Recombinant Mouse Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 (Lrp5), partial
-
中文名称:小鼠Lrp5重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP842018MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Lrp5重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP842018MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Lrp5重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP842018MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Lrp5重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP842018MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Lrp5重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP842018MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
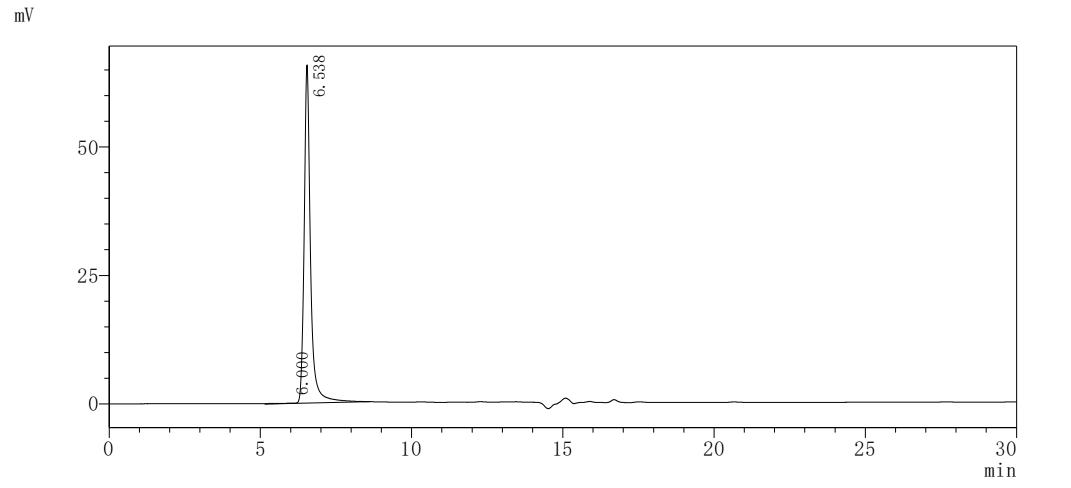
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Lrp5; Lr3; Lrp7; Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5; LRP-5; Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 7; LRP-7
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Acts as a coreceptor with members of the frizzled family of seven-transmembrane spanning receptors to transduce signal by Wnt proteins. Activates the canonical Wnt signaling pathway that controls cell fate determination and self-renewal during embryonic development and adult tissue regeneration. In particular, may play an important role in the development of the posterior patterning of the epiblast during gastrulation. During bone development, regulates osteoblast proliferation and differentiation thus determining bone mass. Mechanistically, the formation of the signaling complex between Wnt ligand, frizzled receptor and LRP5 coreceptor promotes the recruitment of AXIN1 to LRP5, stabilizing beta-catenin/CTNNB1 and activating TCF/LEF-mediated transcriptional programs. Acts as a coreceptor for non-Wnt proteins, such as norrin/NDP. Binding of norrin/NDP to frizzled 4/FZD4-LRP5 receptor complex triggers beta-catenin/CTNNB1-dependent signaling known to be required for retinal vascular development. Plays a role in controlling postnatal vascular regression in retina via macrophage-induced endothelial cell apoptosis.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Heterozygous deletion of the LRP5 gene in mice could alter the profile of the immune cells, influence the balance of immune environment, and modulate bone homeostasis. PMID: 29899194
- Megakaryocytes are increased in the bone marrow of Lrp5G170V/G170V mice. Depletion of megakaryocytes does not affect the Lrp5-induced high bone mass. PMID: 29454962
- The phenotype of the Lrp5(tvrm111B) mutant includes abnormalities of the retinal vasculature and of bone mineral density. PMID: 28356706
- the LRP5 mutation in high bone mass transgenic mice shows altered bone matrix composition PMID: 27230741
- Lrp6 is the key mediator of Wnt3a signaling in osteoblasts and Lrp5 played a less significant role in mediating Wnt3a signaling. PMID: 29176883
- Identification of a link between Wnt-Lrp5 signaling and insulin signaling in the osteoblast that has the potential to influence energy balance and compound the detrimental effects of a HFD on whole-body metabolism. PMID: 28938444
- Lrp5(-/-) mice displayed significantly delayed retinal vascular development, absence of deep layer retinal vessels, leading to increased levels of vascular endothelial growth factor and subsequent pathologic glomeruloid vessels, as well as decreased inner retinal visual function. PMID: 27524797
- A mouse LRP5 ectodomain recombinant was cleaved by VAP1, creating a peptide, VAHLTGIHAVEE, detected by mass spectrometric analysis of the 140-kDa fragment, suggesting that the sessile bond by VAP1 is Glu1206-Val1207. PMID: 28425175
