Recombinant Human Multidrug resistance-associated protein 6 (ABCC6), partial
-
中文名称:Recombinant Human Multidrug resistance-associated protein 6(ABCC6) ,partial
-
货号:CSB-YP001065HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Human Multidrug resistance-associated protein 6(ABCC6) ,partial
-
货号:CSB-EP001065HU
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Human Multidrug resistance-associated protein 6(ABCC6) ,partial
-
货号:CSB-EP001065HU-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Human Multidrug resistance-associated protein 6(ABCC6) ,partial
-
货号:CSB-BP001065HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Human Multidrug resistance-associated protein 6(ABCC6) ,partial
-
货号:CSB-MP001065HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:ABCC6
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:ABC34; Abcc6; Anthracycline resistance-associated protein; ARA; ATP binding cassette sub family C (CFTR/MRP) member 6; ATP binding cassette sub family C member 6; ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 6; EST349056; GACI2; MLP1; MOAT E; MOAT-E; MOATE; MRP 6; MRP6; MRP6_HUMAN; Multi-specific organic anion transporter E; Multidrug resistance associated protein 6; Multidrug resistance-associated protein 6; Multidrug resistance-associated protein 6, URG7 protein; multispecific organic anion transporter E; PXE; PXE1; URG7; URG7 protein
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:ATP-dependent transporter of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) family that actively extrudes physiological compounds, and xenobiotics from cells. Mediates ATP-dependent transport of glutathione conjugates such as leukotriene-c4 (LTC4) and N-ethylmaleimide S-glutathione (NEM-GS) (in vitro), and an anionic cyclopentapeptide endothelin antagonist, BQ-123. Does not appear to actively transport drugs outside the cell. Confers low levels of cellular resistance to etoposide, teniposide, anthracyclines and cisplatin.; Mediates the release of nucleoside triphosphates, predominantly ATP, into the circulation, where it is rapidly converted into AMP and the mineralization inhibitor inorganic pyrophosphate (PPi) by the ecto-enzyme ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase phosphodiesterase 1 (ENPP1), therefore playing a role in PPi homeostasis.; Inhibits TNF-alpha-mediated apoptosis through blocking one or more caspases.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Serum levels of MRP8/MRP14 and MRP6 were up-regulated in patients with Graves' disease (GD) and Hashimoto's thyroiditis (HT). In addition, mRNA expression of MRP proteins in PBMCs and the thyroid gland was markedly elevated in these patients. PMID: 29656212
- High URG7 reduces the ER stress by decreasing the amount of unfolded proteins, by increasing both the total protein ubiquitination and the AKT activation and reducing Caspase 3 activation. PMID: 29704455
- Two compound heterozygous ABCC6 loss-of-function mutations, c.4182_4182delG (p.Lys1394Asnfs*9) and c.2900G > A (p.Trp967*), were found PMID: 29709427
- Genetic analysis revealed three nonsense, four frame-shift, one exon deletion and 13 missense mutations in 73 Japanese pseudoxanthoma elasticum patients. PMID: 28186352
- in a French cohort with pseudoxanthoma elasticum, study identified 538 mutational events with 142 distinct variants, of which 66 were novel PMID: 28102862
- ABCC6 overexpression may also contribute to nilotinib and dasatinib resistance in vitro. With nilotinib and dasatinib now front line therapy options in the treatment of CML, concomitant administration of ABCC6 inhibitors may present an attractive option to enhance TKI efficacy PMID: 29385210
- Using an integrated pathway-based approach, we identified polymorphisms in ABCC6, ABCB1 and CYP2C8 associated with overall survival. These associations were replicated in a large independent cohort, highlighting the importance of pharmacokinetic genes as prognostic markers in Ewing sarcoma PMID: 27287205
