Recombinant Human Nuclear factor of activated T-cells 5 (NFAT5), partial
-
中文名称:人NFAT5重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP015744HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人NFAT5重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP015744HU
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人NFAT5重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP015744HU-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人NFAT5重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP015744HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人NFAT5重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP015744HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Glutamine rich protein H65; KIAA0827; NF AT5; NF-AT5; NFAT 5; NFAT L1; NFAT like protein 1; NFAT5; NFAT5_HUMAN; NFATL 1; NFATL1; NFATZ; Nuclear factor of activated T cells 5; Nuclear factor of activated T cells 5 tonicity responsive; Nuclear factor of activated T cells; Nuclear factor of activated T-cells 5; OREBP; Osmotic response element binding protein; T cell transcription factor NFAT 5; T cell transcription factor NFAT5; T-cell transcription factor NFAT5; TonE binding protein; TonE-binding protein; TonEBP; Tonicity responsive enhancer binding protein; Tonicity-responsive enhancer-binding protein
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Transcription factor involved, among others, in the transcriptional regulation of osmoprotective and inflammatory genes. Mediates the transcriptional response to hypertonicity. Positively regulates the transcription of LCN2 and S100A4 genes; optimal transactivation of these genes requires the presence of DDX5/DDX17. Binds the DNA consensus sequence 5'-[ACT][AG]TGGAAA[CAT]A[TA][ATC][CA][ATG][GT][GAC][CG][CT]-3'.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Results show that higher levels of NFAT5 expression predict a good prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), suggesting that NFAT5 is a potential tumor-suppressing gene, and verify that NFAT5 promotes hepatoma cell apoptosis and inhibits cell growth in vitro. Also, HBV inhibits NFAT5 expression by inducing hypermethylation of the AP1-binding site in the NFAT5 promoter. PMID: 29052520
- the NFAT5 pathway was involved in the regulation of biomechanical stretch-induced human arterial smooth muscle cell (HUASMC) proliferation, inflammation, and migration. Stretch promoted the expression of NFAT5 in human arterial smooth muscle cells and regulated through activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase under these conditions PMID: 28840417
- TonEBP suppresses M2 phenotype via downregulation of the IL-10 in M1 macrophages. PMID: 27160066
- In addition to finding many proteins already known to associate with NFAT5, many new ones whose function suggest novel aspects of NFAT5 regulation, interaction, and function, were also found. PMID: 27764768
- The data suggest that in addition to calcium signaling and activation of inflammatory enzymes, autocrine/paracrine purinergic signaling contributes to the stimulatory effect of hyperosmotic stress on the expression of the NFAT5 gene in retinal pigment epithelial cells. PMID: 28356704
- NFAT5-mediated expression of CACNA1C is evolutionarily conserved. NFAT5-mediated CACNA1C expression is critical for cardiac electrophysiological development and maturation. PMID: 27368804
- Data suggest that protease 2A of CVB3 exhibits substrate specificity that includes human/mouse NFAT5 in cardiomyocytes; NFAT5 inhibits CVB3 replication via mechanism that involves iNOS; anti-CVB3 activity of NFAT5 is impaired during CVB3 infection due to protease 2A-mediated cleavage of NFAT5. (CVB3 = Coxsackievirus 3; NFAT5 = tonicity-responsive nuclear factor of activated T-cells 5; iNOS = nitric oxide synthase type II) PMID: 29220410
