Recombinant Mouse Carbohydrate-responsive element-binding protein (Mlxipl), partial
-
中文名称:小鼠Mlxipl重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP860828MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Mlxipl重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP860828MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Mlxipl重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP860828MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Mlxipl重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP860828MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Mlxipl重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP860828MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
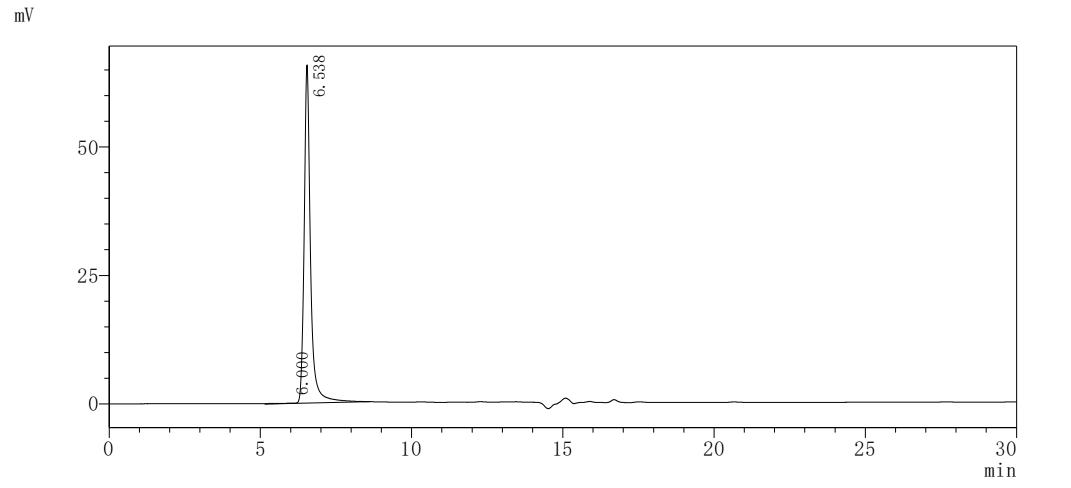
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Mlxipl; Mio; Wbscr14Carbohydrate-responsive element-binding protein; ChREBP; MLX interactor; MLX-interacting protein-like; Williams-Beuren syndrome chromosomal region 14 protein homolog
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Transcriptional repressor. Binds to the canonical and non-canonical E box sequences 5'-CACGTG-3'.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- ChREBP and SHP control the regulation of hepatic microsomal triglyceride transfer protein expression and VLDL Secretion. Adenoviral Overexpression of ChREBP and SHP Respectively Increased and Decreased Mttp Expression. PMID: 29518948
- Data, including data from studies in knockout mice, suggest that ChREBP is involved in coordinate regulation of sucrose and fructose absorption/metabolism by modulating gene expression in intestinal mucosa and liver. PMID: 29534502
- Authors have identified a previously unappreciated negative feedback loop by which glucose-induced ChREBP-beta downregulates ChREBP-alpha-signaling providing new insight into the physiological role of islet ChREBP-beta and into the regulation of glucose-induced gene expression. PMID: 27900263
- loss of adipose-ChREBP is sufficient to cause insulin resistance potentially by regulating AT glucose transport. PMID: 29069585
- Glucose-challenged Chrebp-/- mice exhibit a marked reduction in FGF21 production. PMID: 29020627
- Study identify O-GlcNAcylation on Ser514 in the C-terminus of ChREBP and validate two important sites, Thr517 and Ser839 for O-GlcNAcylation and their function. Ser514 phosphorylation enhances ChREBP O-GlcNAcylation, maintaining the transcriptional activity of ChREBP; Ser839 O-GlcNAcylation is essential for its heterodimerization, DNA-binding activity, and nuclear export. PMID: 28450420
- findings suggest that a previously unknown link exists between ChREBP and the regulation of cholesterol synthesis that affects liver injury. PMID: 28628039
- findings also identified a role for ChREBP in regulating SREBP2-dependent cholesterol metabolism. PMID: 28628040
- these findings support a carbohydrate-mediated, ChREBP-driven mechanism that contributes to hepatic insulin resistance. PMID: 27669460
- a high complex carbohydrate diet selectively increases hepatic ChREBPbeta expression, which associates with hepatic steatosis but not insulin resistance. In contrast, a high fat diet reduces adipose ChREBP, which associates with inflammation and insulin resistance. PMID: 27992582
- The results revealed the novel mechanism by which HNF-4alpha promoted ChREBP transcription in response to glucose, and also demonstrated that ChREBP-alpha and HNF-4alpha synergistically increased ChREBP-beta transcription. PMID: 27029511
- Adipose tissue mTORC2 regulates via Rictor ChREBP-driven de novo lipogenesis and hepatic glucose metabolism. PMID: 27098609
