Recombinant Human Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily KQT member 2 (KCNQ2), partial
-
中文名称:人KCNQ2重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP012090HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人KCNQ2重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP012090HU
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人KCNQ2重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP012090HU-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人KCNQ2重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP012090HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人KCNQ2重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP012090HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:BFNC; BFNS1; EBN 1; EBN; EBN1; EIEE7; ENB 1; ENB1; HNSPC; KCNA 11; KCNA11; KCNQ 2; Kcnq2; KCNQ2_HUMAN; KQT like 2 ; KQT-like 2; KV7.2; KVEBN 1; KVEBN1; KvLQT 2; KvLQT2; Neuroblastoma specific potassium channel alpha subunit KvLQT2 ; Neuroblastoma specific potassium channel protein; Neuroblastoma specific potassium channel subunit alpha; Neuroblastoma specific potassium channel subunit alpha KvLQT2; Neuroblastoma-specific potassium channel subunit alpha KvLQT2; OTTHUMP00000031681; OTTHUMP00000031682; OTTHUMP00000031684; OTTHUMP00000031685; OTTHUMP00000031686; OTTHUMP00000031687; OTTHUMP00000031689; Potassium voltage gated channel KQT like protein 2 ; Potassium voltage gated channel KQT like subfamily member 2; Potassium voltage gated channel subfamily KQT member 2; Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily KQT member 2; Voltage gated potassium channel subunit Kv7.2; Voltage-gated potassium channel subunit Kv7.2
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Associates with KCNQ3 to form a potassium channel with essentially identical properties to the channel underlying the native M-current, a slowly activating and deactivating potassium conductance which plays a critical role in determining the subthreshold electrical excitability of neurons as well as the responsiveness to synaptic inputs. Therefore, it is important in the regulation of neuronal excitability. KCNQ2/KCNQ3 current is blocked by linopirdine and XE991, and activated by the anticonvulsant retigabine. As the native M-channel, the potassium channel composed of KCNQ2 and KCNQ3 is also suppressed by activation of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor CHRM1.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- An optimum cholesterol level in the plasma membrane is required for the proper functioning of Kv7.2/Kv7.3 channels. PMID: 29474891
