Recombinant Mouse MKL/myocardin-like protein 1 (Mkl1), partial
-
中文名称:小鼠Mkl1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP809115MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Mkl1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP809115MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Mkl1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP809115MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Mkl1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP809115MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Mkl1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP809115MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:Mkl1
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Mrtfa; Bsac; Mal; Mkl1; Myocardin-related transcription factor A; MRTF-A; Basic SAP coiled-coil transcription activator; MKL/myocardin-like protein 1; Megakaryoblastic leukemia 1 protein homolog; Megakaryocytic acute leukemia protein homolog
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Transcription coactivator that associates with the serum response factor (SRF) transcription factor to control expression of genes regulating the cytoskeleton during development, morphogenesis and cell migration. The SRF-MRTFA complex activity responds to Rho GTPase-induced changes in cellular globular actin (G-actin) concentration, thereby coupling cytoskeletal gene expression to cytoskeletal dynamics. MRTFA binds G-actin via its RPEL repeats, regulating activity of the MRTFA-SRF complex. Activity is also regulated by filamentous actin (F-actin) in the nucleus.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Study have demonstrated a stress-dependent p38MAPK/MK2-driven phosphorylation of two defined, well conserved serine residues of MRTF-A in various cultured cell lines as well as in vitro. These observation suggests that the modulation of MRTF-A activity by MK2-mediated phosphorylation could represent a novel crosstalk between myogenic and stress signaling. PMID: 27492266
- these data indicate that Emerin, a conserved nuclear lamina protein, couples extracellular matrix mechanics and SRF-Mkl1-dependent transcription. PMID: 28576971
- Among a group of tumor cells, there is correlation between activation of the MRTF-dependent transcription and activated FAK-dependent regulation of cell migration. PMID: 27708220
- Here, the authors show that Rho-dependent MRTF phosphorylation reflects its nuclear accumulation and dissociation from G-actin, and identify multiple sites for MRTF phosphorylation, which contribute to transcriptional activation. PMID: 27304076