- we revealed miR-375-3p negatively regulated osteogenesis by targeting LRP5 and beta-catenin PMID: 28158288
- lung myeloid cells are responsive to Lrp5/beta-catenin signaling, leading to differentiation of an alveolar macrophage subtype that antagonizes the resolution of lung fibrosis. PMID: 27668462
- LRP5 is a novel anti-inflammatory macrophage marker that positively regulates migration, phagocytosis, lipid uptake and metabolism. PMID: 26739212
- These results revealed a new role of the canonical Lrp5/6-beta-catenin pathway in regulating the morphogenesis of the cerebellum during postnatal development. PMID: 26772978
- LRP5 function in mice causes retinal hypovascularization during development as well as retinal neovascularization in adulthood with disorganized and leaky vessels. PMID: 27031698
- Lrp5 is required for glucose uptake, and glucose uptake regulates the growth rate of mammary epithelial cells in culture. PMID: 26711269
- Data show that LDL receptor-related protein 5 (LRP5) gain-of-function mutations do not activate beta-catenin signaling in osteoblasts. PMID: 26681532
- These in vivo data support in vitro studies regarding the mechanism of HBM-causing mutations, and imply that HBM LRP5 receptors differ in their relative sensitivity to inhibition by SOST and DKK1. PMID: 25808845
- Lrp5 A214V and G171V were partially or fully protected from the bone loss that normally results frommechanical disuse using two models, tail suspension and Botulinum toxin-induced muscle paralysis, in two different Lrp5 HBM knock-in mouse models. PMID: 26554834
- In hypercholesterolemia LRP5(-/-) mice Wnt/beta-catenin pathway was shut down. An antiatherogenic role for LRP5 was demonstrated as HC LRP5(-/-) mice developed larger aortic atherosclerotic lesions than WT mice. PMID: 25748163
- Report accelerated lung regeneration by platelet-rich plasma extract through Lrp5/Tie2 pathway. PMID: 26091161
- Data show that low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 (LRP5) and the canonical Wnt pathway down-regulation regulate the dyslipidaemic profile by promoting lipid and macrophage retention in the vessel wall. PMID: 25656427
- Lrp5 binds to Frizzled, preventing Frz-regulated non-canonical Wnt pathway activation and further non-canonical pathway-mediated tumour metastasis. PMID: 25902418
- Sclerostin inhibits bone formation through Lrp5 interaction. PMID: 25640331
- Our findings indicate that LRP5 plays an essential role in osteoarthritis cartilage destruction PMID: 24479426
- Wnt-Lrp5 signaling regulates basic cellular activities. PMID: 25802278
- Findings strongly suggest that Wise and Sost are key modulators of bone development through the ability of their encoded proteins to interact with Lrp5 and control the balance or levels of Wnt signaling. PMID: 24789067
- Col1a2(+/p.G610C) ;Lrp5(+/p.A214V) offspring had significantly increased bone mass and strength compared to Col1a2(+/p.G610C) ;Lrp5(+/+) littermates. PMID: 24677211
- Bone formation was more reduced in Col1a1-Krm2 than in Lrp5-/- mice, whereas osteoclast number was similarly increased in both genotypes in comparison with wild-type mice PMID: 25061805
- Hgf as an important transactivator of canonical Wnt signaling that is mediated by Met-stimulated, Gsk3-dependent Lrp5/6 phosphorylation PMID: 24692544
- Knockdown of LRP5 expression by siRNA prevents tissue plasminogen activator (tPA)-induced neurite extension. PMID: 23925701