- TonEBP expression correlated with canonical osmoregulatory targets TauT/SLC6A6, SMIT/SLC5A3, and AR/AKR1B1, supporting in vitro findings that the inflammatory milieu during IDD does not interfere with TonEBP osmoregulation. In summary, whereas TonEBP participates in the proinflammatory response to TNF-alpha PMID: 28842479
- results provide evidence that NFAT5 expression in macrophages enhances chronic arthritis by conferring apoptotic resistance to activated macrophages. PMID: 28192374
- genetic variation in NFAT5 expression and function in the central nervous system may affect the regulation of systemic water balance PMID: 28360221
- The hyperosmotic AR gene expression was dependent on activation of metalloproteinases, autocrine/paracrine TGF-beta signaling, activation of p38 MAPK, ERK1/2, and PI3K signal transduction pathways, and the transcriptional activity of NFAT5. PMID: 27628063
- Conclusion. miR-20b acts as a tumor suppressor in the development of thymoma and thymoma-associated myasthenia gravis. The tumor suppressive function of miR-20b in thymoma could be due to its inhibition of NFAT signaling by repression of NFAT5 and CAMTA1 expression. PMID: 27833920
- The hyperosmotic, but not the hypoxic, PlGF gene expression was in part mediated by NFAT5. PMID: 27230578
- Proteins associated with and binding NH2-terminal region of NFAT5.NUP160 and NUP205 contribute to regulation of NFAT5 transcriptional activity PMID: 26757802
- Our data demonstrates the involvement of TonEBP in the mechanisms responsible for osmoadaptation to hyperosmolar stress in retinal pigment epithelium cells. PMID: 26912969
- Additionally, in peritoneal dialysis the cells of the peritoneal cavity are repeatedly exposed to a rise and fall in osmotic concentrations. Here we review the current information about NFAT5 in uremic patients and patients on peritoneal dialysis. PMID: 26495302
- Results suggest that the NFAT5 gene, which is upregulated a few hours after cocaine exposure, may be involved in the genetic predisposition to cocaine dependence. PMID: 26506053
- NFAT5 pathway activation might have a relevant role in inflammatory breast cancer pathogenesis PMID: 25928084
- Real-time PCR and Western blot analysis confirmed up-regulation of NFAT5 mRNA and NFAT5 nuclear content in human preeclamptic placentas PMID: 25995271
- These results indicate that NFAT5 plays important roles in proliferation and migration of human lung adenocarcinoma cells through regulating AQP5 expression, providing a new therapeutic option for lung adenocarcinoma therapy. PMID: 26299924
- The hyperosmotic induction of AQP5 and VEGF in retinal pigment epithelial cells was in part dependent on activation of NFAT5. PMID: 25878490
- Upregulation of NFAT5 in peritoneal dialysis patients is associated with NFkappaB induction, potentially resulting in the recruitment of macrophages PMID: 25834072
- NFAT5 participates in the regulation of intestinal homeostasis via the suppression of mTORC1/Notch signaling pathway. PMID: 25057011
- PKC-alpha contributes to high NaCl-dependent activation of NFAT5 through ERK1/2. PMID: 25391900
- Data indicate that nuclear factor of activated T cells 5 (NFAT5) is a direct target of miR-568. PMID: 24355664
- these data support a novel function of the XO-NFAT5 axis in macrophage activation and TLR-induced arthritis PMID: 25044064
- Suggest that biomechanical stretch is sufficient to activate NFAT5 both in native and cultured VSMCs where it regulates the expression of tenascin-C. PMID: 24614757
- NFAT5 regulation of intestinal cell differentiation may be through inhibition of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. PMID: 23764852