- ABCC6 knockdown HepG2 cells show: 1) intracellular reductive stress; 2) cell cycle arrest in G1 phase; 3) upregulation of p21Cip p53 independent; and 4) downregulation of lamin A/C. the absence of ABCC6 profoundly changes the HepG2 phenotype, suggesting that Pseudoxanthoma elasticum syndrome is a complex metabolic disease that is not exclusively related to the absence of pyrophosphate in the bloodstream. PMID: 28536638
- ABCC6 deficiency can be rescued by 4-phenylbutyrate therapy in a mouse model expressing human variants PMID: 27826008
- Biochemical and cell biological analyses demonstrate these mutations influence multiple steps in the biosynthetic pathway, minimally altering local domain structure but adversely impacting ABCC6 assembly and trafficking. The differential impacts on local and global protein structure are consistent with hierarchical folding and assembly of ABCC6. PMID: 27994049
- The results suggest that a transmembrane domain is not required for transport function and that a cytosolic loop maintains ABCC6 in a targeting-competent state for the basolateral membrane and might be involved in regulating the nucleotide binding domains. PMID: 26942607
- The results of this study showed that mtDNA(atp6) variants were actively involved in schizophrenia in some families with maternal inheritance of this PMID: 26822593
- Pseudoxanthoma elasticum is due to mutation of the ABCC6 gene on chromosome 16. PMID: 26564082
- Membrane insertion and topology of the amino-terminal domain TMD0 of multidrug-resistance associated protein 6 PMID: 26545497
- A direct relationship between reduced ABCC6 levels and the expression of pro-mineralization genes in hepatocytes. PMID: 25169437
- Minimal rescue of the morpholino-induced phenotype was achieved with eight of the nine mutant human ABCC6 mRNAs tested, implying pathogenicity. This study demonstrates that the Chinese PXE population harbors unique ABCC6 mutations. PMID: 25615550
- Virtual screening expands this possibility to explore more compounds that can interact with ABCC6, and may aid in understanding the mechanisms leading to pseudoxanthoma elasticum PMID: 25062064
- The increase in ABCC6 expression accompanied by the induction of cholesterol biosynthesis supposes a functional role for ABCC6 in human lipoprotein and cholesterol homeostasis. PMID: 25064003
- ABCC6 gene is important to determine the genotype of patients diagnosed with pseudoxanthoma elasticum. PMID: 23675997
- Hepatic ABCC6-mediated ATP release is the main source of circulating PPi, revealing an unanticipated role of the liver in systemic PPi homeostasis. PMID: 24969777
- This study describes the URG7 expression in E.coli and a structural study of it by using circular dichroism and fluorescence spectroscopy. PMID: 24555429
- This study showed that the expression of ABCC6 in liver is an important determinant of calcification in cardiac tissues in response to injuries PMID: 24479134
- Case Report:ABCC6 mutations in pseudoxanthoma elasticum families from different ethnic backgrounds. PMID: 23572048
- analysis of pseudoxanthoma elasticum-causing missense mutants of ABCC6, and the correction of their mislocalization by chemical chaperone 4-phenylbutyrate PMID: 24352041
- Our findings provide additional evidence that the ABCC6 gene product inhibits calcification under physiologic conditions and confirm a second locus for generalized arterial calcification of infancy. PMID: 24008425
- ABCC6 prevents ectopic mineralization seen in pseudoxanthoma elasticum by inducing cellular nucleotide release. PMID: 24277820
- nonsense mutations in the ABCC6 gene have a role in pseudoxanthoma elasticum and may be suppressed by PTC124 PMID: 23702584