- BRG1 promotes transcription of endothelial Mrtfa and Mrtfb, which elevates expression of SRF and SRF target genes that establish embryonic capillary integrity. PMID: 28729363
- knockdown of MKL1 induces a significant increase in the transcriptional activity of PPARgamma target genes and MKL1 interacts with PPARg, suggesting that SRF and MKL1 independently inhibit brown adipogenesis and that MKL1 exerts its effect mainly by modulating PPARgamma activity PMID: 28125644
- further found that hypericin ameliorates inflammatory response by suppressing MKL1, which is the essential cofactor of p65 during the transcription process. In an Abeta injection AD mouse model, animals orally administrated hypericin (50 mg/kg) for seven days significantly decreased pro-inflammatory cytokines expression and NO production in hippocampus, meanwhile, hypericin improved oAbeta42-induced learning and memory... PMID: 27825966
- Study demonstrates that WH2 domains activate MRTF-A and contribute to target gene regulation by a competitive mechanism, independently of their role in actin filament formation. PMID: 26976641
- The transcriptional co-activator MRTF-A was activated by sphingosine-1-phosphate as assessed by its nuclear accumulation and induction of a RhoA/MRTF-A luciferase reporter. PMID: 27094722
- MRTF-A regulates liver fibrosis by epigenetically tuning the TGF-beta signaling pathway in HSCs PMID: 26693892
- Exploration of the molecular causes of enhanced cardiac hypertrophy revealed significant activation of beta-catenin/GSK-3beta signaling, whereas MAPK and MKL1/serum-response factor pathways were inhibited. PMID: 26719331
- MRTF-A is a critical for epithelial to mesenchymal transition and can be stereoselectively inhibited by CCG-1423. PMID: 26295164
- MKL1 plays a significant role in mediating the fibrotic response to bleomycin injury. Loss of MKL1 attenuated early neutrophil influx, as well as myofibroblast-mediated remodeling. PMID: 25885656
- MRTF-A/B depletion results in an increase in the cell surface expression of ICAM-1 and interactions between HAoECs and leukocytes PMID: 26024305
- knockdown of MRTF-A synthesis abolishes the systemic sclerosis myofibroblast enhanced basal contractility and synthesis of type I collagen and inhibits the matricellular profibrotic protein, connective tissue growth factor (CCN2/CTGF PMID: 25955164