- Diet-induced obesity increases basal expression of ChREBPbeta, which may increase the risk of developing hepatic steatosis, and fructose-induced activation is independent of gluconeogenesis. PMID: 26526060
- Targeted deletion of ChREBP in bone marrow cells resulted in accelerated atherosclerosis progression in Ldlr-/- mice with increased monocytosis, lesional macrophage accumulation, and plaque necrosis. PMID: 26411684
- Evaluation of the conservation of ChREBP and MondoA sequences demonstrate that MondoA is better conserved and potentially mediates more ancient function in glucose metabolism. PMID: 26910886
- Data show that the weight gain was blunted in male, but not female, fatty acid binding protein 4-Cre-driven promoter (FaChOX) mice when placed on either a normal chow diet or an obesogenic Western diet. PMID: 26248218
- Data show that carbohydrate-response element-binding protein (ChREBP) activation induces peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPARgamma) activity and ChREBP inhibition impairs differentiation. PMID: 26181104
- Data suggest expression of ChREBPbeta isoform is up-regulated in pancreatic beta-cells in response to elevated glucose (i.e., hyperglycemic conditions); RNA interference of ChREBPbeta prevents beta-cell proliferation in response to hyperglycemia. PMID: 26384380
- hyperinsulinemia may cause glycolipid metabolic disorders by up-regulating the expression of ChREBP PMID: 25212036
- The effects of ethanol on AMPK and PP2A may result in activation of ChREBP, providing another potential mechanism for ethanol-induced hepatic steatosis. PMID: 23266705
- Depletion of ChREBP decreased glucose-stimulated proliferation in beta-cells isolated from ChREBP(-/-) mice, in INS-1-derived 832/13 cells, and in primary rat and human beta-cells PMID: 22586588
- Data indicate that ChREBP is a key transcription factor that mediates many of the hyperglycaemia-induced activations in a gene expression programme that underlies beta cell glucotoxicity at the molecular, cellular and whole animal levels. PMID: 22382520
- ChREBP overexpression induced expression of stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 (Scd1), the enzyme responsible for the conversion of saturated fatty acids (SFAs) into MUFAs PMID: 22546860
- adipose ChREBP is a major determinant of adipose tissue fatty acid synthesis and systemic insulin sensitivity PMID: 22466288
- an important mechanism by which importin-alpha and 14-3-3 control movement of ChREBP in and out of the nucleus in response to changes in glucose levels in liver PMID: 21665952
- ChREBP was unexpectedly required during fasting for maximal Rgs16 transcription in liver and in cultured primary hepatocytes during gluconeogenesis. PMID: 21357625
- Results reveal that O-GlcNAcylation represents an important novel regulation of ChREBP activity in the liver under both physiological and pathophysiological conditions. PMID: 21471514
- ChREBP is a critical and direct mediator of glucose repression of PPARalpha gene expression in pancreatic beta-cells PMID: 21282101
- Carbohydrate response element-binding protein (ChREBP), a glucose-dependent transcription factor downstream of Protein phosphatase 2A, partially mediated the effects of glucose on metabolic markers. PMID: 21215280
- The db/db mouse exhibits significantly higher liver ChREBP activity, which may be associated with the development of hepatic steatosis frequently occurring in type 2 diabetes. PMID: 19727214
- Data showed that the steatosis is accompanied by altered expression of a number of genes, including increased expression of ChREBP, which acts as one of the central determinants of lipid synthesis in the liver. PMID: 21103071