- The virus-mediated anti-apoptotic effect of URG7 could arise from the C-terminal cytosolic tail binding a pro-apoptotic signaling factor and retaining it to the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. PMID: 23912081
- ABCC6 is in the basolateral membrane, mediating the sinusoidal efflux of a metabolite from the hepatocytes to systemic circulation. PMID: 23625951
- Mutations in the underlying disease genes ENPP1, ABCC6, NT5E, and SLC20A2, respectively, lead to arterial media calcification. PMID: 23122642
- The expression pattern of ABCC6P2 in 39 human tissues was highly similar to that of ABCC6 and ABCC6P1 suggesting similar regulatory mechanisms for ABCC6 and its pseudogenes. PMID: 22873774
- We identified three DNase I hypersensitive sites (HSs) specific to cell lines expressing ABCC6. PMID: 22763786
- ABCC6 mutations accounted for a significant subset of generalized arterial calcification of infancy patients, and ENPP1 mutations could also be associated with pseudoxanthoma elasticum lesions in school-aged children. PMID: 22209248
- ABCC6 does not transport adenosine. PMID: 21813308
- The heterozygosity for ABCC6 R1141X did not associate with risk of ischemic heart disease, myocardial infarction, ischemic cerebrovascular disease, or ischemic stroke. PMID: 21831958
- These results show that VK3GS is not the essential metabolite transported by ABCC6 from the liver and preventing the symptoms of pseudoxanthoma elasticum. PMID: 22056557
- The nucleotide-binding domain 2 of the human transporter protein MRP6. PMID: 21748403
- Angioid streaks in pseudoxanthoma elasticum are associated with the p.R1268Q mutation in the ABCC6 gene. PMID: 21179111
- regulatory pathway of ABCC6 expression showing that the ERK1/2-HNF4alpha axis has an important role in regulation of the gene PMID: 20463007
- The R1141X loss-of-function mutation of the ABCC6 gene is a strong genetic risk factor for coronary artery disease. PMID: 19929409
- Nine novel deletion mutations in ABCC6 cause pseudoxanthoma elasticum. PMID: 20075945
- The classic forms of pseudoxanthoma elasticum are due to loss-of-function mutations in the ABCC6 gene, which encodes ABCC6, a transmembrane efflux transporter expressed primarily in the liver PMID: 20032990
- Studies show that individuals homozygous for the c.3775delT mutation in the ABCC6 gene can have a highly variable phenotype. PMID: 19904211
- Loss of ATP-dependent transport activity in pseudoxanthoma elasticum-associated mutants of human ABCC6 (MRP6). PMID: 11880368
- Presence of the R1141X mutation in the ABCC6 gene is associated with a sharply increased risk of premature coronary artery disease PMID: 12176944
- We suggest that the severity of the Pseudoxanthoma elasticum phenotype is not directly correlated with the level of ABCC6/MRP6 activity. PMID: 12673275
- A specific founder effect for the R1141X mutation exists in Dutch patients with PXE (pseudoxanthoma elasticum). PMID: 12714611
- Using linkage analysis and mutation detection techniques, mutations in the ABCC6 gene were recently implicated in the etiology of pseudoxanthoma elasticum. PMID: 12850230
- Asn15, which is located in the extracellular N-terminal region of human ABCC6, is the only N-glycosylation site in this protein. PMID: 12901863
- Twenty-three different mutations were identified, among which 11 were new, in Italian patients with pseudoxanthoma elasticum PMID: 15459974
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE); Arterial calcification of infancy, generalized, 2 (GACI2)
-
亚细胞定位:[Isoform 1]: Basolateral cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.; [Isoform 2]: Endoplasmic reticulum membrane; Single-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:ABC transporter superfamily, ABCC family, Conjugate transporter (TC 3.A.1.208) subfamily
-
组织特异性:Expressed in kidney and liver. Very low expression in other tissues.