- Either MRTF-A or MRTF-B is dispensable for cardiac development, whereas deletion of both causes a spectrum of abnormalities ranging from reduced cardiac contractility and adult onset heart failure to neonatal lethality accompanied by sarcomere disarray. PMID: 26386146
- Ddx19 is an RNA export factor required for nuclear import of the SRF coactivator MKL1 PMID: 25585691
- Expression analysis showed that MKL1 is highly expressed in human and mouse brains; results revealed that genetic variants in MKL1 might confer risk to schizophrenia. PMID: 25380769
- Results found that MKL1 expression was upregulated during cell cycle arrest induced by a temperature switch in podocytes through p21 transcription activation suggesting a physiological roles in the maturation and development of podocytes. PMID: 25888165
- These data support a central role of the SRF/MRTF pathway in the pathobiology of lung fibrosis. PMID: 25681733
- MRTF-A promotes microvessel growth (via CCN1) and maturation (via CCN2), thereby enabling functional improvement of ischaemic muscle tissue PMID: 24910328
- we data have unveiled a MRTF-A-containing complex that links ET-1 transactivation in endothelial cells to cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis by Ang II. PMID: 25446178
- the actin, myocardin-related transcription factors and serum response factor (actin-Mrtf-Srf) pathway is specifically downregulated in the muscle atrophy that is induced through disuse in mice. PMID: 25344251
- These results identify SRF and its MRTF cofactors as major transcriptional regulators of endothelial cell junctional stability, guaranteeing physiological functions of the cerebral microvasculature. PMID: 26221020
- TGF-beta stimulated the binding of MKL1 on the promoters of pro-fibrogenic genes and promoted the interaction between MKL1 and SMAD3 PMID: 26241940
- MRTFA regulates renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy. PMID: 25349198
- MKL1/MRTF-A, by coordinating key epigenetic alterations on CAM promoters, provides a critical link to hypoxia-induced endothelial malfunction and contributes to the pathogenesis of hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. PMID: 25646298
- Study identified a BMP7-controlled signaling and transcriptional circuit involving MRTFA, which enhances the development of beige adipocytes in white adipose tissue, resulting in protection from diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance. PMID: 25579684
