Recombinant Mouse Dystonin (Dst), partial
-
中文名称:小鼠Dst重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP821036MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Dst重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP821036MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Dst重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP821036MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Dst重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP821036MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Dst重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP821036MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:Dst
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Dst; Bpag1; Macf2Dystonin; Bullous pemphigoid antigen 1; BPA; Dystonia musculorum protein; Hemidesmosomal plaque protein; Microtubule actin cross-linking factor 2
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Cytoskeletal linker protein. Acts as an integrator of intermediate filaments, actin and microtubule cytoskeleton networks. Required for anchoring either intermediate filaments to the actin cytoskeleton in neural and muscle cells or keratin-containing intermediate filaments to hemidesmosomes in epithelial cells. The proteins may self-aggregate to form filaments or a two-dimensional mesh. Regulates the organization and stability of the microtubule network of sensory neurons to allow axonal transport. Mediates docking of the dynein/dynactin motor complex to vesicle cargos for retrograde axonal transport through its interaction with TMEM108 and DCTN1.; plays a structural role in the assembly of hemidesmosomes of epithelial cells; anchors keratin-containing intermediate filaments to the inner plaque of hemidesmosomes. Required for the regulation of keratinocyte polarity and motility; mediates integrin ITGB4 regulation of RAC1 activity.; required for bundling actin filaments around the nucleus.