- low SIK2 activity was associated with increased p300 HAT activity, ChREBP hyperacetylation, and hepatic steatosis PMID: 21084751
- ChREBP is an attractive target to alleviate derangements in lipid metabolism observed in patients with glycogen storage disease. PMID: 20854262
- ChREBP inactivation in clonal pancreatic MIN6 beta-cells results in an increase in Pdx-1 expression at low glucose and to a small, but significant, increase in Ins2, GcK and MafA gene expression at high glucose concentrations. PMID: 20934404
- Data demonstrate that expression of carbohydrate response element-binding protein (ChREBP or Mlxipl), an important transcriptional regulator of carbohydrate metabolism, is significantly affected in compound Foxa1/a2 mutant beta-cells. PMID: 20534694
- These multiple lines of evidence support the conclusion that G-6-P mediates the activation of ChREBP. PMID: 20382127
- ChREBP acts as a novel repressor of the ARNT/HIF-1beta gene and thus may contribute to beta-cell dysfunction induced by glucotoxicity. PMID: 19833882
- ChREBP is important modulator of adipocytes and its expression in adipose tissue is subject to combined regulation by glucose and insulin. Induction of ChREBP may serve as novel pharmacological pathway for troglitazone-mediated hypoglycemic effects. PMID: 15100094
- is required both for basal and carbohydrate-induced expression of several liver enzymes essential for coordinated control of glucose metabolism, fatty acid, and the synthesis of fatty acids and triglycerides in vivo PMID: 15118080
- role of ChREBP in the glucose regulation of two key liver lipogenic enzymes, acetyl-CoA carboxylase and fatty acid synthase PMID: 15496471
- The results of this study suggest that inactivation of ChREBP expression not only reduces fat synthesis and obesity in ob/ob mice but also results in improved glucose tolerance and appetite control. PMID: 16705063
- results demonstrate that carbohydrate responsive element-binding protein (ChREBP) is central for the regulation of lipogenesis in vivo and plays a determinant role in the development of the hepatic steatosis and of insulin resistance in ob/ob mice PMID: 16873678
- ChREBP is a critical regulator of lipogenic genes in the beta cell and may play a role in the development of glucolipotoxicity and beta cell failure through alteration of gene expression in type 2 diabetes PMID: 16891625
- The shift from fat utilization to pyruvate and lactate utilization resulted in a decrease in the energy of ATP hydrolysis and a hypo-energetic state in the livers of ChREBP(-/-) mice. PMID: 18042547
- ChREBP can regulate metabolic gene expression to convert excess carbohydrate into triglyceride rather than glycogen.[review] PMID: 18490833
- Phosphorylation of ChREBP was essential for its interaction with CRM1 for export to the cytosol, whereas nuclear import of ChREBP requires dephosphorylated ChREBP to interact with importin alpha. PMID: 18606808
- The transcription factor ChRepsilonBP is a major mediator of glucose action on lipogenic genes & a key determinant of lipid synthesis in vitro. In mice, it plays a central role in hepatic steatosis & insulin resistance physiopathology. Review. PMID: 18950580
- study demonstrated that thyroid hormone up-regulated ChREBP mRNA and protein expression in liver PMID: 19324998
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus.
-
组织特异性:Expressed in the ventricular and intermediate zones of the developing spinal cord of E12.5 embryos. In later embryos expressed in a variety of tissues.