- Suggest role for nuclear RhoA signaling in MRTF-dependent gene expression in smooth muscle cells. PMID: 24906914
- Myocardin-related transcription factor (MRTF)-A and MRTF-B (MKL1 and MKL2, respectively) are enriched in the perinuclear space of epicardial cells during development. PMID: 25516967
- Data show that the binding of WIP to actin controls the actin dynamics MRTFA-SRF-Focal adhesion assembly signaling cascade. PMID: 24797074
- Data indicate that RNA interference mediated loss of MKL1 (megakaryoblastic leukemia 1) drives adipocyte differentiation. PMID: 24569594
- MKL1/2 and ELK4 co-regulate distinct serum response factor (SRF) transcription programs in macrophages. PMID: 24758171
- TGF-beta1-induced epithelial-myofibroblast transition via MRTF-A signaling is regulated by cell adhesion and shape PMID: 24340092
- MRTF-A knockdown leads to increase in S and G2/M populations and downregulation of cyclin-CDK inhibitors p27Kip1, p18Ink4c and 19Ink4d as well as upregulation of p21Waf1 and cyclin D1. PMID: 23656782
- Isoxazole stimulates myofibroblast differentiation via induction of MRTF-A-dependent gene expression. PMID: 24082095
- lamin-A/C-deficient and Lmna(N195K/N195K) mutant cells have impaired nuclear translocation and downstream signalling of MKL1, a myocardin family member that is pivotal in cardiac development and function PMID: 23644458
- Activated mDia promoted rapid and reversible nuclear actin network assembly, subsequent MAL nuclear accumulation, and SRF activity. PMID: 23558171
- Data suggest that MKL1 and MKL2 are expressed in megakaryocytes and platelets; megakaryocytes lacking expression of MKL1 and/or MKL2 have both defective megakaryocytopoiesis and thrombopoiesis. PMID: 22806889
- A role for MAL in TNF signaling and implicate the MAL-SRF transcription module in regulating the proapoptotic Bcl-2 family network. PMID: 22185759
- The cytoskeleton-associated factors integrin alpha5, Pkp2 and FHL1 were newly characterised as transcriptionally regulated actin-MAL-SRF target genes, and they were in part responsible for the impaired migration of cells harbouring activated MAL. PMID: 22223881
- MRTF-A nuclear accumulation following stimulation with serum, actin drugs or acute mechanical stress is prevented within mechanically loaded, anchored matrices at tensional homeostasis. PMID: 21799516
- MRTF-A is an important regulator of collagen synthesis in lung fibroblasts and exhibits a dependence on both SRF and Sp1 function to enhance collagen expression PMID: 22049076
