Recombinant Mouse E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase CBL (Cbl), partial
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase CBL(Cbl) ,partial
-
货号:CSB-YP004578MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase CBL(Cbl) ,partial
-
货号:CSB-EP004578MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase CBL(Cbl) ,partial
-
货号:CSB-EP004578MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase CBL(Cbl) ,partial
-
货号:CSB-BP004578MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase CBL(Cbl) ,partial
-
货号:CSB-MP004578MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Cbl; E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase CBL; EC 2.3.2.27; Casitas B-lineage lymphoma proto-oncogene; Proto-oncogene c-Cbl; RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase CBL; Signal transduction protein CBL
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Adapter protein that functions as a negative regulator of many signaling pathways that are triggered by activation of cell surface receptors. Acts as an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase, which accepts ubiquitin from specific E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes, and then transfers it to substrates promoting their degradation by the proteasome. Ubiquitinates SPRY2. Ubiquitinates EGFR. Recognizes activated receptor tyrosine kinases, including KIT, FLT1, FGFR1, FGFR2, PDGFRA, PDGFRB, EGFR, CSF1R, EPHA8 and KDR and terminates signaling. Recognizes membrane-bound HCK, SRC and other kinases of the SRC family and mediates their ubiquitination and degradation. Participates in signal transduction in hematopoietic cells. Plays an important role in the regulation of osteoblast differentiation and apoptosis. Essential for osteoclastic bone resorption. The 'Tyr-737' phosphorylated form induces the activation and recruitment of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase to the cell membrane in a signaling pathway that is critical for osteoclast function. May be functionally coupled with the E2 ubiquitin-protein ligase UB2D3. In association with CBLB, required for proper feedback inhibition of ciliary platelet-derived growth factor receptor-alpha (PDGFRA) signaling pathway via ubiquitination and internalization of PDGFRA.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Cbls were highly expressed in GC light zone (LZ) B cells, where they promoted the ubiquitination and degradation of Irf4, a transcription factor facilitating PC fate choice. PMID: 29562201
- Cbl, Cbl-b, and Cbl-c have a role in protecting mammary epithelial cellsfrom proteotoxic stress-induced cell death by promoting turnover of active c-Src PMID: 27930322
- The establishment of a new model of concurrent tissue-selective CBL/CBL-B deletion should allow a clear assessment of the tumor-intrinsic roles of CBL/CBL-B in non-myeloid malignancies and help test the potential for CBL/CBL-B inactivation in immunotherapy of tumors. PMID: 27276677
- These findings highlight a hitherto unexplored and novel role for Cbl and PI3K in modulating the osteogenic response of periosteal cells during the early stages of fracture repair. PMID: 27884787
