Recombinant Mouse Bromodomain-containing protein 4 (Brd4), partial
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse Bromodomain-containing protein 4(Brd4) ,partial
-
货号:CSB-YP887677MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse Bromodomain-containing protein 4(Brd4) ,partial
-
货号:CSB-EP887677MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse Bromodomain-containing protein 4(Brd4) ,partial
-
货号:CSB-EP887677MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse Bromodomain-containing protein 4(Brd4) ,partial
-
货号:CSB-BP887677MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse Bromodomain-containing protein 4(Brd4) ,partial
-
货号:CSB-MP887677MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Brd4; Mcap; Bromodomain-containing protein 4; Mitotic chromosome-associated protein; MCAP
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Chromatin reader protein that recognizes and binds acetylated histones and plays a key role in transmission of epigenetic memory across cell divisions and transcription regulation. Remains associated with acetylated chromatin throughout the entire cell cycle and provides epigenetic memory for postmitotic G1 gene transcription by preserving acetylated chromatin status and maintaining high-order chromatin structure. During interphase, plays a key role in regulating the transcription of signal-inducible genes by associating with the P-TEFb complex and recruiting it to promoters. Also recruits P-TEFb complex to distal enhancers, so called anti-pause enhancers in collaboration with JMJD6. BRD4 and JMJD6 are required to form the transcriptionally active P-TEFb complex by displacing negative regulators such as HEXIM1 and 7SKsnRNA complex from P-TEFb, thereby transforming it into an active form that can then phosphorylate the C-terminal domain (CTD) of RNA polymerase II. Promotes phosphorylation of 'Ser-2' of the C-terminal domain (CTD) of RNA polymerase II. According to a report, directly acts as an atypical protein kinase and mediates phosphorylation of 'Ser-2' of the C-terminal domain (CTD) of RNA polymerase II; these data however need additional evidences in vivo. In addition to acetylated histones, also recognizes and binds acetylated RELA, leading to further recruitment of the P-TEFb complex and subsequent activation of NF-kappa-B. Also acts as a regulator of p53/TP53-mediated transcription: following phosphorylation by CK2, recruited to p53/TP53 specific target promoters.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Genetic and pharmacological inhibition of BRD4 suppressed IL-1beta-induced expression and translocation of HMGB1. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) showed the enrichment of BRD4 around the HMGB1 upstream non-promoter region, which diminished with JQ1 treatment. PMID: 28844955
- Brd4 deletion prevents enhancer RNA production, cell identity gene induction and cell differentiation. Interestingly, Brd4 is dispensable for maintaining cell identity genes in differentiated cells. These findings identify Brd4 as an enhancer epigenomic reader that links active enhancers with cell identity gene induction in differentiation. PMID: 29263365
- Bromodomain protein BRD4 promotes cell proliferation in skin squamous cell carcinoma. PMID: 29050985
- By modulating the translation of IkappaBalpha via the Mnk2-eIF4E pathway, Brd4 provides an additional layer of control for NF-kappaB-dependent inflammatory gene expression and inflammatory response. PMID: 28461486
- Long-term treatment with bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4) inhibitors caused telomere shortening in both mouse and human cells, suggesting BRD4 plays a role in telomere maintenance in vivo. PMID: 28854735