- structural, biochemical and cell biological evidence that MAL has a classical bipartite nuclear localization signal (NLS) in the N-terminal 'RPEL' domain containing Arg-Pro-X-X-X-Glu-Leu (RPEL) motifs was presented. PMID: 21964294
- Promoter-reporter and chromatin immunoprecipitation experiments unraveled a SAP-dependent, SRF-independent interaction of MKL1 with the proximal promoter region of TNC. PMID: 21705668
- Structure of a pentavalent G-actin*MRTF-A complex reveals how G-actin controls nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of a transcriptional coactivator. PMID: 21673315
- Presents evidence that strongly suggests a dual role for MKL1 in oncogenic mechanisms, as a tumor-promoting or tumor-suppressing molecule. PMID: 20816842
- Data show that MRTF-A contains an unusually long bipartite nuclear localisation signal embedded within the RPEL domain, that uses the importin (Imp)alpha/beta-dependent import pathway, and that import is inhibited by G-actin. PMID: 20818336
- Expression of brain natriuretic peptide and other serum response factor-dependent fetal cardiac genes in response to acute mechanical stress was blunted in mice lacking Mrtf-A. PMID: 20606005
- MRTF-A regulates myofibroblast activation and fibrosis in response to the renin-angiotensin system and post-myocardial infarction remodeling. PMID: 20558820
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm. Nucleus.
-
组织特异性:Expressed in heart, brain, spleen, lung, liver, muscle, kidney and testis.
-
数据库链接:
Most popular with customers
-
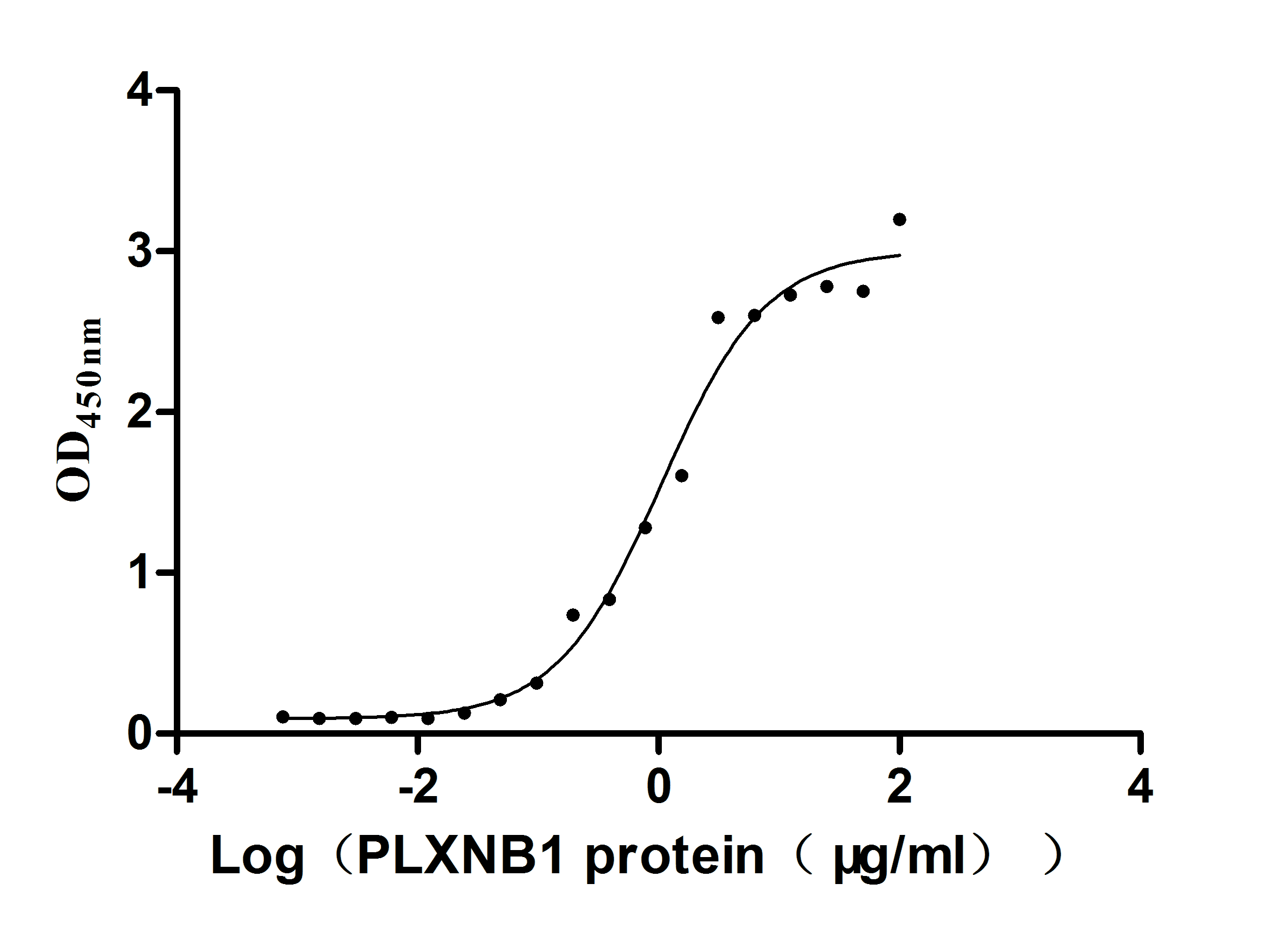
Recombinant Human Plexin-B1 (PLXNB1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Claudin-6 (CLDN6)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human IL12B&IL12A Heterodimer Protein (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Trophoblast glycoprotein (TPBG), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Human Dickkopf-related protein 1 (DKK1) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
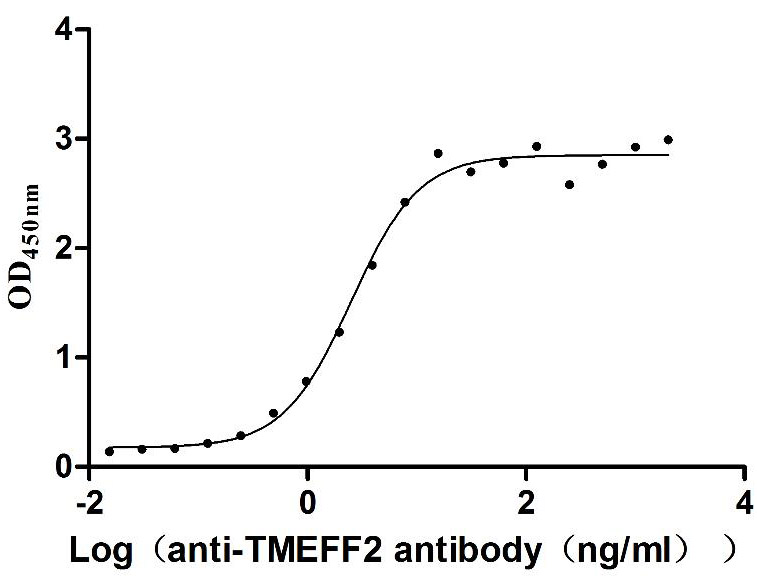
Recombinant Human Tomoregulin-2 (TMEFF2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
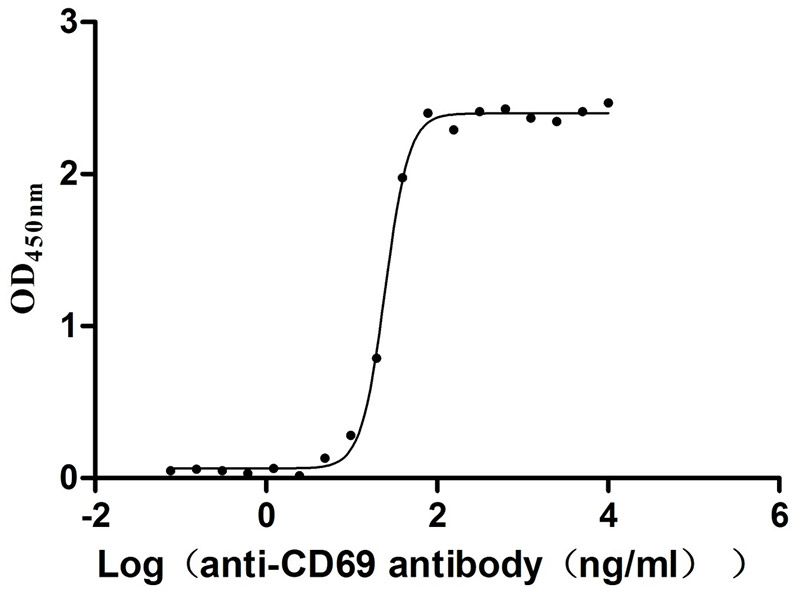
Recombinant Human Early activation antigen CD69 (CD69), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
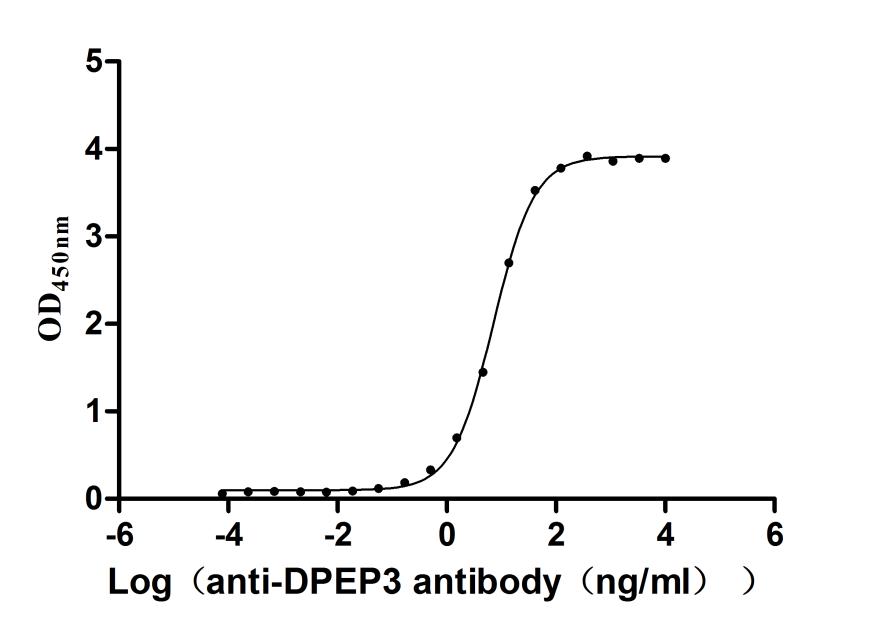
Recombinant Human Dipeptidase 3(DPEP3), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)
-AC1.jpg)