- c-Cbl negatively regulates IFN-beta signaling and cellular antiviral response by promoting IRF3 ubiquitination and degradation. PMID: 27503123
- This study demonstrate an unprecedented role for c-Cbl in microglia-mediated neuroinflammation involving PI3K/Akt/NF-kappaB pathway. PMID: 27156691
- c-Cbl's linker helix region mutations are only oncogenic when they disrupt the native state and fail to ubiquitinate protein tyrosine kinases. PMID: 27609087
- These studies reveal a novel, cell-autonomous requirement of CBL and CBL-B in epithelial stem cell maintenance during organ development and remodeling through modulation of mTOR signaling. PMID: 28100467
- mutant CBL proteins effectively compete with the remaining wild type CBL-B and juxtapose tyrosine kinase-binding domain-associated protein tyrosine kinases with proline-rich region-associated signaling proteins to hyper-activate signaling downstream of hematopoietic growth factor receptors PMID: 28082680
- results demonstrate that c-Cbl mediates the ubiquitination/degradation of integrin beta1, which leads to COMP deficiency-induced dilated cardiomyopathy. PMID: 27693578
- Gem, a gene encoding a GTPase that is upregulated by Cbl(Q367P) , enhanced hematopoietic stem cell activity and induced myeloid cell proliferation. In addition, Evi1, a gene encoding a transcription factor, was found to cooperate with Cbl(Q367P) and progress CMML to AML. PMID: 28209720
- Fasudil, a clinically safe ROCK inhibitor, decreases disease burden in a Cbl/Cbl-b deficiency-driven murine model of myeloproliferative disorders. PMID: 26177294
- Cbl down-regulation protects mice against high-fat diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance. PMID: 26296084
- Cbl-b and c-Cbl regulate the degradation of Osterix through the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. PMID: 25744063
- Overexpression of Smad7 in human HaCaT keratinocyte cells and mouse skin tissues elevated EGF receptor (EGFR) activity by impairing ligand-induced ubiquitination and degradation of activated receptor, which is induced by the E3 ubiquitin ligase c-Cbl. PMID: 26055326
- Erbin promotes tumourigenesis and tumour growth in colorectal cancer by stabilizing epidermal growth factor receptor PMID: 25521828
- Whereas Cbl-PI3K interaction regulates differentiation and survival, bone resorption is predominantly regulated by Cbl-b in osteoclasts. PMID: 24470255
- c-Cbl activation promotes myocyte apoptosis, inhibits angiogenesis, and causes adverse cardiac remodeling after myocardial infarction. PMID: 24583314
- Data indicate a Cbl/p85/epsin-1 pathway in erythropoietin receptor (EpoR) endocytosis. PMID: 24113870
- These results support the notion that the distal cytoplasmic domain of CD5, including Y463, plays a relevant role in the downmodulation of TCR signals in thymocytes via c-Cbl. PMID: 23376399
- c-Cbl conjugates neural precursor cell-expressed, developmentally downregulated 8 (NEDD8), a ubiquitin-like protein, to TbetaRII at Lys556 and Lys567. PMID: 23290524