- Study describes the interactions of hposphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate with both the open and closed states of a KCNQ2 channel. Through these methods, results show that a lipid can migrate between different binding sites in a protein and this migration modulates protein functions. PMID: 29058190
- A distinctive ictal amplitude-integrated EEG pattern occurs in newborns with neonatal epilepsy associated with KCNQ2 mutations. PMID: 28926830
- patients with the KCNQ2 E515D mutation are susceptible to seizures. PMID: 28038823
- he present study involves identification of newer anti-epileptic agents by means of a computer-aided drug design adaptive protocol involving both structure-based virtual screening of Asinex library using homology model of KCNQ2 and 3D-QSAR based virtual screening with docking analysis, followed by dG bind and ligand efficiency calculations with ADMET studies, of which 20 hits qualified all the criterions. PMID: 28856943
- This study provided evidence to suggests that the p.R213Q mutation has a dominant-negative effect on the current amplitude of homomeric wild-type and mutant KCNQ2 constructs, which correlates with clinical seizure frequencies and neurodevelopmental outcomes. PMID: 28399683
- Mutations in STXBP1 encoding the syntaxin binding protein 1 can produce a phenotype similar to that of KCNQ2 mutations PMID: 29067685
- whole exome sequencing in families with ID and history of autosomal dominant inheritance pattern with or without seizures, may further broaden the phenotypic spectrum of KCNQ2 associated epileptic encephalopathy or encephalopathy PMID: 28602030
- The direct effect of heat on KCNQ2 channels may be involved in excitability regulation of neurons, and the P-loop region is critical for temperature-dependent modulation of the expression and trafficking of KCNQ2 channels. PMID: 28372301
- Epileptic encephalopathy with burst suppression without brain malformations is associated with pathogenic variation in KCNQ2. PMID: 28133863
- Heterozygous KCNQ2 R201C and R201H gain-of-function variants present with profound neonatal encephalopathy in the absence of neonatal seizures. PMID: 28139826
- This study provide evidence for a new phenotypic and functional profile in KCNQ2-related epilepsy. PMID: 27861786
- In the present work, a pharmacophore-based 3D-QSAR model was generated for a series of N-pyridyl and pyrimidine benzamides possessing KCNQ2/Q3 opening activity. The pharmacophore model generated contains one hydrogen bond donor (D), one hydrophobic (H), and two aromatic rings (R). They are the crucial molecular write-up detailing predicted binding efficacy of high affinity and low affinity ligands for KCNQ2/Q3 opening a PMID: 27607834