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- The present study identified novel mutant mice with a mild dt phenotype of sensory neurodegeneration and movement disorder. PMID: 27693510
- oligodendrocytes do not have an intrinsic requirement for neuronal dystonin for differentiation and myelination. PMID: 26886550
- Novel Dst(Gt) mice showed that a loss-of-function mutation in the actin-binding domain-containing Dystonin isoforms led to typical dystonia musculorum phenotypes PMID: 25195653
- In the C2.7 cell line, knockdown of BPAG1a/b had no major effect on the organization of microtubules and microfilaments, but negatively affected endocytosis and Golgi apparatus structure and decreased cell migration but not cell adhesion. PMID: 25244344
- Restoration of dystonin-a2 expression in the nervous system prevented the disorganization of organelle membranes and microtubule networks in a mouse model of hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy. PMID: 24381311
- This study provides insight into the mechanism of dt neuropathology and proposes a role for dystonin-a2 as a mediator of normal ER structure and function. PMID: 22190742
- novel functions of the dystonin-a2 isoform in mediating microtubule stability, Golgi organization, and flux through the secretory pathway. PMID: 22412020
- Microtubule associated protein 1B, a microtubule stabilizing protein, and clathrin heavy chain, the major component of the clathrin triskelion, were identified as interaction partners for dystonin-a PMID: 21936565