- LRP5 signaling is a prerequisite for neovascularization in VLDLR knockout mice. LRP5 may be an effective target for inhibiting intraretinal neovascularization. PMID: 24058663
- The Wnt coreceptor, Lrp5, is a genetic driver of lung fibrosis in mice and a marker of disease progression and severity in humans with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. PMID: 24921217
- The current study is the first to reveal that dioscin can promote osteoblasts proliferation and differentiation via Lrp5 and ER pathway. PMID: 24742230
- In the absence of LRP5, the anabolic effects of SOST depletion can occur via other receptors (such as LRP4/6) PMID: 24225945
- Lack of LRP5 has a more pronounced effect on gene expression than the high bone mass-causing LRP5 missense mutation. PMID: 23553928
- tissue stiffness modulated by the extracellular matrix cross-linking enzyme, lysyl oxidase, regulates postnatal lung development through LRP5-Tie2 signaling PMID: 23841513
- These results indicate that expression of both Lrp5 and Lrp6 are required within mature osteoblasts for normal postnatal bone development. PMID: 23675479
- Lrp5-mediated Wnt signaling significantly contributes to maintenance of mechanical properties and bone mass. PMID: 23356985
- LRP5-Tie2-Ang signaling axis plays a central role in control of both angiogenesis and alveolarization during postnatal lung development PMID: 22848540
- Results show that loss of function of Lrp5 increases cartilage degradation in mild instability-induced OA models in mice PMID: 22850184
- Peptide-mediated disruption of N-cadherin-LRP5/6 interaction increases Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and osteoblast function in vitro and promotes calvaria bone formation in vivo. PMID: 22576936
- The importance of Lrp5 in bone cell mechanotransduction, is reported. PMID: 22750014
- study hypothesizes that calcific aortic valve disease develops secondary to Wnt3a/Lrp5 activation via oxidative-mechanical stress in eNOS null mice PMID: 22359381
- Data suggest that Lrp5 loss and gain of function mutations result in cell-autonomous alterations in osteoblast proliferation and apoptosis but do not alter the proliferative response of osteoblasts to mechanical strain in vitro. PMID: 22567110
- Both LRP5 and LRP6 receptors are required to respond to physiological Wnt ligands in mammary epithelial cells and fibroblasts. PMID: 22433869
- Lrp5 and Lrp6 play redundant roles in intestinal epithelium development, and that Lrp5/6 might regulate intestinal stem/precursor cell maintenance by regulating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. PMID: 21866564
- Data suggest that Lrp5 regulates multiple groups of genes that influence retinal angiogenesis and may contribute to the pathogenesis of familial exudative vitreoretinopathy (FEVR). PMID: 22272305
- Insulin signaling also involves the Wnt co-receptor LRP5, which has a positive effect on insulin signaling. PMID: 22337886
- Lrp5/6 is necessary for calcification in the aortic valve in the presence of experimental hypercholesterolemia. PMID: 21678468
- Data indicate an important role for mesenchymal Lrp5/6 signaling in limb patterning. PMID: 21924256
- These studies uncover a new and important molecular tuning mechanism for differential regulation of LRP5 and LRP6 phosphorylation and signaling activity. PMID: 21887268
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Endoplasmic reticulum.
-
蛋白家族:LDLR family
-
组织特异性:Widely expressed, with the highest expression levels in liver, heart, and lung and the lowest levels in brain and spleen.