- Nfat5 may be involved in regulating chondrogenic differentiation of these cells under both normal and increased osmolarities and might regulate chondrogenic differentiation through influencing early Sox9 expression PMID: 23219947
- It was concluded that specific DNA binding of NFAT5 contributes to its nuclear localization, by mechanisms as yet undetermined, but independent of ones previously described. PMID: 22992674
- Non-invasive imaging of nuclear factor of activated T-cell 5 (NFAT5) activation follows middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) in NFAT5-luciferase-expressing mice. PMID: 21749466
- NFAT5 is induced by hypoxia and could be a protective factor against ischemic damage. PMID: 22768306
- NFAT5 contributes to osmolality-induced MCP-1 expression in mesothelial cells PMID: 22619484
- The nuclear transport of NFAT5a involves reversible palmitoylation. PMID: 22071693
- the innate immune response to MTb infection induces NFAT5 gene and protein expression, and NFAT5 plays a crucial role in MTb regulation of HIV-1 replication via a direct interaction with the viral promoter. PMID: 22496647
- These data indicate that NS5A modulates Hsp72 via NFAT5 and reactive oxygen species activation for hepatitis C virus propagation. PMID: 22497815
- These results suggested that TonEBP played an important role in the epithelial cells of renal proximal tubule upon hypertonic stress by enhancing AAD expression, which could promote dopamine secretion to negative regulate Na+/K+-ATPase activity. PMID: 21982764
- Compared with control group, the levels of OREBP, HSP70-2 and MUC5AC in supernatant significantly increased after HBE16 cells were exposed to hypertonic media. PMID: 21418859
- Identify NFAT5 as a novel regulator of vascular smooth muscle cell phenotypic modulation. PMID: 21757659
- NF-AT5 regulates synovial proliferation and angiogenesis in chronic arthritis. PMID: 21717420
- this study demonstrates that hyperosmotic stress induces S100A4 through NFAT5, and Src and chromatin remodeling are involved. PMID: 21289293
- High NaCl-induced increase of the overall abundance of TonEBP/OREBP, by itself, eventually raises its effective level in the nucleus, but its rapid CDK5-dependent nuclear localization accelerates the process. PMID: 21209322
- These findings reveal a novel role for TonEBP and Akt in NF-kappaB activation on the onset of hypertonic challenge. PMID: 20685965
- NFAT5-null mice have constitutive, pronounced hypernatremia and suffer severe immunodeficiency with T cell lymphopenia, altered CD8 naive/memory homeostasis, and inability to reject allogeneic tumors. PMID: 21037089
- c-Abl is the kinase responsible for high NaCl-induced phosphorylation of TonEBP/OREBP-Y143 PMID: 20585028
- TonEBP/OREBP is extensively regulated by phosphatases, including SHP-1, whose inhibition by high NaCl increases phosphorylation of TonEBP/OREBP at Y143, contributing to the nuclear localization and activation of TonEBP/OREBP PMID: 20351292
- The loss of nucleosome(s) was found to be initiated by an OREBP-independent mechanism, but was significantly potentiated in the presence of OREBP. PMID: 20041176
- TonEBP/OREBP becomes phosphorylated at Y143, resulting in binding of PLC-gamma1 to that site, which contributes to TonEBP/OREBP transcriptional activity. PMID: 20080774
- NFAT5 exclusion from mitotic chromatin resets its nucleo-cytoplasmic distribution in interphase PMID: 19750013
- present in placenta at RNA and protein levels PMID: 19886771
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus. Cytoplasm.
-
组织特异性:Widely expressed, with highest levels in skeletal muscle, brain, heart and peripheral blood leukocytes.