- dystonin does not significantly influence the structural organization of cardiac muscle fibers during early postnatal development PMID: 20209123
- BPAG1-b was detectable in vitro and in vivo as a high molecular mass protein in striated and heart muscle cells, co-localizing with alpha-actinin-2 and partially with the cytolinker plectin as well as with the intermediate filament protein desmin. PMID: 19932097
- BPAG1 has three kinds of cytoskeletal binding domains and seems to play an important role in linking the different types of cytoskeletons. PMID: 11751855
- Transcripts for both neural isoforms of Bpag1 (a1 and a2) were detected in optic nerves and spinal cords of wild-type mice. PMID: 12111805
- Bpag1 may be involved in the maintenance rather than the establishment of muscle cell architecture. Cytoskeletal disruptions are seen in muscle of postnatal dystonia musculorum mice. Early phases of myogenic differentiation occur independently of Bpag1. PMID: 12190986
- BPAG1n4 is a novel neuronal isoform which plays an essential role in retrograde axonal transport in sensory neurons. PMID: 14581450
- The overall structure and subcellular localizations of Bpag1 indicate possible functions in nuclear envelope structuring, nuclear tethering, and organization of membranous structures surrounding the nucleus. PMID: 16289082
- These data together suggest that the survival of vagal and glossopharyngeal sensory neurons is dependent upon dystonin. PMID: 16289886
- Alterations likely result in reduced or absent dystonin/Bpag1 protein levels. Thus, distinct genetic defects lead to a common outcome of reduced transcript expression causing the same phenotype in multiple dt alleles. PMID: 16341670