- This study demonstrated that Mutations in the KCNQ2 gene encoding the voltage-gated potassium channel subunit Kv7.2 cause early onset epileptic encephalopathy . PMID: 27030113
- This work shows for the first time the association between KCNQ2 mutations and startle attacks in 38% of patients, which opens the possibility to define electroclinical phenotypes associated to KCNQ2 mutations. It also demonstrates that KCNQ2 mutations contribute to an important percentage of Spanish patients with epilepsy. PMID: 27535030
- USP36 actions extend beyond TrkA because the presence of USP36 interferes with Nedd4-2-dependent Kv7.2/3 channel regulation. PMID: 27445338
- a structural mechanism for the gating of the Kv7.3 PM and for the site of action of RTG as a Kv7.2/Kv7.3 K(+) current activator. PMID: 26627826
- There is a variable clinical expression in infantile epilepsy patients with mosaicism for KCNQ2 mutations. PMID: 25959266
- Our data indicate that the TW site is dispensable for function, contributes to the stabilization of the CaM-Kv7.2 complex and becomes essential when docking to either helix A or when helix B is perturbed. PMID: 26148514
- all the patients carrying the p.A294V mutation of KCNQ2 presented the clinical and EEG characteristics of early onset epileptic encephalopathy PMID: 26007637
- Kcnq2 protein and mRNA expression and DNA methylation status did not differ significantly between bipolar disorder patients and controls. PMID: 25041603
- A novel and rare mutation was identified in KCNQ2 and was likely responsible for the benign seizures. PMID: 25046240
- Phosphorylation of KCNQ2 and KCNQ3 anchor domains by protein kinase CK2 augments binding to AnkG. PMID: 25998125
- The results of thus study suggested that the type of KCNQ2 mutation might influence Antiepileptic drug response epilepsy as well as developmental outcome. PMID: 25880994
- Epileptic encephalopathy related to mutations in the KCNQ2 genes. PMID: 25818041
- Collectively, this work reveals that residue C106 in S1 can be very close to several N-terminal S4 residues for stabilizing different KCNQ2 resting conformations. PMID: 25385787
- the present results suggest that gain-of-function mutations in Kv7.2/3 currents may cause human epilepsy with a severe clinical course PMID: 25740509
- The results of this study suggested that the loss of Kv7.2 activity increases the excitability of primary sensory neurons. PMID: 24687876