-
数据库链接:
Most popular with customers
-
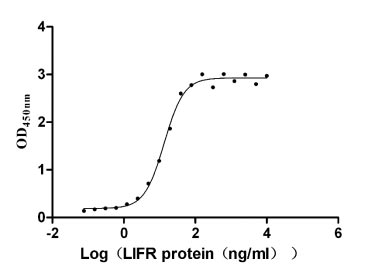
Recombinant Human Leukemia inhibitory factor receptor (LIFR), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
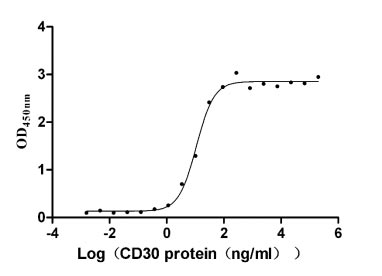
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 8 (TNFSF8), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
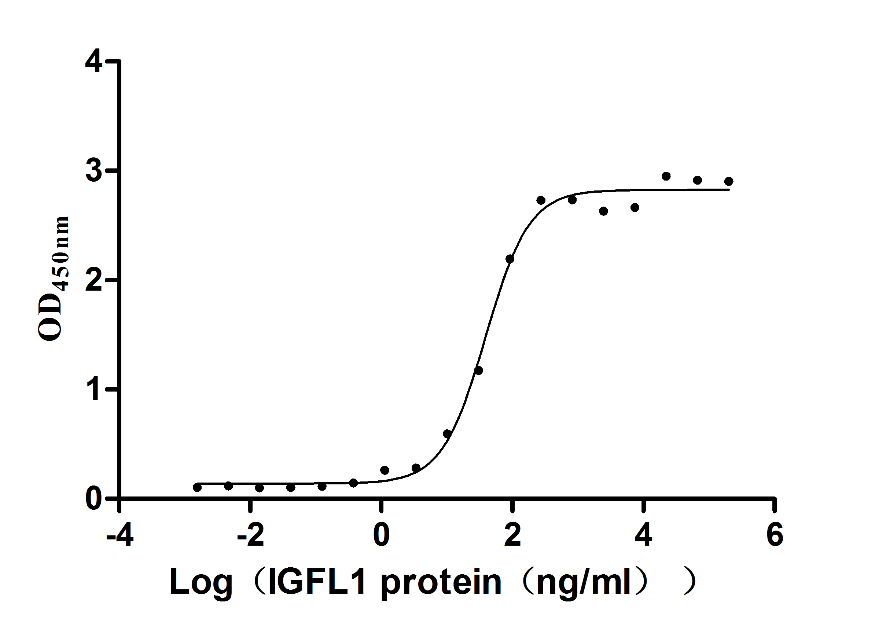
Recombinant Human IGF-like family receptor 1 (IGFLR1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
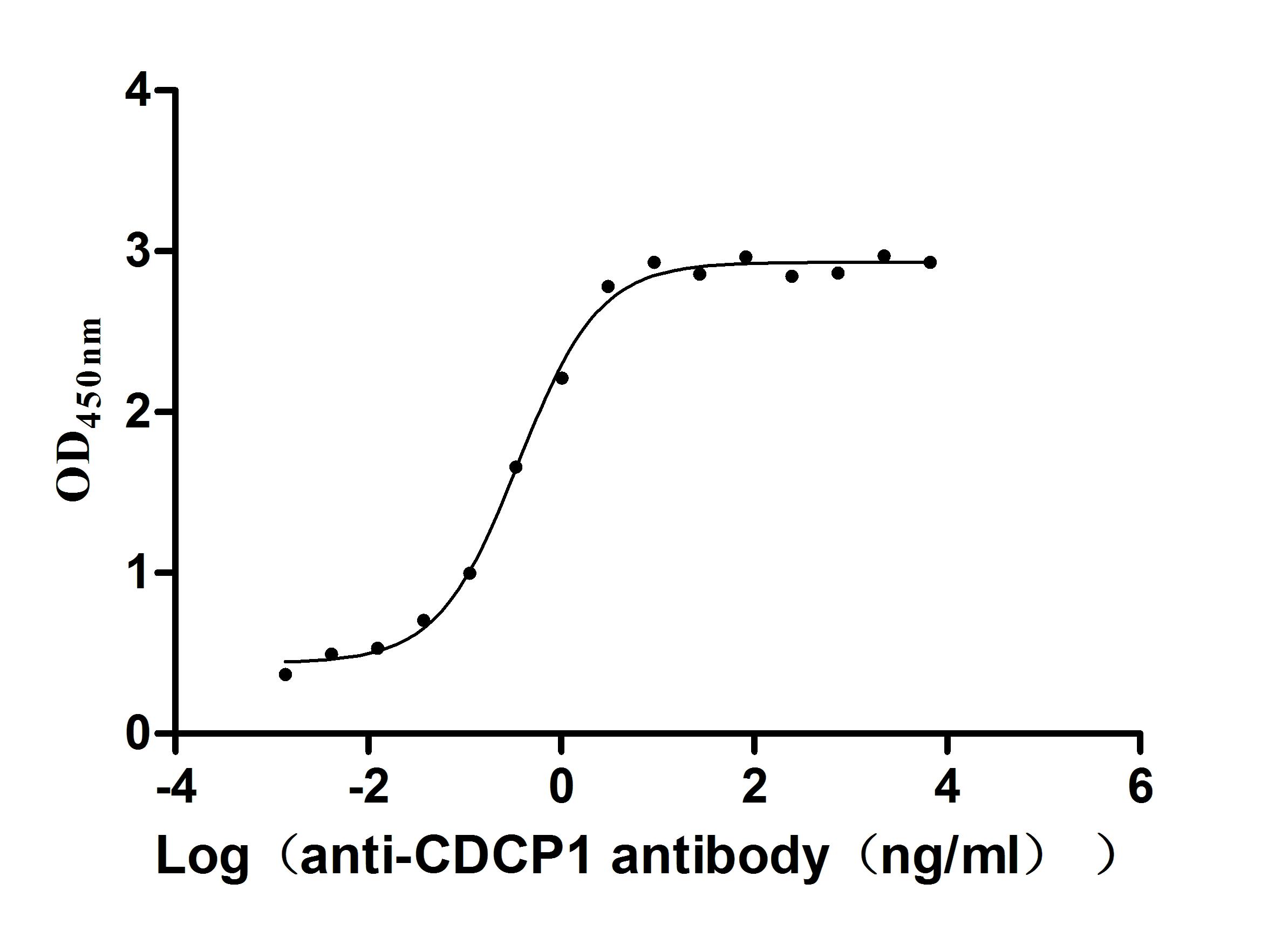
Recombinant Human CUB domain-containing protein 1 (CDCP1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
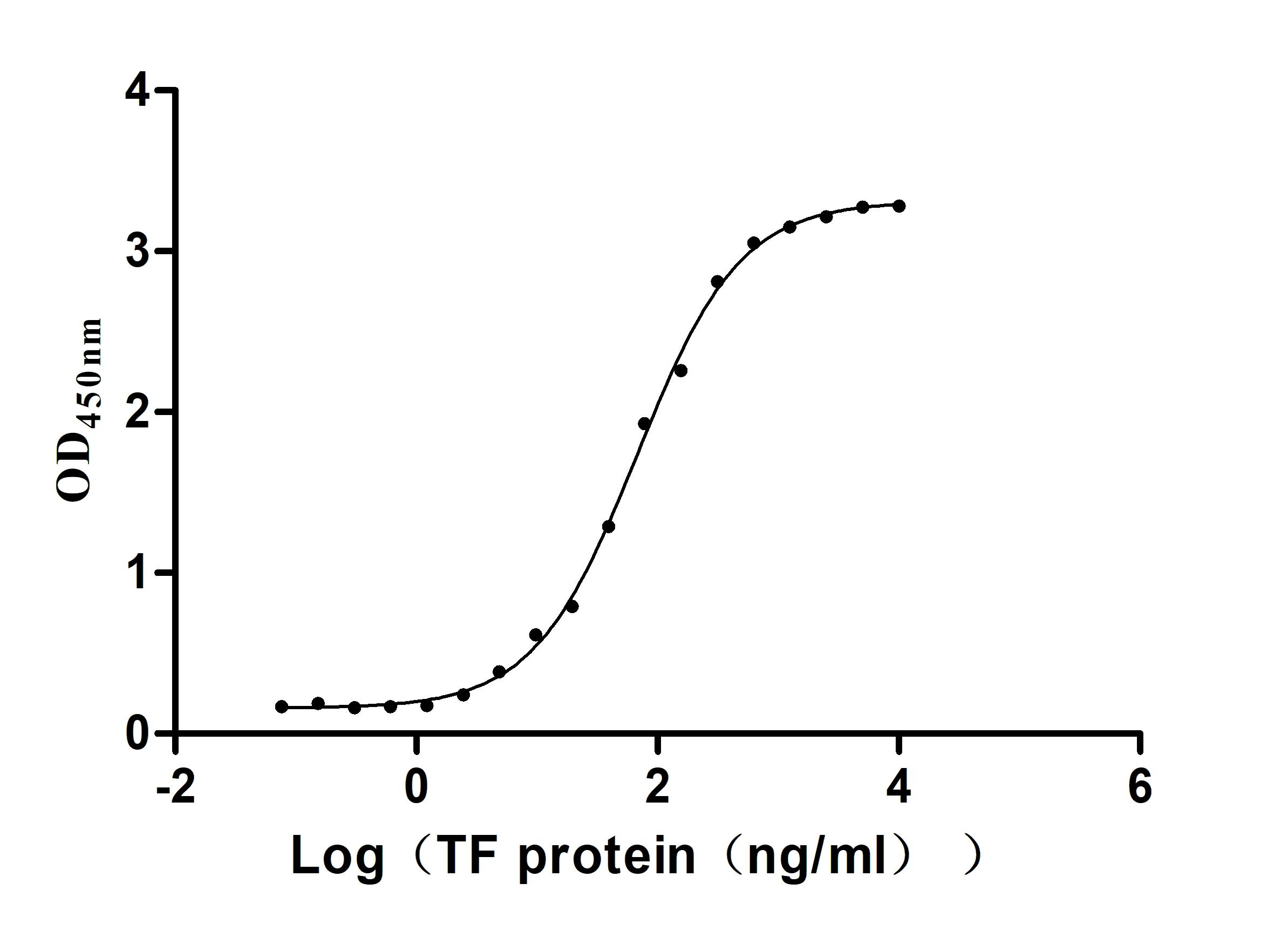
Recombinant Human Serotransferrin(TF) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
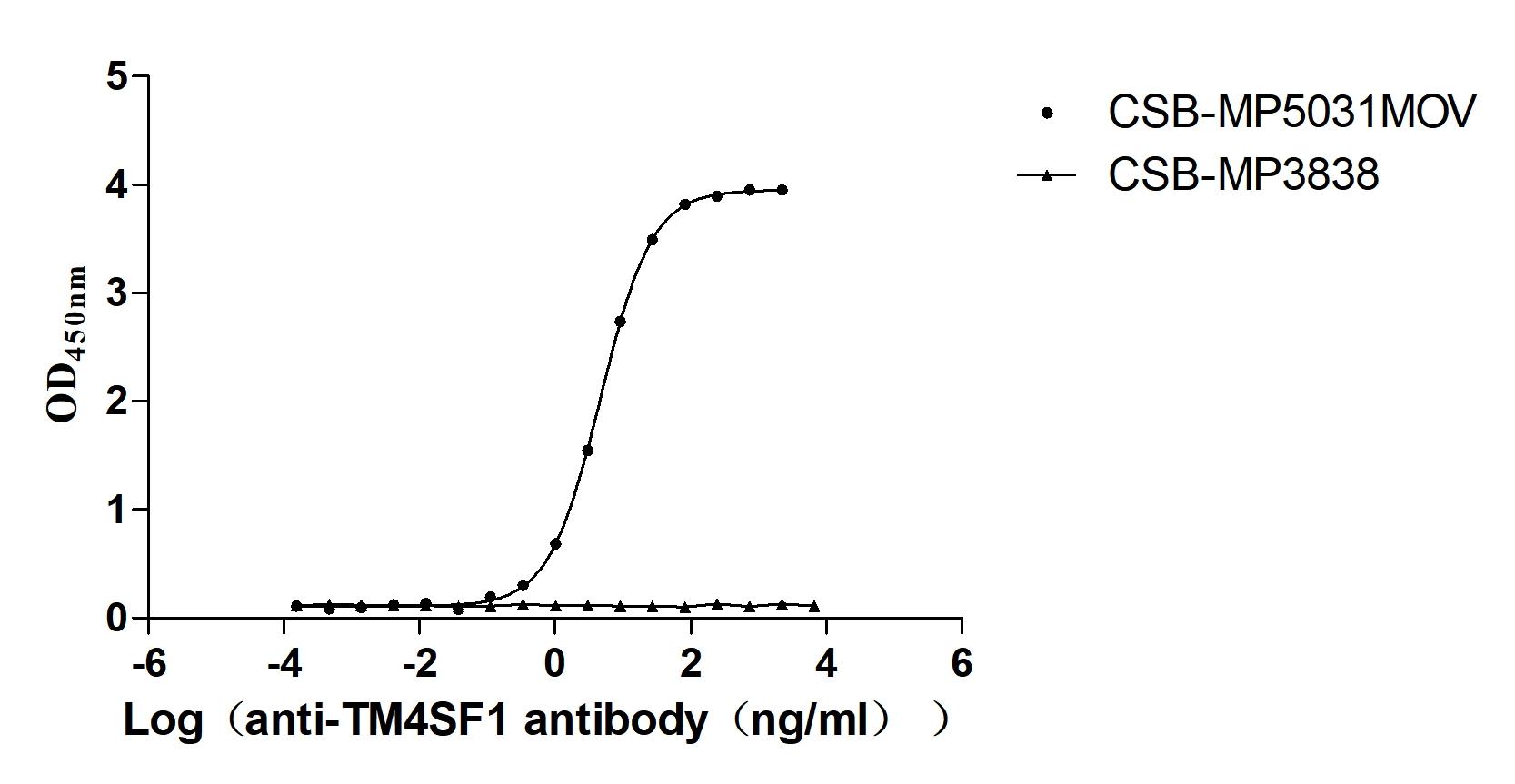
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Transmembrane 4 L6 