- Fmr1 knockout (KO) mice show widespread changes in histone marks as well as transcriptional misregulation resulting in increased expression of many critical synaptic genes. Data suggest that one chromatin target of FMRP, the reader protein Brd4, appears to be significantly involved in this transcriptional disruption. PMID: 28823556
- The functional domains of mouse BRD4 and its role in transcription are described. Review. PMID: 27450555
- Brd2 and Brd4 genetic transcription required for Th17 cell development and adaptive immunity. PMID: 28262505
- These data provide a detailed mechanism for how activated NF-kappaB and BRD4 control epithelial-mesenchymal transition initiation and transcriptional elongation in model airway epithelial cells in vitro and in a murine pulmonary fibrosis model in vivo. PMID: 27793799
- DOT1L, via dimethylated histone H3 K79, facilitates histone H4 acetylation, which in turn regulates the binding of BRD4 to chromatin in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. PMID: 27294782
- Acute induction of genes related to lipid accumulation in the livers of mice force-fed with fructose is associated with the induction of histone acetylation and BRD4 binding around these genes PMID: 27621183
- Both mouse and human BRD4 have intrinsic histone acetyltransferase activity. PMID: 27159561
- the interaction between BRD4 and Mediator has functional importance for gene-specific transcriptional activation and for acute myeloid leukemia maintenance. PMID: 27068464
- our data demonstrate the fundamental role of Brd4 in monitoring cell differentiation through its interaction with acetylated histone marks and disruption of Brd4 may cause aberrant differentiation. PMID: 26847871
- Data show that CCAAT-enhancer-binding protein-alpha (C/EBPalpha) directly regulates Kruppel-like factor 4 (Klf4) expression and increasing the levels of histone demethylase Lsd1 and transcription factor Brd4 in B cell. PMID: 26974661
- BRD4 can act as a global genomic regulator to direct the fibrotic response through its coordinated regulation of myofibroblast transcription. PMID: 26644586
- BRD4 is critical for the maintenance of ESC pluripotency and that this occurs primarily through the maintenance of Nanog expression. PMID: 25393219
- The BET family member BRD4 interacts with OCT4 and regulates pluripotency gene expression PMID: 25684227
- Brd4 provides a critical link between neuronal activation and the transcriptional responses that occur during memory formation PMID: 26301327
- Aire's collaboration with the bromodomain-containing protein, Brd4, uncovered correspondence between those genes induced by Aire and those inhibited by a small-molecule bromodomain blocker. PMID: 26216992
- Data suggest that Brd4 is essential for Toll-like receptor-stimulated interferon-beta (IFNB) gene transcription by permitting transcription factors to interact with the IFNB promoter in macrophages. PMID: 25891802
- Data show that hematopoietic transcription factors (TFs) promote bromodomain containing 4 protein (BRD4) recruitment to their occupied sites. PMID: 25982114
- BRD4, a member of the bromodomain and extraterminal domain (BET) family of epigenetic readers, regulates the self-renewal ability and pluripotency of ESCs. PMID: 25263550
- BRD4 associates with BRG1, a key regulator of embryonic stem cell self-renewal and pluripotency, in the Nanog regulatory regions to regulate Nanog expression. PMID: 25146928
- Immunofluorescence of spermatogenic cells revealed BRD4 in a ring around the nuclei of spermatids containing hyperacetylated histones. PMID: 25691659
- Brd4-suppressed intestines are sensitive to organ stress and show impaired regeneration following irradiation, suggesting that concurrent Brd4 suppression and certain cytotoxic therapies may induce undesirable synergistic effects. PMID: 25242322
- this study reveals a novel function of BRD4 in controlling the germinal center B cell development pathway. PMID: 25656449