-
数据库链接:
Most popular with customers
-
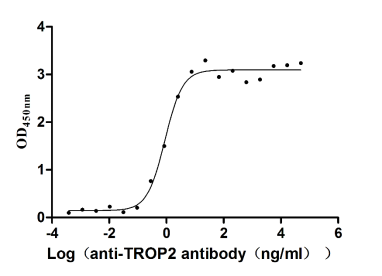
Recombinant Human Tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 2 (TACSTD2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
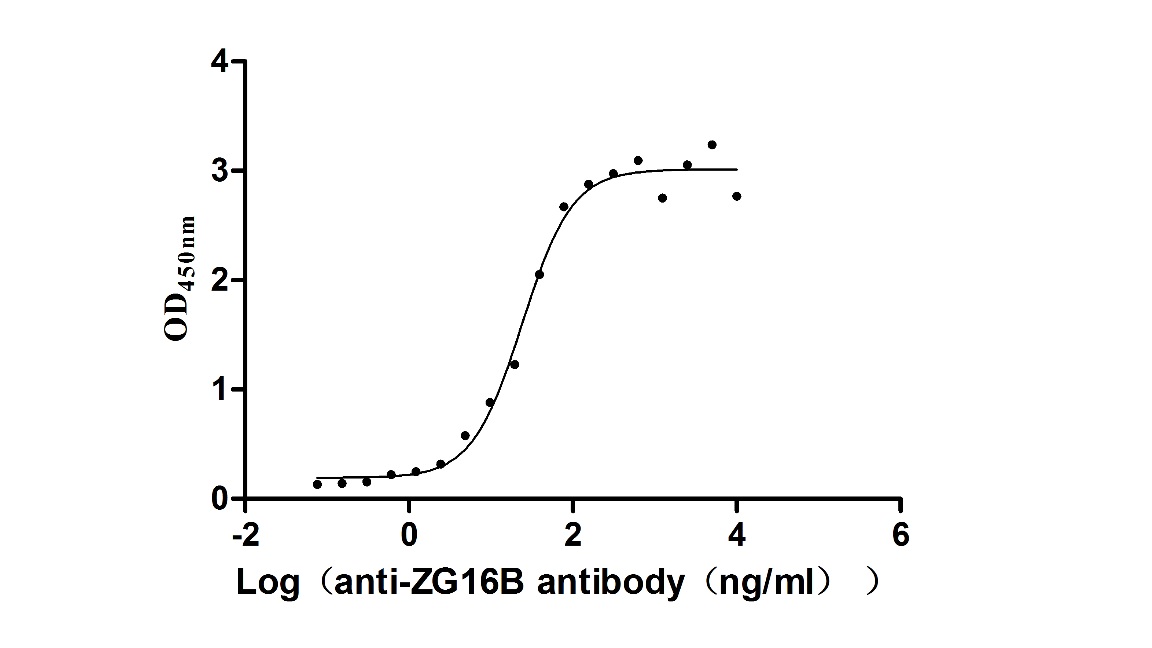
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis zymogen granule protein 16 homolog B (ZG16B) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
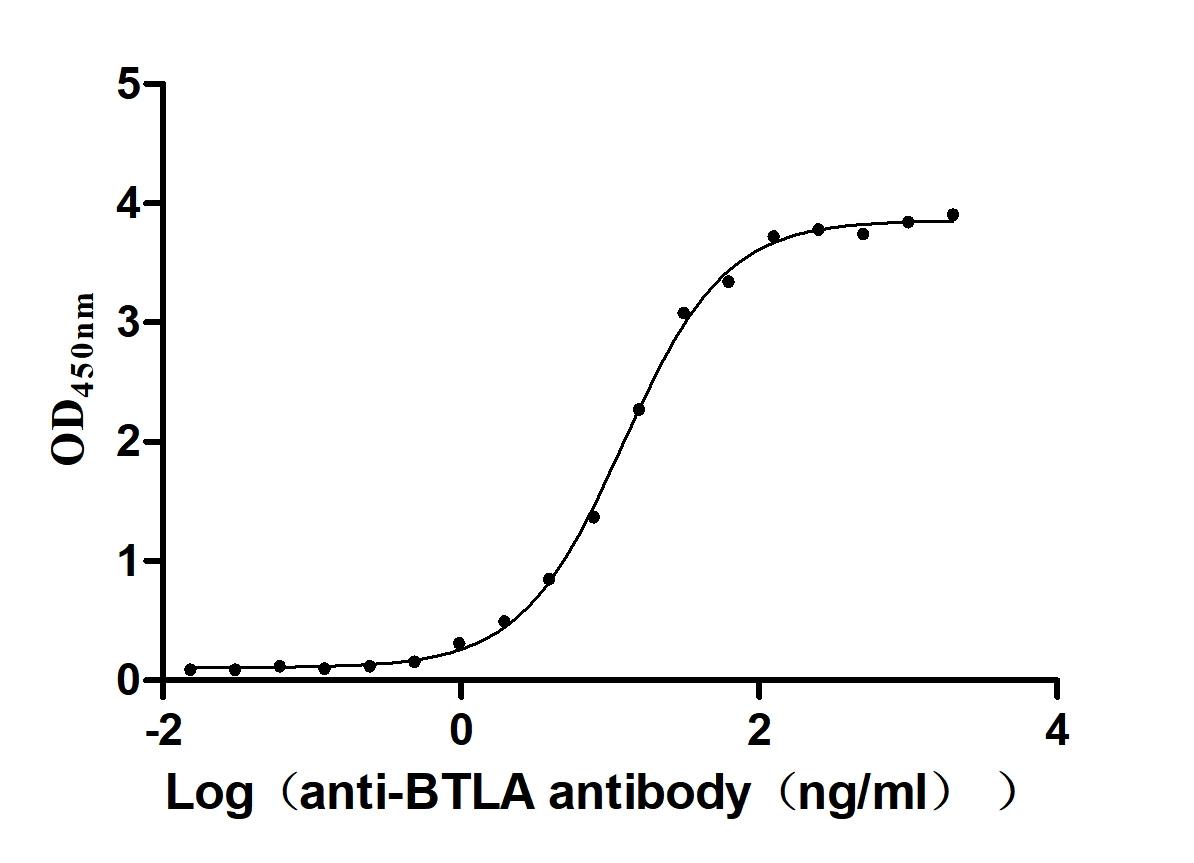