-
数据库链接:
Most popular with customers
-
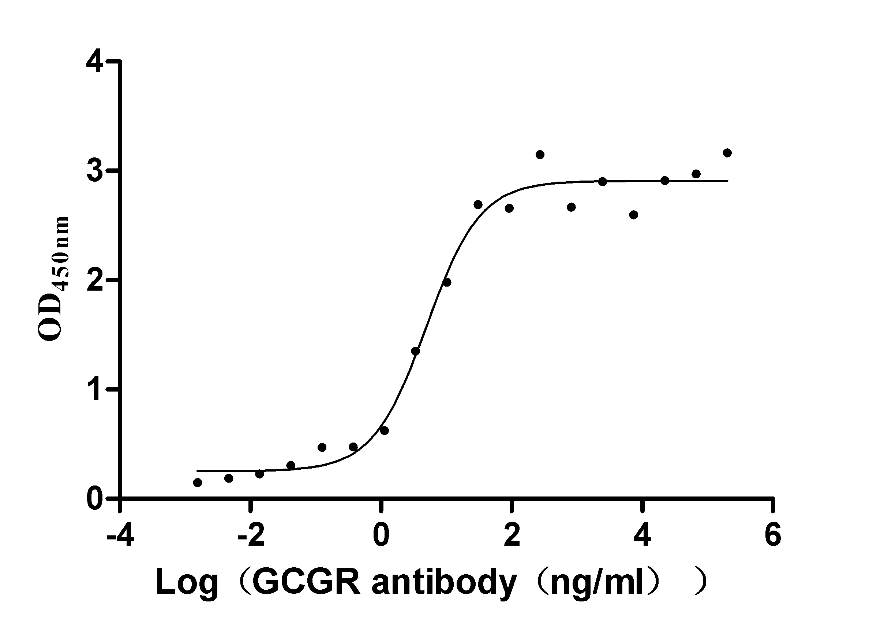
Recombinant Human Glucagon receptor (GCGR), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
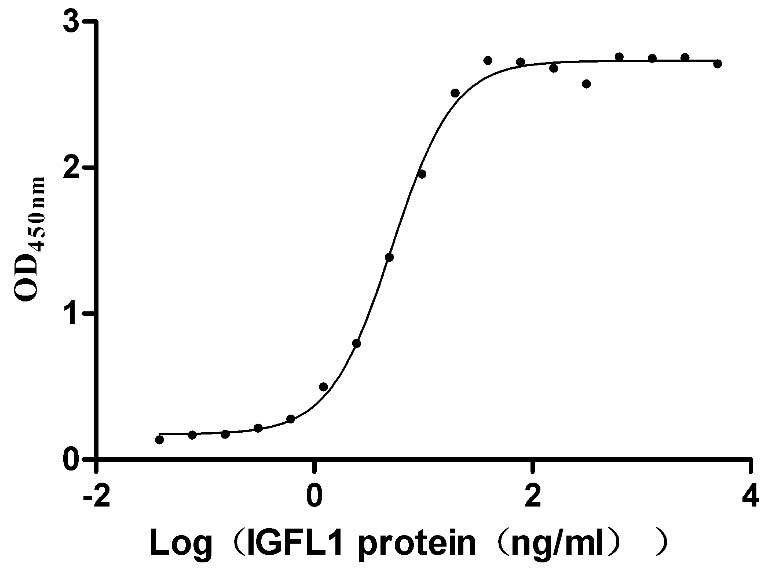
Recombinant Human IGF-like family receptor 1 (IGFLR1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
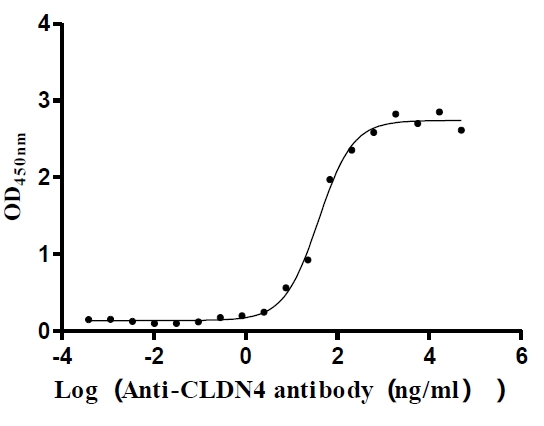
Recombinant Human Claudin-4 (CLDN4)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