- BRD4 is involved in multiple steps of the transcription hierarchy, primarily by facilitating transcript elongation both at enhancers and on gene bodies independently of P-TEFb. PMID: 25383670
- The effect of a selective small molecule inhibitor of BRD4, JQ1, to inhibit SOCS3 expression demonstrated the functional role of BRD4 for STAT3-dependent transcription. PMID: 24657799
- BET bromodomain inhibition abrogates super enhancer-mediated inflammatory transcription, atherogenic endothelial responses, and atherosclerosis in vivo. PMID: 25263595
- Brd4 serves as a chromatin platform required for the recruitment of repair components during CSR and general DNA damage. PMID: 24954901
- Brd4 is upregulated in MPNSTs. Brd4 downregulation induces apoptosis through induction of proapoptotic Bim. PMID: 24373973
- these results identify a novel function of Brd4 in maintaining the persistently active form of NF-kappaB found in tumors, and they suggest that interference with the interaction between acetylated RelA and Brd4 could be a potential therapeutic approach for the treatment of NF-kappaB-driven cancer. PMID: 23686307
- A structural basis for BRD2/4-mediated host chromatin interaction and oligomer assembly of Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus and murine gammaherpesvirus LANA proteins. PMID: 24146614
- Data show that infection of macrophages with Listeria monocytogenes caused binding of the BET proteins Brd2, Brd3, and, most prominently, Brd4 to the Nos2 promoter. PMID: 24248598
- Brd4 as a key regulator for Tax-mediated NF-kappaB gene expression PMID: 24189064
- BRD4, bound to interferon-stimulated genes through acetylated histones, recruits P-TEFb and NELF/DSIF and orchestrates positive and negative transcription elongation of interferon-stimulated genes PMID: 23589332
- BRD4 recruits P-TEFb to acetylated histones, promoting phosphorylation of paused RNA polymerase II and the repressive complexes DSIF and NELF by CDK9, thereby allowing productive mRNA elongation. PMID: 22912406
- Down-regulation of NF-kappaB transcriptional activity in HIV-associated kidney disease by BRD4 inhibition. PMID: 22645123
- BRD4 is an atypical kinase that binds to the carboxyl-terminal domain (CTD) of RNA polymerase II and directly phosphorylates its serine 2 (Ser2) sites both in vitro and in vivo under conditions where other CTD kinases are inactive. PMID: 22509028
- identification of the protein bromodomain-containing 4 (Brd4) as being critically required for acute myeloid leukaemia disease maintenance PMID: 21814200
- Findings suggest that BRD4 may be altering the predisposition of tumors to undergo conversion to a more de-differentiated or primitive state during metastatic progression. PMID: 21389092
- Results suggest Brd4 marks mitosis/G1 phase genes for transcriptional memory during mitosis, and upon exiting mitosis, this mark acts as a signal for initiating their prompt transcription in daughter cells. PMID: 19812244
- Growth and early postimplantation defects in mice deficient for the bromodomain-containing protein Brd4. PMID: 11997514
- brd4 binds to replication factor C and inhibits progression to S phase PMID: 12192049
- interaction of Brd4 with chromatin in living cells PMID: 12840145
- E2 protein interacts with Brd4 and tethers the viral DNA to the host mitotic chromosomes. PMID: 15109495
- Brd4 plays an integral part in a cellular response to drug-induced mitotic stress by preserving a properly acetylated chromatin status. PMID: 16339075
- E2 proteins from many papillomaviruses, including the clinically important alpha genus human papillomaviruses, interact with Brd4 to mediate transcriptional activation function PMID: 16973557
- Histone acetylation is necessary but not sufficient for chromosomal localization of BRD4 during meiosis in mouse oocytes. PMID: 17267518
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus. Chromosome.