family member 1 (TM4SF1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 9 (CCR9)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
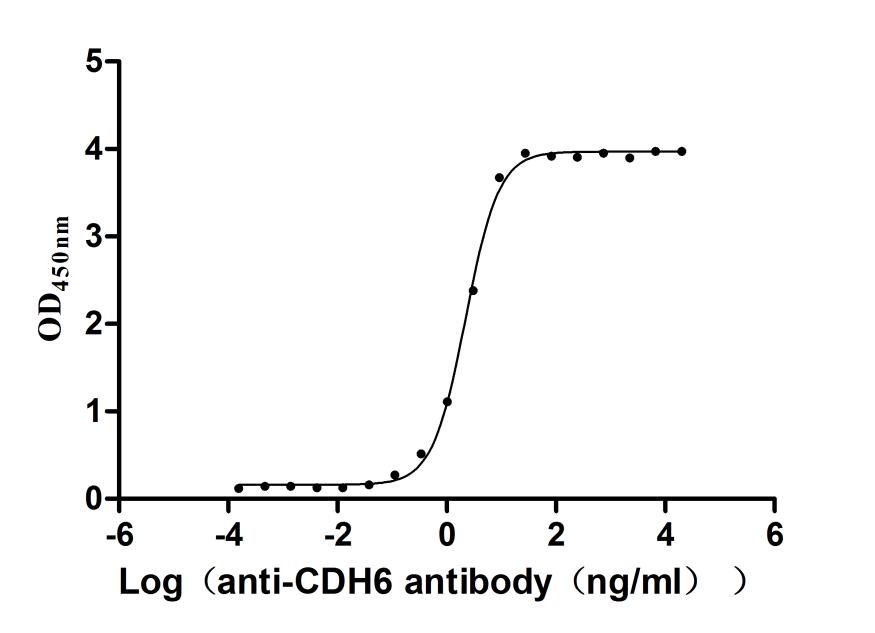
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Cadherin 6(CDH6),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)