-
数据库链接:
Most popular with customers
-
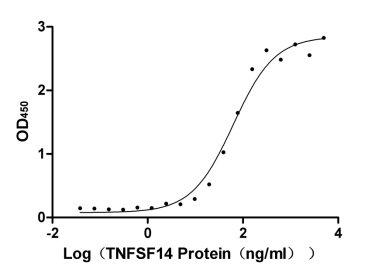
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 14 (TNFRSF14), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Semaphorin-4D (SEMA4D), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
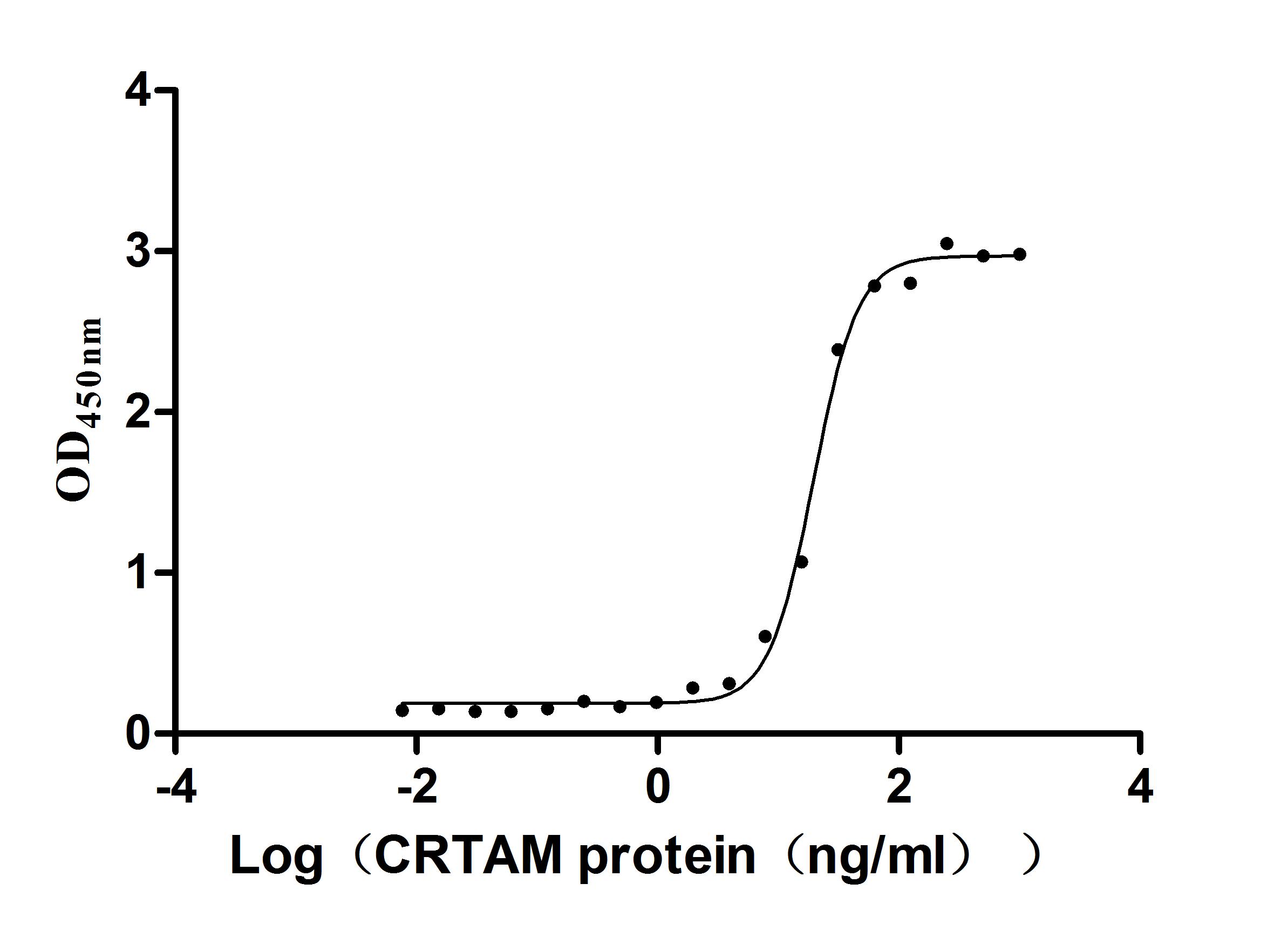
Recombinant Human Cell adhesion molecule 1 (CADM1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