-
数据库链接:
Most popular with customers
-
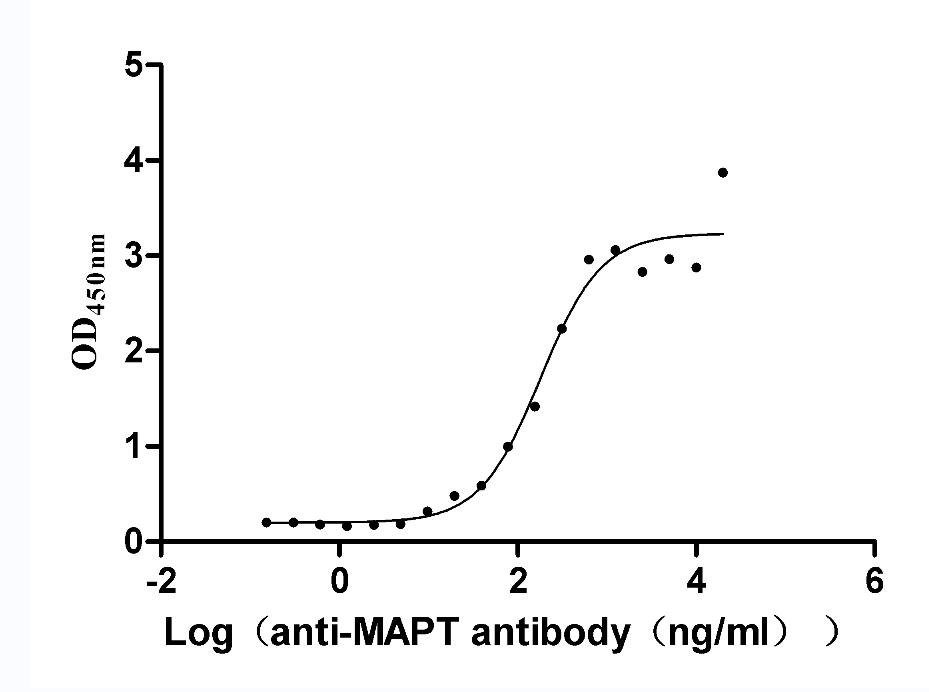
Recombinant Rat Microtubule-associated protein tau (Mapt) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
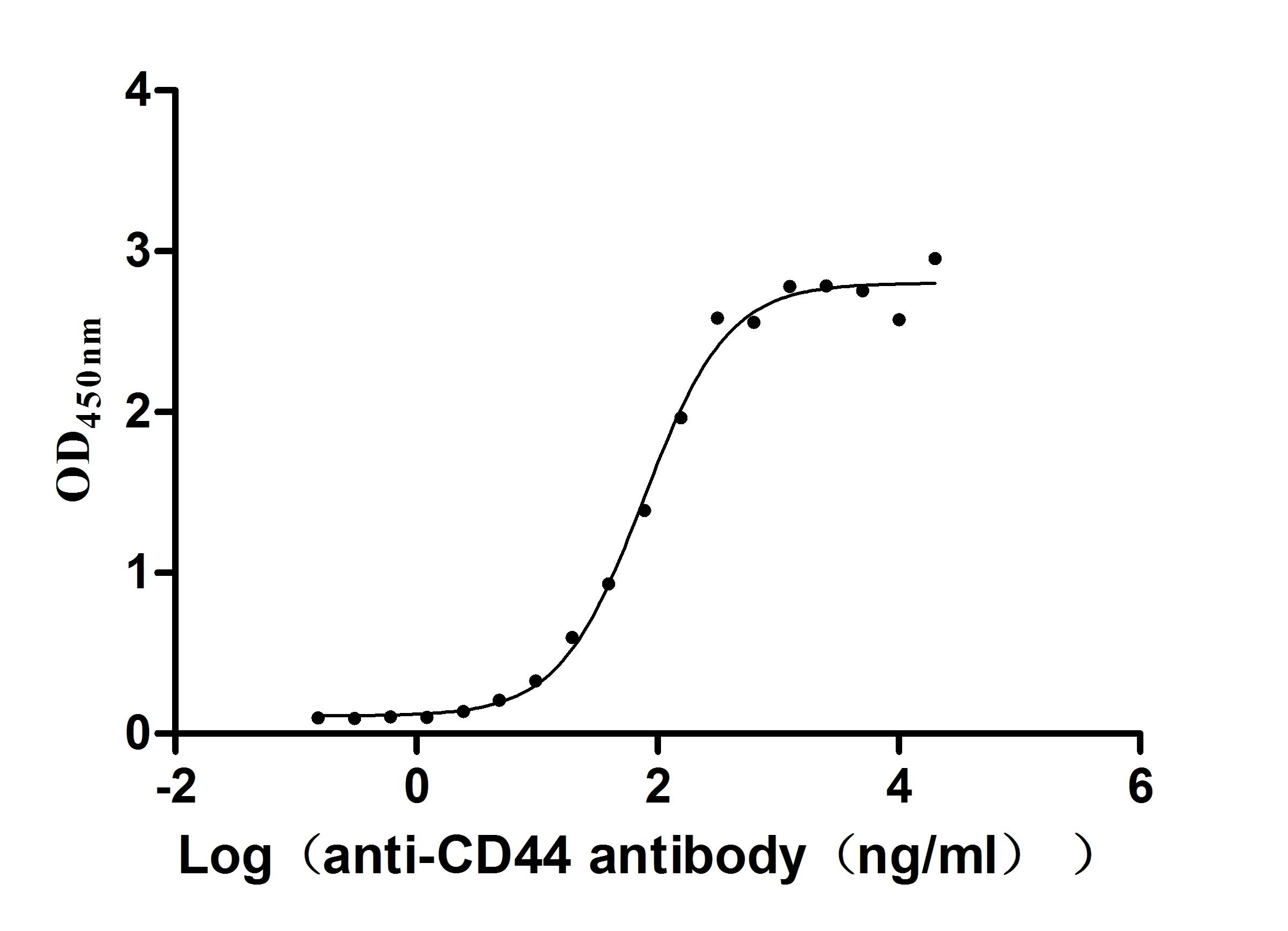
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis CD44 antigen (CD44), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Mouse Cell adhesion molecule 1 (Cadm1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