- XRCC1 107 and 194, hOGG1, KCNQ2, and AT1R are not associated with endometriosis susceptibility. PMID: 22084859
- The molecular events underlying the association between CaM and Kv7.2 and their regulation by Ca(2+), was examined. PMID: 24489773
- This study demonistrated that KCNQ2 mutation association with epilepsy. PMID: 25052858
- We described clinical, genetic, and functional data from 17 families with a diagnosis of benign familial neonatal epilepsy caused by KCNQ2 or KCNQ3 mutations and we showed that some mutations lead to a reduction of Q2 channel regulation by syntaxin-1A. PMID: 24375629
- We monitored KCNQ2/3 channel currents and translocation of PHPLCdelta1 domains as real-time indicators of PI(4,5)P2, and translocation of PHOSH2x2, and PHOSH1 domains as indicators of plasma membrane and Golgi PI(4)P, respectively. PMID: 24843134
- The development of severe epilepsy and cognitive decline in children carrying KCNQ2 mutations can be related to a dominant-negative reduction of the resulting potassium current at subthreshold membrane potentials PMID: 24318194
- Kv7.2/7.3 channels increase action potential amplitude in neocortical myelinated axons. PMID: 24599470
- This report on 3 new cases of KCNQ2 encephalopathy diagnosed in the neonatal period and studied with continuous video-EEG recording. We describe a distinct electroclinical phenotype and report on efficacy of antiepileptic drug (AED) therapies. PMID: 24371303
- This study confirms that KCNQ2 is frequently mutated de novo in neonatal onset epileptic encephalopathy. PMID: 23692823
- KCNQ2 mutations cause approximately 13% of unexplained neonatal epileptic encephalopathy. Patients present with a wide spectrum of severity. PMID: 24107868
- A medium-throughput assay reliably detects changes in the biophysical properties of three classes of KCNQ2/3 channels and peak current amplitude and therefore may serve as a reliable assay to evaluate KCNQ2/3 openers and blockers. PMID: 23002961
- CaM can bridge two binding domains, anchoring helix A of one subunit to helix B of another subunit, in this way influencing the function of Kv7.2 channels. PMID: 23203804
- This study demonistrated that early onset epileptic encephalopathies caused by KCNQ2 mutation. PMID: 23621294
- the single KCNQ channel in Drosophila (dKCNQ) has similar electrophysiological properties to neuronal KCNQ2/3 PMID: 23209695
- This study demonistrated that a KCNQ2 mutation in an Emirati family with benign familial neonatal seizures type 1. PMID: 23290024
