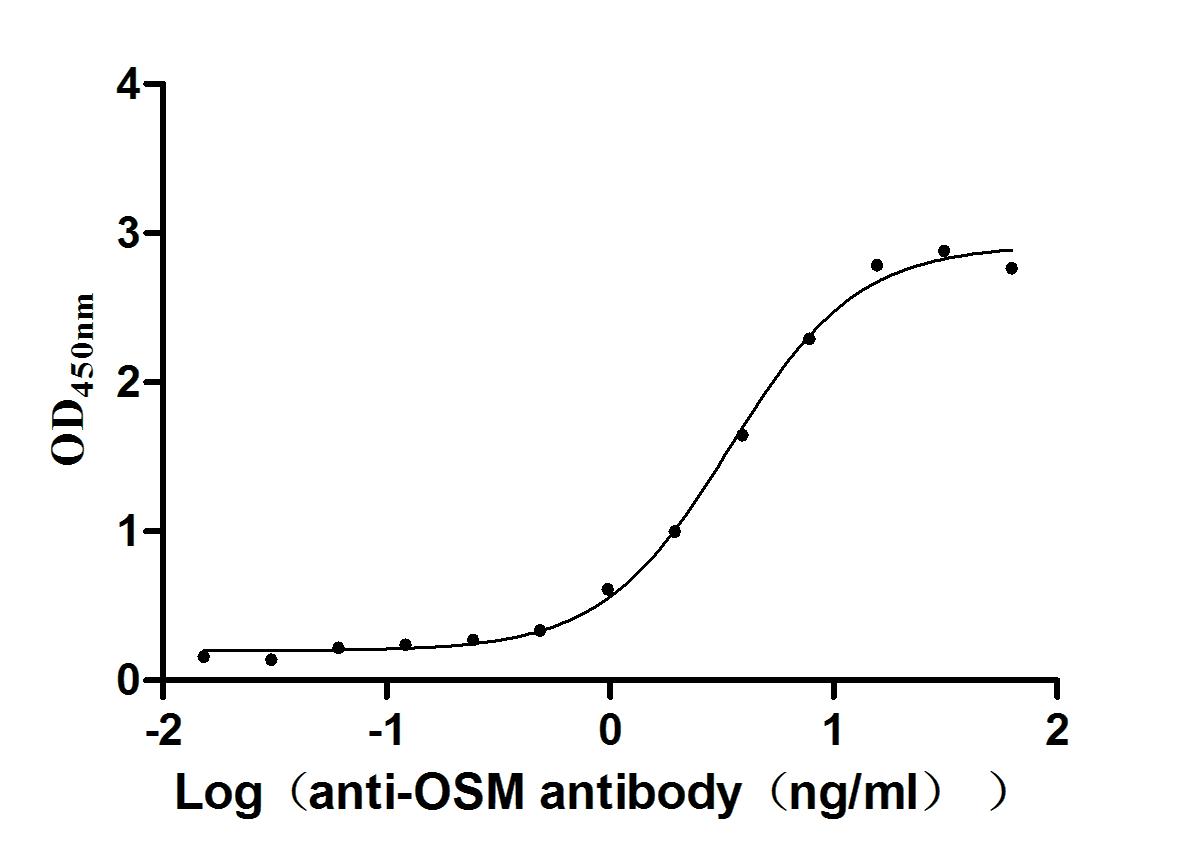
Recombinant Human Oncostatin-M (OSM), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
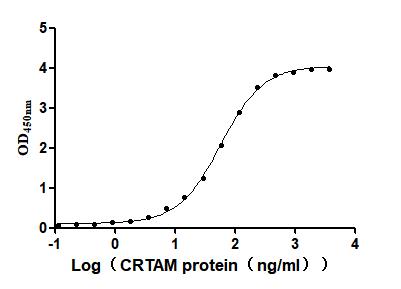
Recombinant Mouse Cytotoxic and regulatory T-cell molecule (Crtam), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
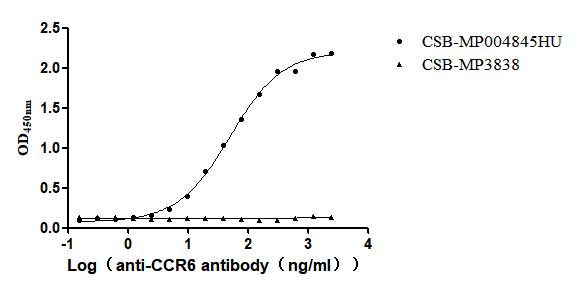
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 6(CCR6)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Cadherin-6(CDH6),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant DT3C (Diphtheria toxin & spg 3C domain) for Antibody Internalization Assay (Active)
Express system: E.coli
Species: N/A