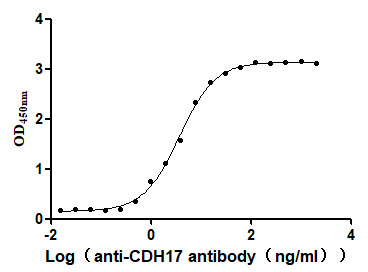
Recombinant Human Cadherin-17 (CDH17), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
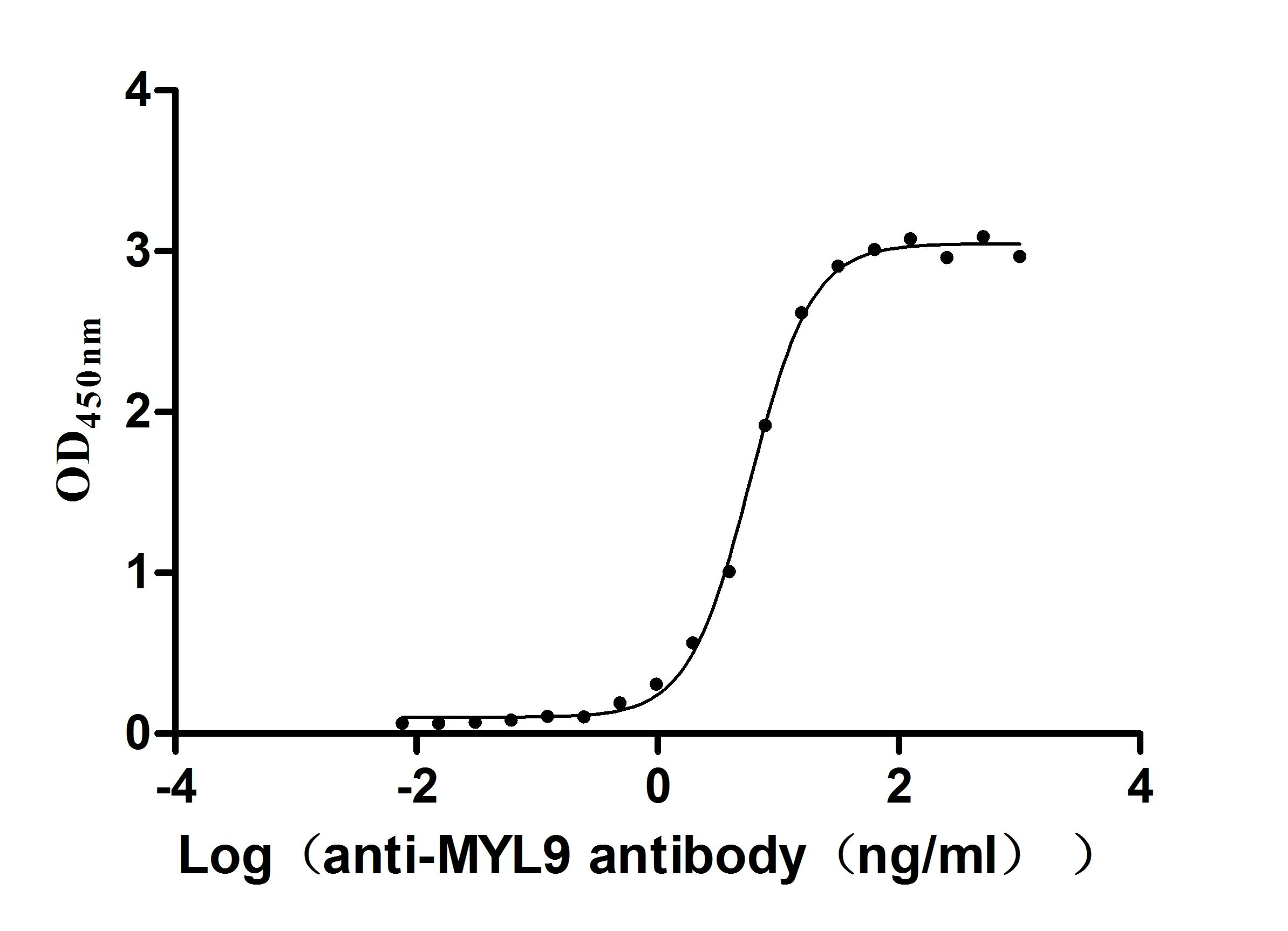
Recombinant Human Myosin regulatory light chain 12A (MYL12A) (Active)
Express system: E.coli
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
-
Recombinant Human Kidney-associated antigen 1(KAAG1) (Active)
Express system: E.coli
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)