- the novel role for Syk signaling and the Syk-binding ubiquitin ligase c-Cbl in the BCR-mediated processing and presentation of cognate antigen and PMID: 22451666
- Casitas b-lineage lymphoma (c-Cbl) is involved in focal adhesion and myofibrillar protein stability and turnover in myocytes PMID: 22203672
- c-Cbl has a crucial, RING-domain-dependent role in regulating dendritic cell maturation, probably by facilitating the regulatory function of p105 and/or p50. PMID: 21799517
- Results indicate that c-Cbl and particularly its phosphorylated residue Y731 plays an important role in platelet outside-in signaling contributing to platelet-spreading and clot retraction. PMID: 21967979
- c-Cbl as well as Cbl-b may play important roles in Hsp90 inhibitor-induced degradation of Flt3-ITD through the ubiquitin proteasome system PMID: 21768087
- Cbl inactivation reverses the deficiency of T cell development in Vav1 knockout mice PMID: 21490975
- identify a surprising but pivotal role for dynein and the microtubule network alongside Grb2, Dok-3, and Cbl in antigen gathering during B cell activation PMID: 21703542
- propose c-Cbl as an angiogenic suppressor protein where upon activation it uniquely modulates PLCgamma1 activation by ubiquitination and subsequently inhibits VEGF-driven angiogenesis PMID: 21242968
- Data show that degradation of BCR-ABL by As4S4 was mediated by c-CBL, a RING-type E3 ligase that was also shown to be involved in ubiquitination for many other receptor/protein tyrosine kinases. PMID: 21118980
- loss of Cbl-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase interaction perturbs RANKL-mediated signaling, inhibiting bone resorption and promoting osteoclast survival. PMID: 20851882
- Mice with a mutation in the RING finger domain of c-Cbl show that E3 ubiquitin ligase activity of c-Cbl is required to restrict myeloid leukemia development. PMID: 20951944
- show that, in contrast to Cbl or Cbl-b single-deficient mice, concurrent loss of Cbl and Cbl-b in the HSC compartment leads to an early-onset lethal myeloproliferative disease in mice PMID: 20805496
- document that a deficiency of the E3 ubiquitin ligase c-Cbl in lymphocytes results in an age-dependent lymphopenia. PMID: 20404156
- Abrogation of the Cbl-PI3K interaction, although not affecting M-CSF-induced proliferation and differentiation of precursors, is required for regulation of survival and actin cytoskeletal reorganization of mature osteoclasts. PMID: 20392263
- Data show that that the increased Notch3-IC degradation correlates with higher levels of c-Cbl tyrosine phosphorylation in Notch3-IC/pTalpha(-/-) double-mutant thymocytes. PMID: 19966856
- Cbl-b (and c-Cbl) accumulation at the anergic synapse may play an important role in anergy maintenance, induction, or both. PMID: 20207996
- a BCR-ABL mutant lacking direct binding sites for the GRB2, CBL and CRKL adapter proteins fails to induce leukemia in mice PMID: 19823681
- NFATc1 interacts endogenously with c-Src, c-Cbl, and Cbl-b in osteoclasts. PMID: 20037154
- Data indicate that Fyn was not required for the induction of central tolerance by negative selection, the adaptor protein role of c-Cbl, or the normal development and function of Treg. PMID: 19904769