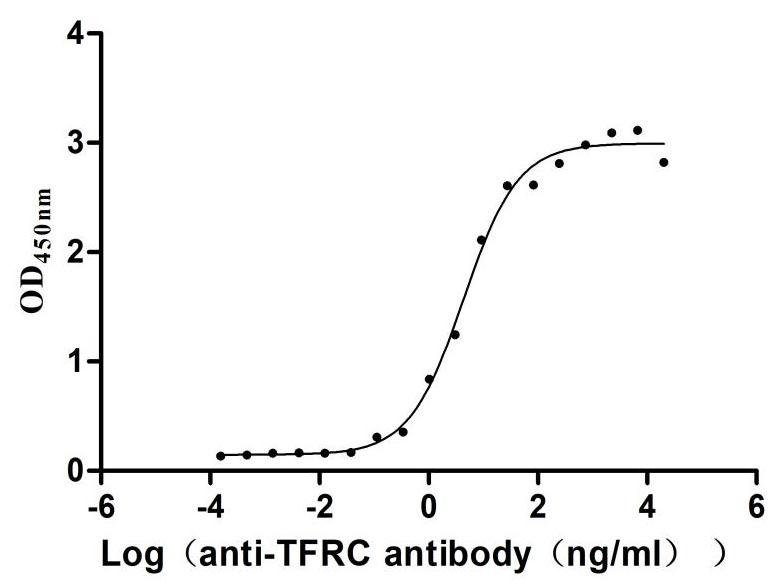
Recombinant Human Transferrin receptor protein 1 (TFRC), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
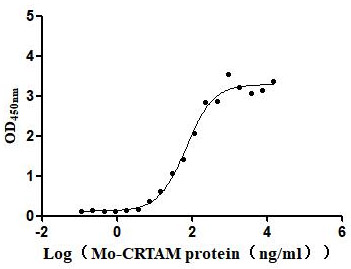
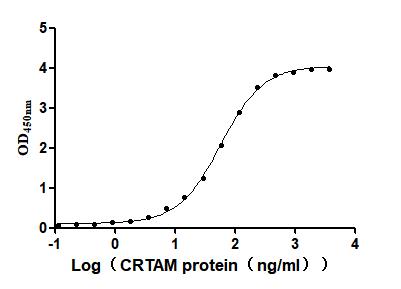
Recombinant Mouse Cytotoxic and regulatory T-cell molecule (Crtam), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