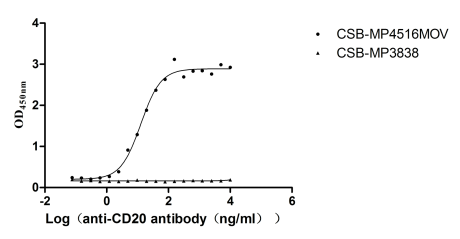
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Membrane spanning 4-domains A1 (MS4A1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
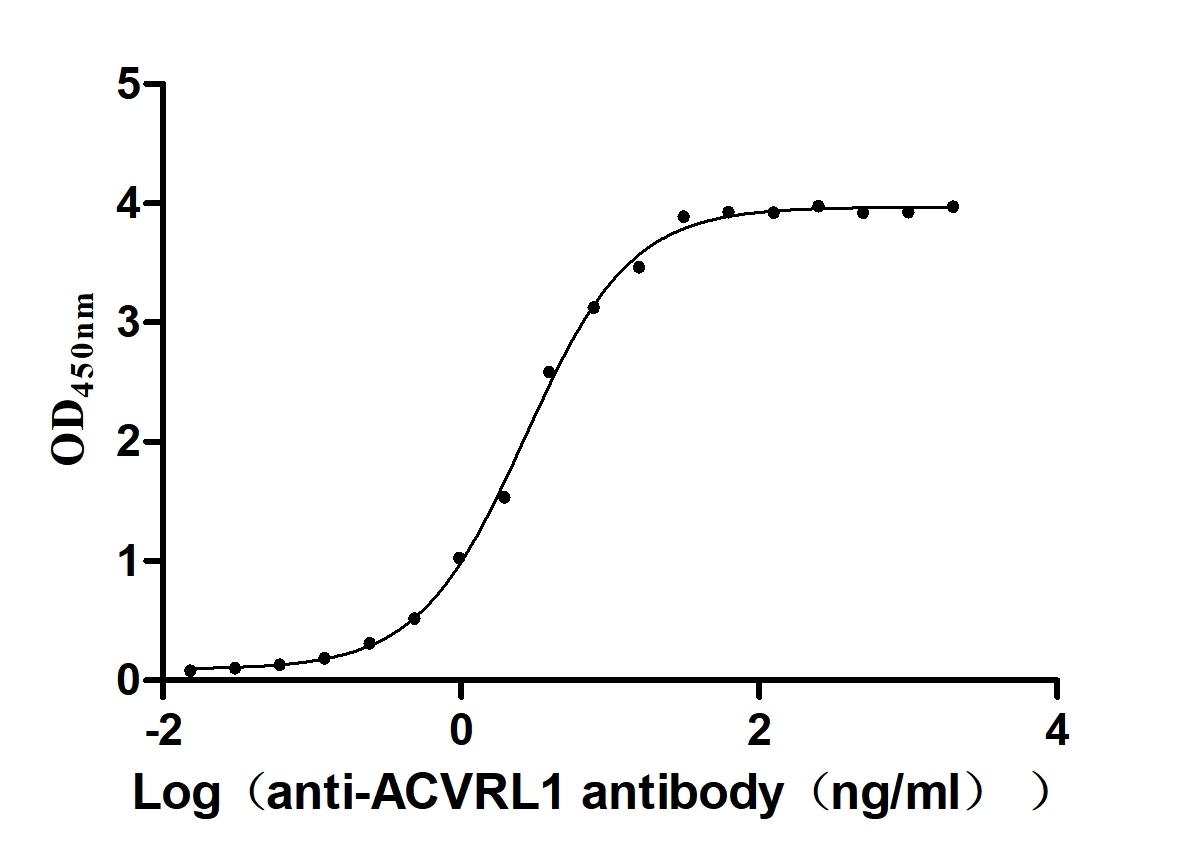
Recombinant Human Serine/threonine-protein kinase receptor R3 (ACVRL1), partial (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
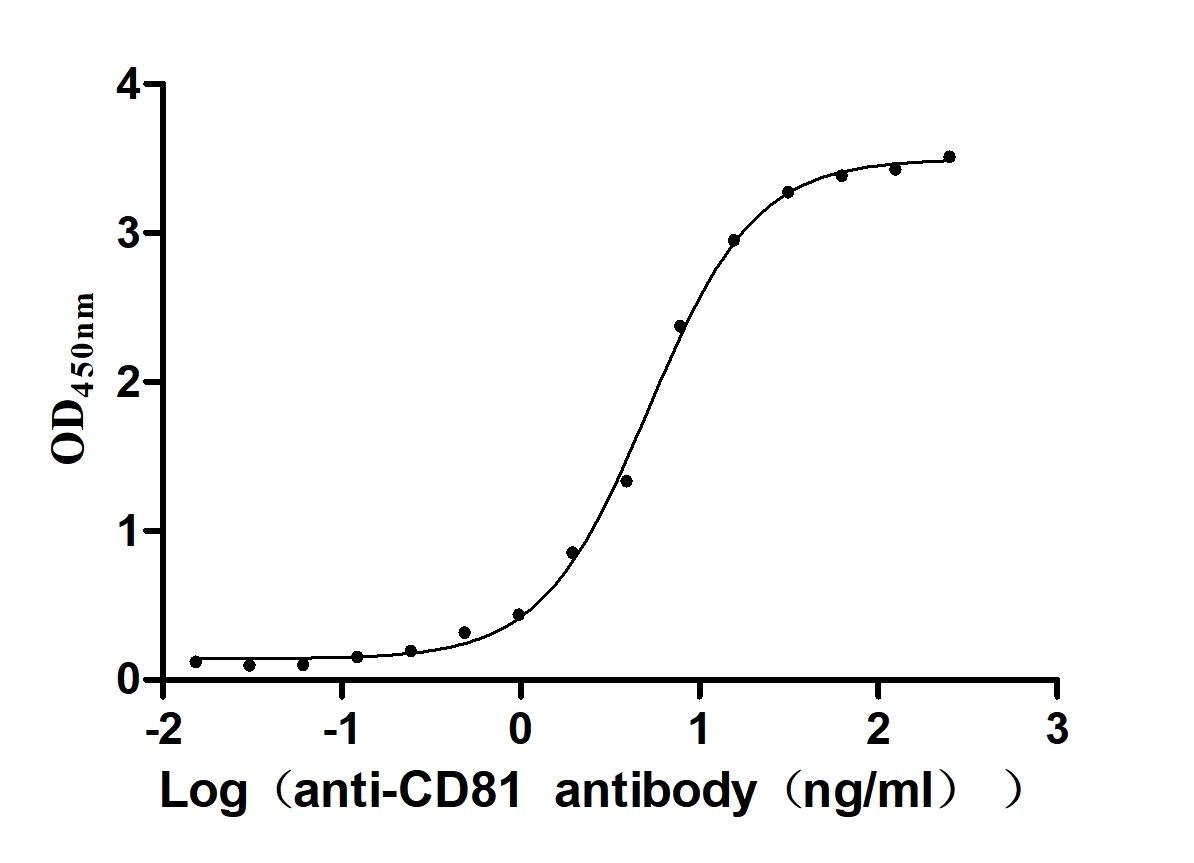
Recombinant Human CD81 antigen (CD81), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
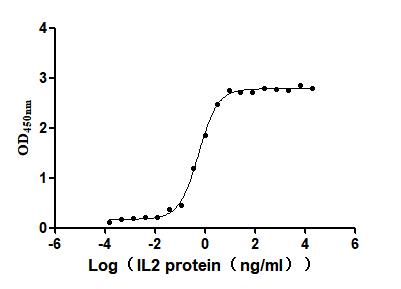
Recombinant Human Interleukin-2 (IL2) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
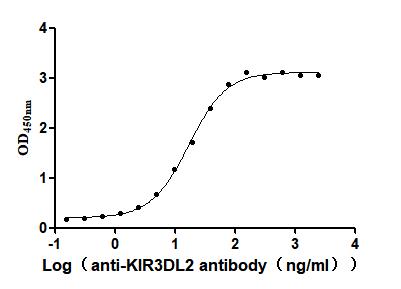
Recombinant Human Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 3DL2 (KIR3DL2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)