Recombinant Human B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator(BTLA), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
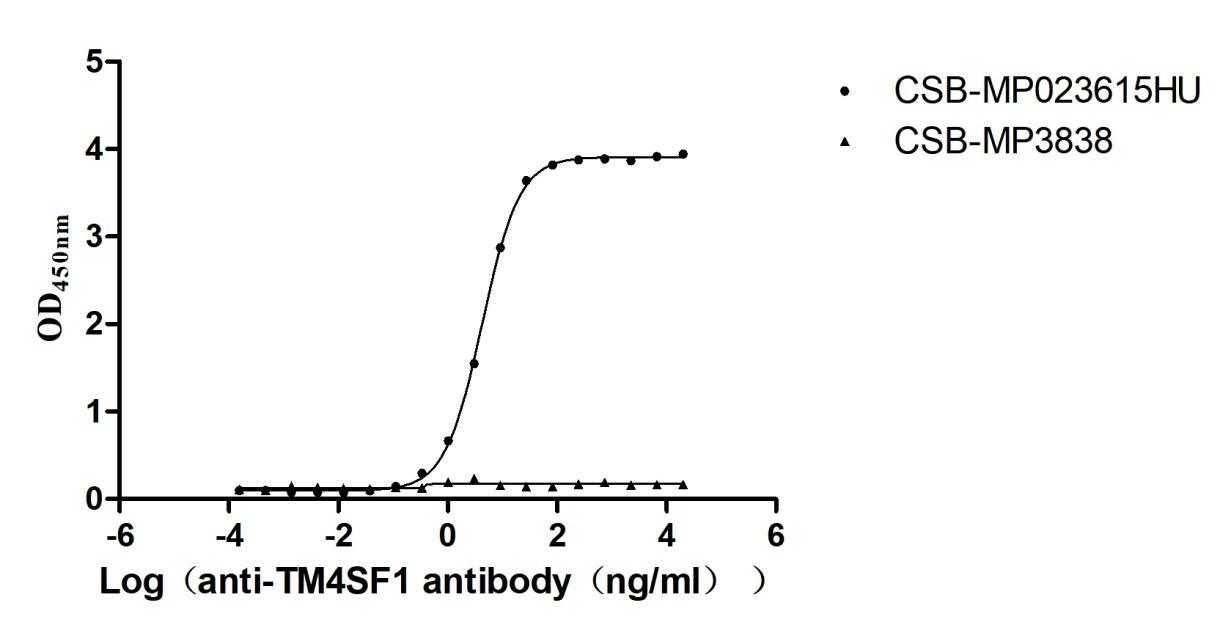
Recombinant Human Transmembrane 4 L6 family member 1(TM4SF1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 9 (CCR9)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor UFO(AXL),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)