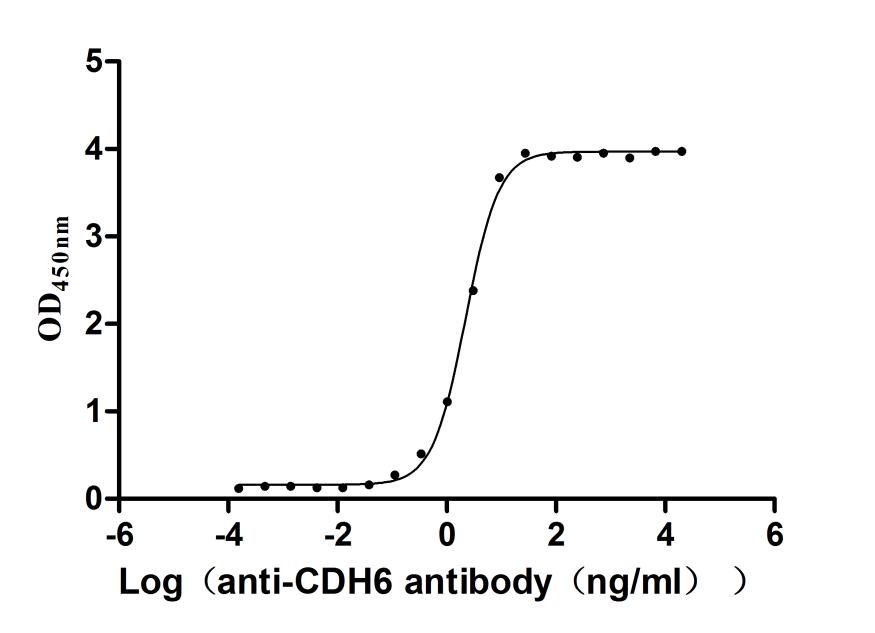
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Cadherin 6(CDH6),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 15(TNFSF15) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
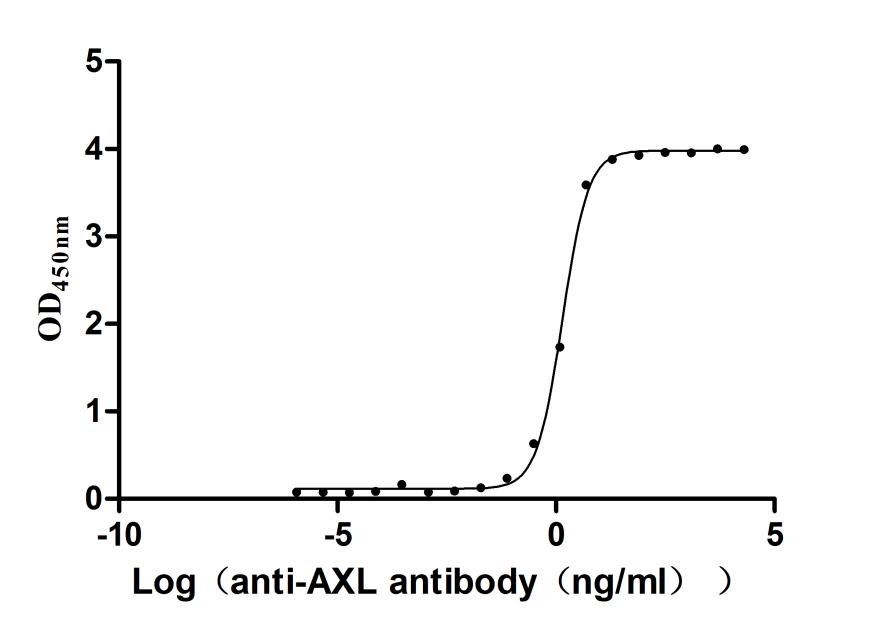
Recombinant Human Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor UFO(AXL),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)