- This study demonistrated that benign neonatal sleep myoclonus can show autosomal dominant inheritance but not allelic to KCNQ2. PMID: 22447848
- Genotype-phenotype correlations in neonatal epilepsies caused by mutations in the voltage sensor of K(v)7.2 potassium channel subunits. PMID: 23440208
- Occurrence of afebrile seizures during follow-up is associated with KCNQ2 mutations and may represent a predictive factor. PMID: 23360469
- We report here a girl with benign neonatal convulsions followed by BECTS, for whom a mutation of KCNQ2 was identified. PMID: 22884718
- Subclinical dysfunction of Kv7.2 in peripheral axons can be reliably detected non-invasively in adulthood; related alterations in neuronal excitability may contribute to epilepsy associated with KCNQ2 mutations. PMID: 23065794
- KCNQ2 mutations can present with a neonatal onset multifocal myoclonus-like dyskinesia PMID: 22169383
- the Kv7.2-Kv7.3 heteromer assembles as a tetramer with a predominantly 2:2 subunit stoichiometry and with a random subunit arrangement. PMID: 22334706
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Seizures, benign familial neonatal 1 (BFNS1); Epileptic encephalopathy, early infantile, 7 (EIEE7)
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:Potassium channel family, KQT (TC 1.A.1.15) subfamily, Kv7.2/KCNQ2 sub-subfamily
-
组织特异性:In adult and fetal brain. Highly expressed in areas containing neuronal cell bodies, low in spinal chord and corpus callosum. Isoform 2 is preferentially expressed in differentiated neurons. Isoform 6 is prominent in fetal brain, undifferentiated neurobla
-
数据库链接:
Most popular with customers
-
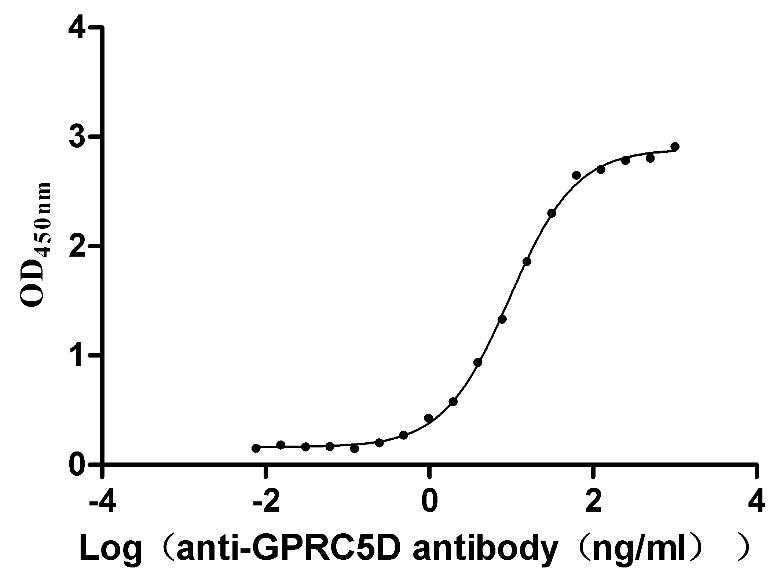
Recombinant Human G-protein coupled receptor family C group 5 member D (GPRC5D)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
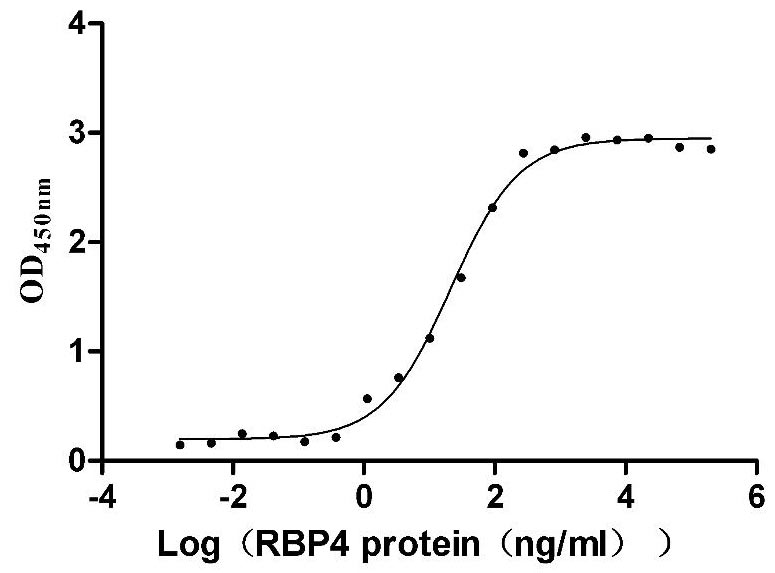
Recombinant Mouse Transthyretin (Ttr) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
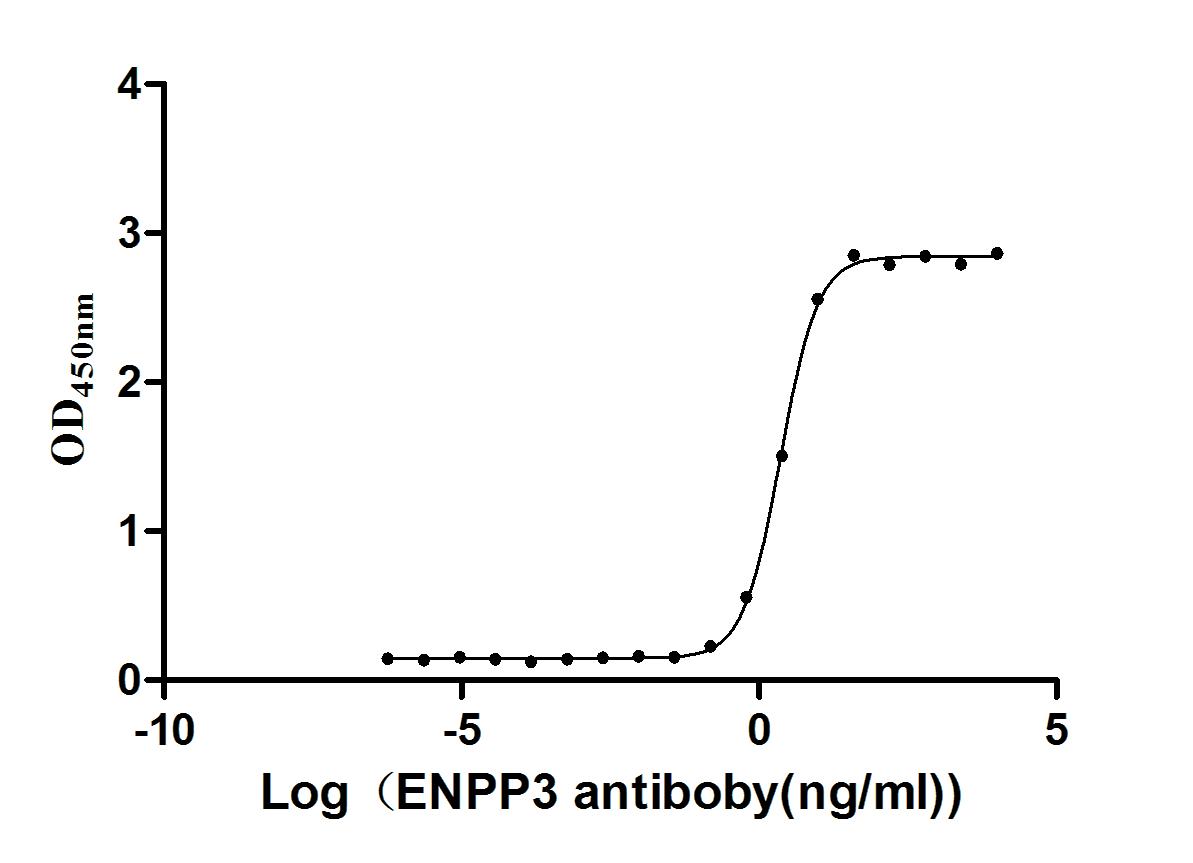
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
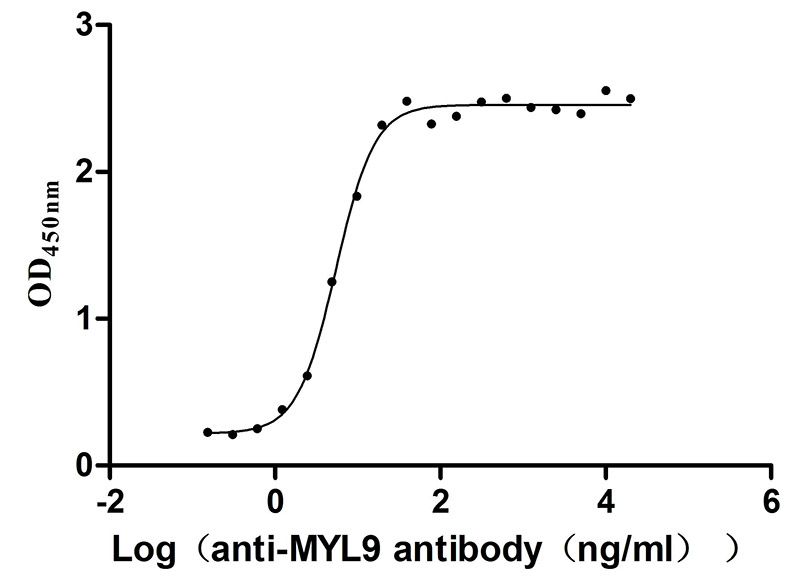
Recombinant Human Myosin regulatory light polypeptide 9 (MYL9) (Active)
Express system: Yeast
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Mouse Cytotoxic and regulatory T-cell molecule (Crtam), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human Kidney-associated antigen 1(KAAG1) (Active)
Express system: E.coli
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor UFO(AXL),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)