- Dystonin/Bpag1 is not essential for microtubule network assembly since it is intact in short-term cultures of sensory neurons. Dystonin/Bpag1 is not an essential part of the dynein motor complex for mitochondrial transport. PMID: 16374799
- we characterized these N-terminal isoforms and evaluated the influence of these unique N-terminal sequences to the actin-binding properties. The N-terminal region of isoform 1 is very short and did not affect the property of the ABD that followed it. PMID: 16797530
- These data together suggest that dystonin is required for the innervation and development of fungiform papillae and taste buds. PMID: 17156752
- retrolinkin acts with BPAG1n4 to specifically regulate retrograde axonal transport PMID: 17287360
- Elucidating the roles of dystonin most relevant to neuronal function and survival should help to shed light on some of the common mechanisms underlying neurodegeneration. PMID: 17849487
- These data together suggest that dystonin is necessary for survival of nociceptors but not proprioceptors in the trigeminal nervous system. PMID: 18619576
- Defects in Dystonin mutant mice, as demonstrated here, may ultimately result in pathogenesis involving ER dysfunction and contribute significantly to the dt phenotype. PMID: 18638474
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, stress fiber. Cell projection, axon.; [Isoform 1]: Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton.; [Isoform 2]: Cell membrane, sarcolemma. Cytoplasm, myofibril, sarcomere, Z line. Cytoplasm, myofibril, sarcomere, H zone. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton.; [Isoform 6]: Nucleus. Nucleus envelope. Membrane; Single-pass membrane protein. Endoplasmic reticulum membrane; Single-pass membrane protein. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, stress fiber.; [Isoform 7]: Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton. Cytoplasm, cell cortex. Cell membrane; Lipid-anchor.
-
蛋白家族:Plakin or cytolinker family
-
组织特异性:Isoform 1 and 2 are expressed in striated and heart muscle cells. Isoform 5 is expressed in the skin. Isoform 6 is expressed in sensory neural cells of the dorsal root ganglion and with low level in the skin (at protein level). Isoform 1 is expressed pred
-
数据库链接:
Most popular with customers
-
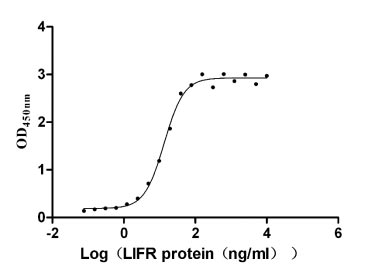
Recombinant Human Leukemia inhibitory factor receptor (LIFR), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
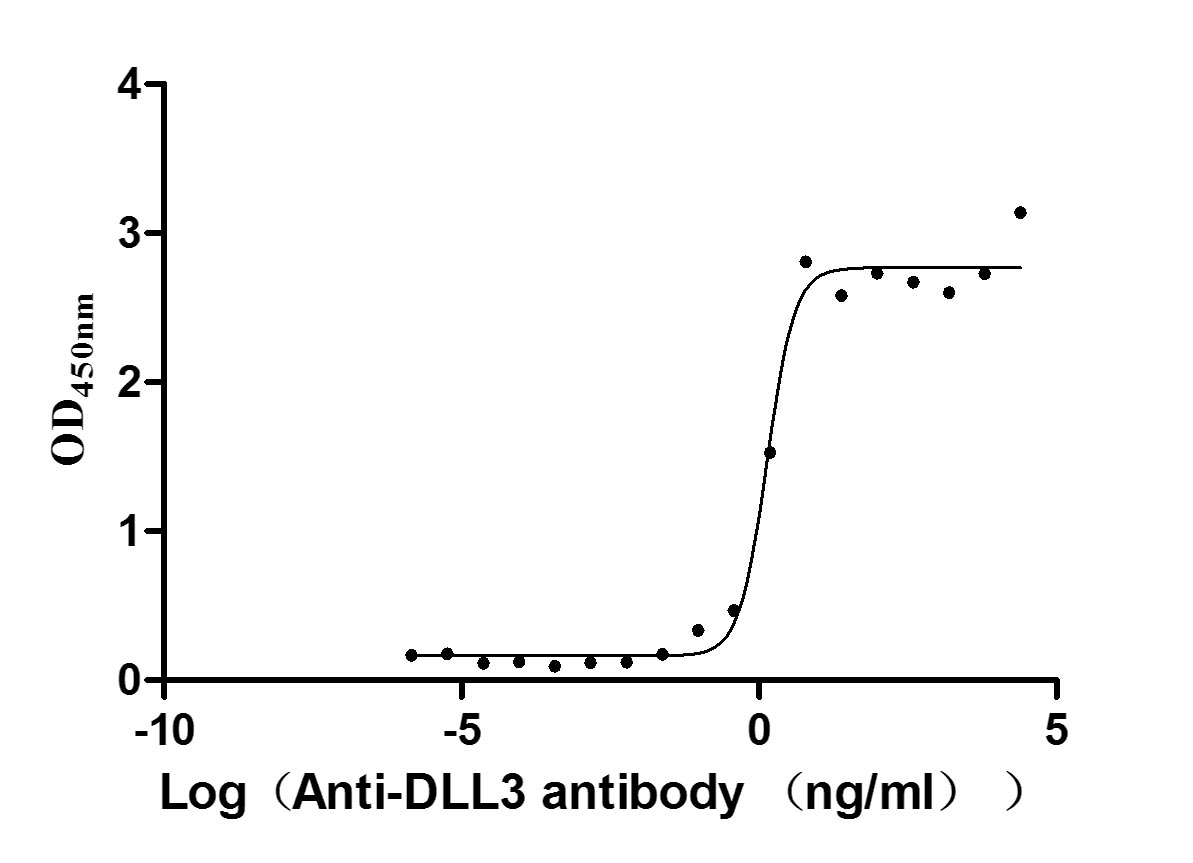
Recombinant Human Delta-like protein 3 (DLL3), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
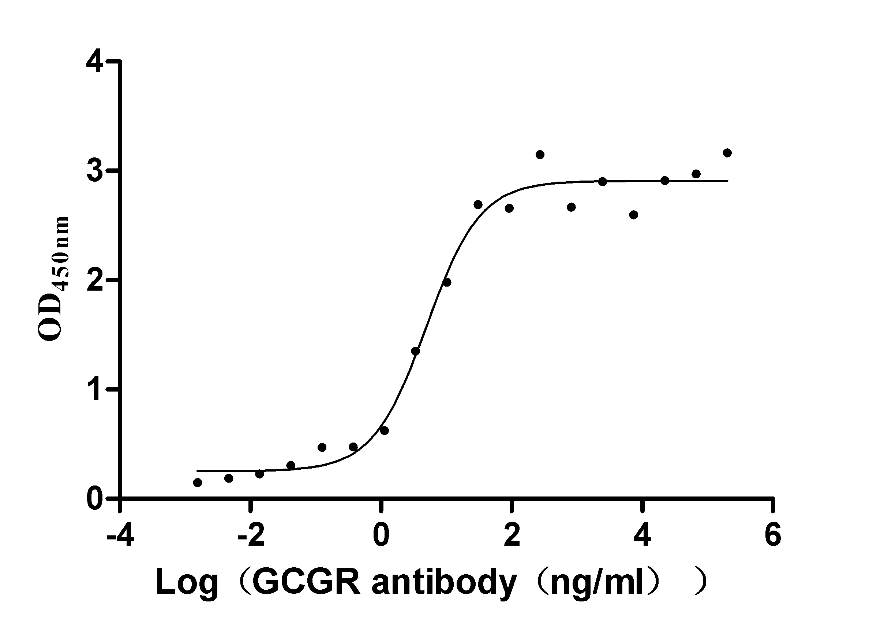
Recombinant Human Glucagon receptor (GCGR), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
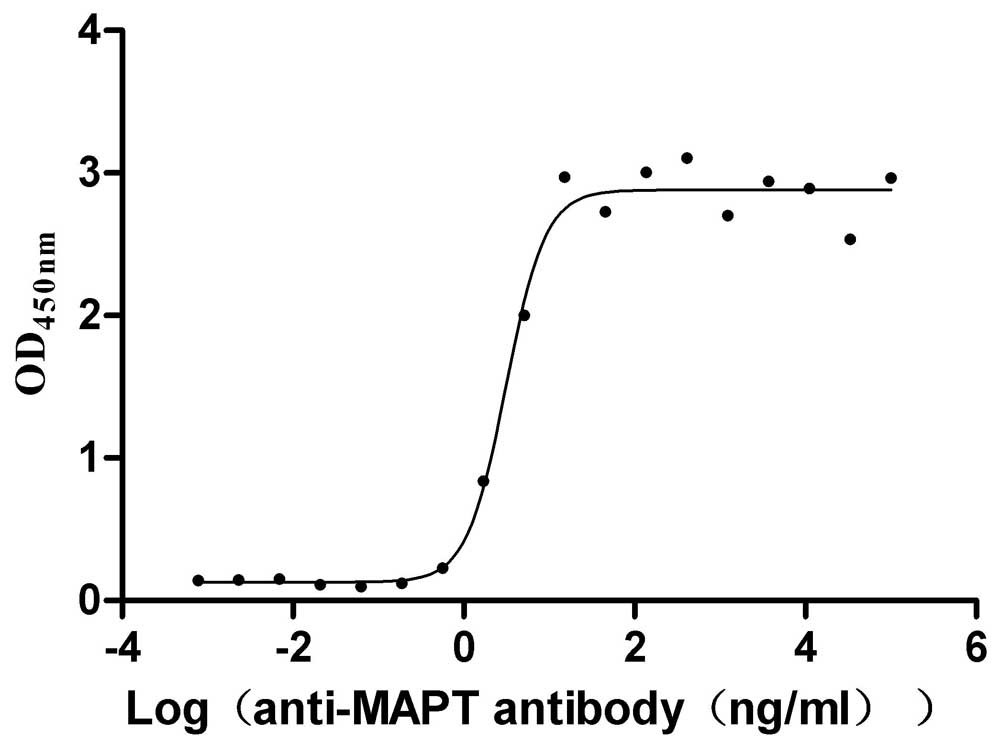
Recombinant Macaca mulatta Microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca mulatta (Rhesus macaque)
-
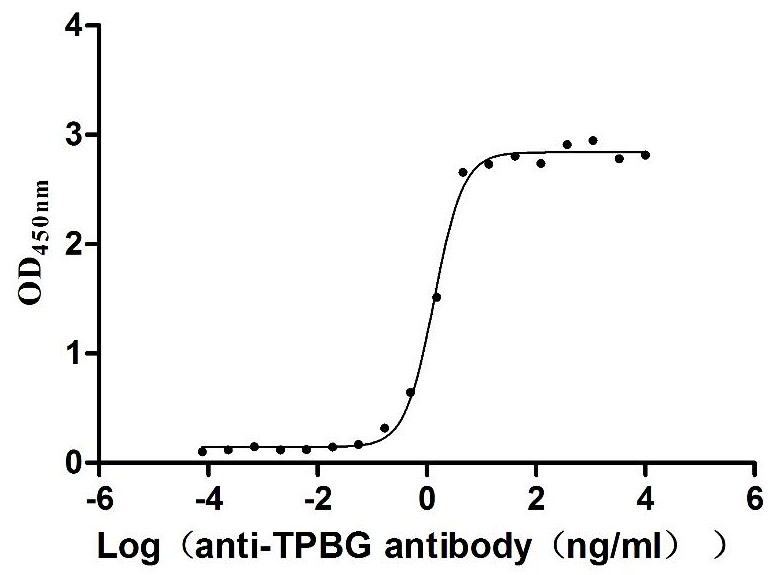
Recombinant Human Trophoblast glycoprotein (TPBG), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Claudin-6 (CLDN6)-VLPs, Fluorescent (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
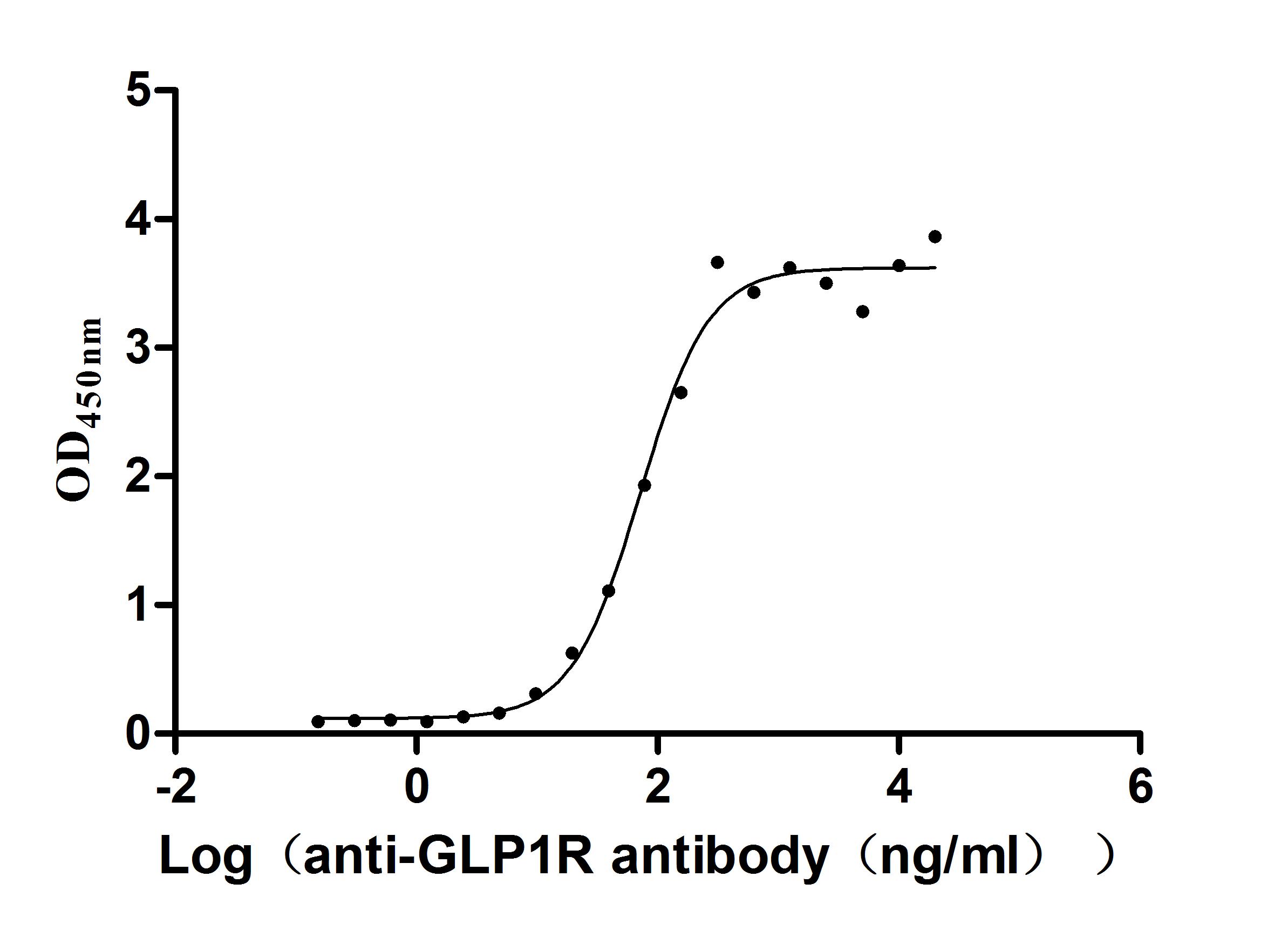
Recombinant Human Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (GLP1R), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 8 (CCR8)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


f4-AC1.jpg)