- transmembrane form of Notch1 was tyrosine-phosphorylated and specifically coprecipitated with the ubiquitin ligase c-Cbl PMID: 11777909
- Cbl-b knockout mice are available. Negative regulation of immune responses by three new E3 ubiquitin-protein ligases, Cbl, Cbl-b, & Itch is mediated by TCR, PI3-K, Notch and Lck. PMID: 11826757
- APS facilitates c-Cbl tyrosine phosphorylation and GLUT4 translocation in response to insulin in 3T3-L1 adipocytes PMID: 11997497
- Isolation and characterization of a novel, transforming allele of the c-Cbl proto-oncogene from a murine macrophage cell line. PMID: 12032836
- EGF-inducible direct association of PLC-gamma1 with c-Cbl in vivo that is mediated by the SH3 domain of PLC-gamma1. PMID: 12061819
- Cbl-b protein and CIN85 downregulate receptor tyrosine kinases PMID: 12177062
- c-Cbl is a negative regulator of GH-stimulated STAT5-mediated transcription by direction of STAT5 for proteosomal degradation PMID: 12193575
- Both PMA-treated wild type and hck(-/-)fgr(-/-) macrophages were defective in spontaneous and chemotactic migration and tyrosine phosphorylation of the Cbl protooncoprotein was decreased in both. PMID: 12652654
- Loss of c-Cbl expression leads to an increase in dual TCR alpha chain expression on the surface of double positive thymocytes, suggesting that regulation of TCR degradation via ubiquitination is key in phenotypic allelic exclusion. PMID: 12707333
- findings establish Cbl protein as the major endogenous ubiquitin ligase responsible for epidermal growth factor receptor degradation PMID: 12754251
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Can be converted to an oncogenic protein by deletions or mutations that disturb its ability to down-regulate RTKs.
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm. Cell membrane. Cell projection, cilium. Golgi apparatus.
-
数据库链接:
Most popular with customers
-
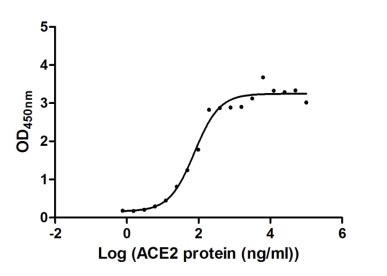
Recombinant Human Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
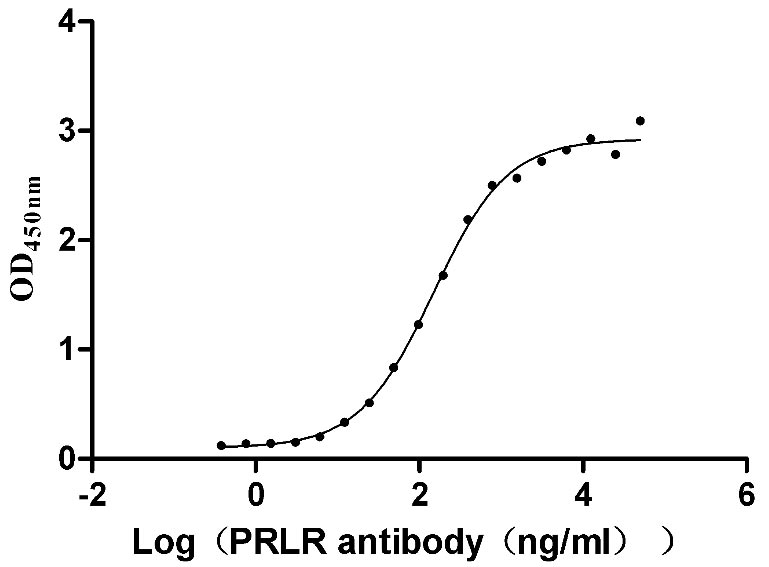
Recombinant Human Prolactin receptor (PRLR), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
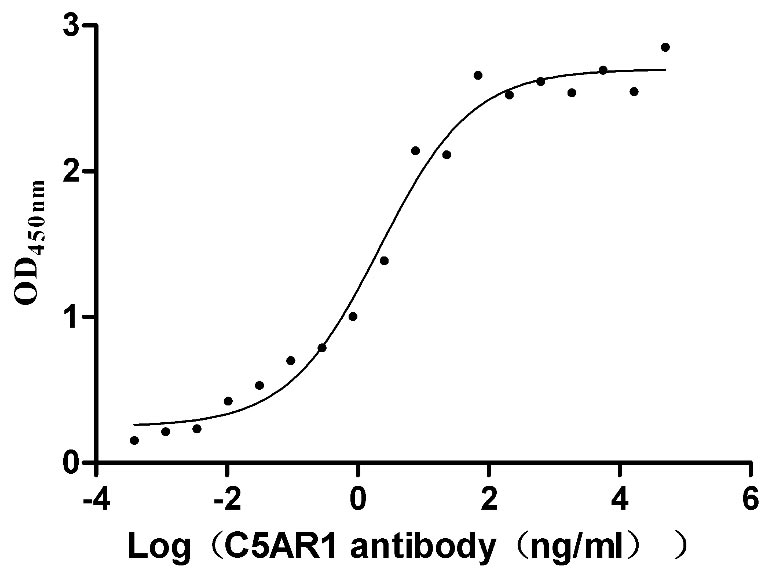
Recombinant Human C5a anaphylatoxin chemotactic receptor 1 (C5AR1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
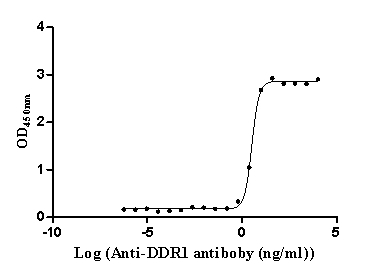
Recombinant Human Epithelial discoidin domain-containing receptor 1 (DDR1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Claudin-6 (CLDN6)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
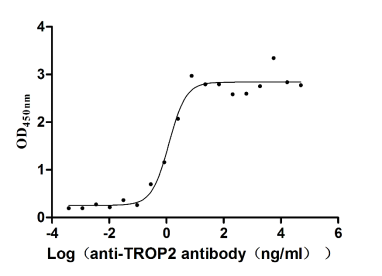
Recombinant Human Tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 2 (TACSTD2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
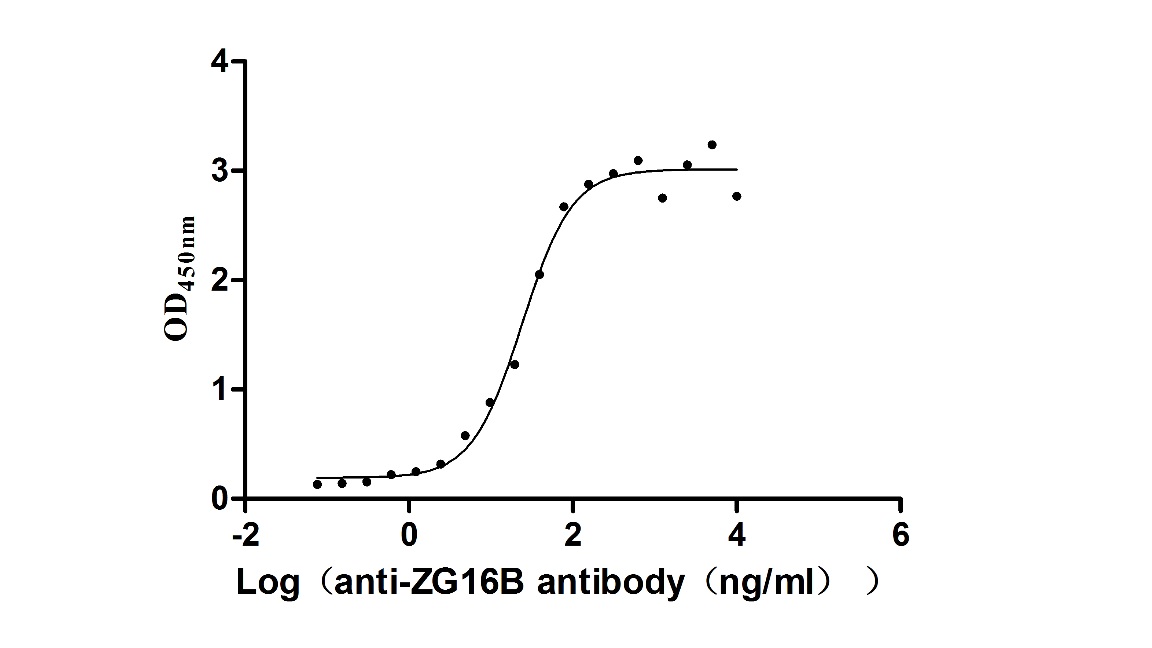
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis zymogen granule protein 16 homolog B (ZG16B) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
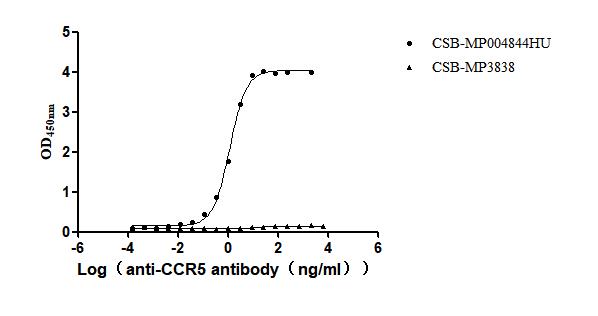
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 5 (CCR5)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)