Recombinant Human Dentin sialophosphoprotein (DSPP), partial
-
中文名称:人DSPP重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP007209HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人DSPP重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP007209HU
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人DSPP重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP007209HU-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人DSPP重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP007209HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人DSPP重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP007209HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
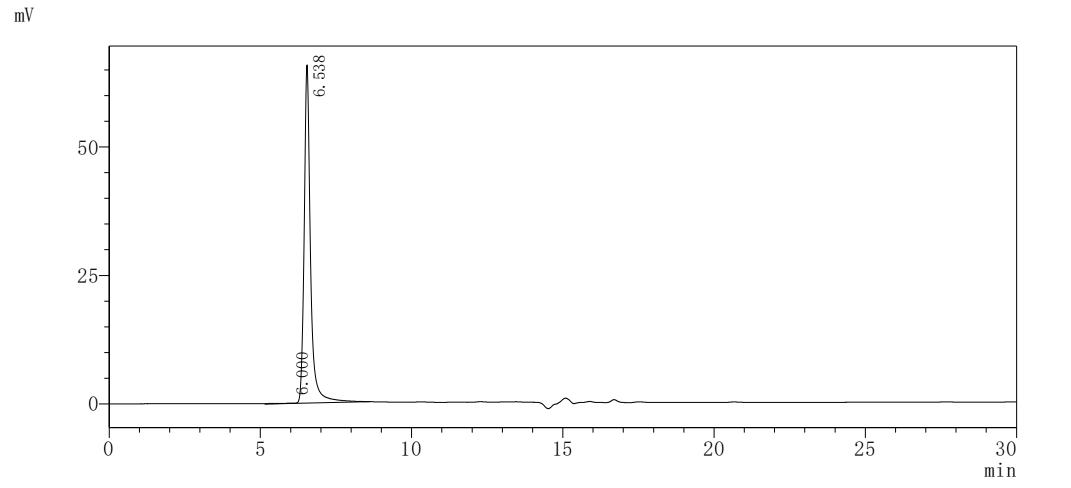
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:DSPP
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Dentin phosphophoryn; Dentin phosphoprotein; dentin phosphoryn; Dentin sialophosphoprotein; Dentin sialophosphoprotein precursor; Dentin sialoprotein; dentinogenesis imperfecta 1; DFNA39; DGI1; DMP3; DPP; DSP; Dspp; DSPP_HUMAN; DTDP2
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:DSP may be an important factor in dentinogenesis. DPP may bind high amount of calcium and facilitate initial mineralization of dentin matrix collagen as well as regulate the size and shape of the crystals.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Taken together, these findings indicate that knockdown of DSPP inhibits glioma cells migration and invasion, suggesting that targeting DSPP might be a potentially effective therapeutic strategy for treating glioma. PMID: 30309696
- Study provide evidence to suggest that DSPP may be involved in endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress mechanisms in oral squamous cell carcinoma, since its downregulation in OSC2 cells led to significant alterations in the levels of major ER stress-associated proteins, and subsequent collapse of the unfolded protein response system. PMID: 30015841
- mutations c.3085A > G and c.3087C > T resulted in p.N1029D and co-segregated with deafness phenotype in Chinese family PMID: 29741433
- The levels of DSPP silencing-induced downregulation differed amongst CSC markers, with ABCG2 and CD44 showing more pronounced downregulations. PMID: 30002682
- the transgenic expression of DPP significantly improved the dentin defects in Dspp-null mice. These data provide in vivo evidence that DPP may promote the deposition of hydroxyapatite crystals during the formation and mineralization of dentin, which is in agreement with the in vitro findings described in earlier reports. PMID: 29672573
- Data demonstrate for the first time that the dentin sialoprotein (DSP) domain acts as a ligand in a Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD)-independent manner and is involved in intracellular signaling via interacting with integrin beta6. The DSP domain regulates DSPP expression and odontoblast homeostasis via a positive feedback loop. PMID: 27430624
- This study expands the spectrum of DSPP variants, highlighting their associated phenotypic continuum. PMID: 27973701
- These data indicate that secretome derived from salivary gland cancer cells can influence the expression of two potential biomarkers of oral cancer-namely, bone sialoprotein (BSP) and dentin sialoprotein (DSP)-in normal salivary gland cells. PMID: 27881474
- DSPP-MMP20 pair may play a role in the normal turnover of cell surface proteins and/or repair of pericellular matrix proteins of the basement membranes in the metabolically active duct epithelial system of the nephrons. PMID: 27666430
- BMP2 and RUNX2 are expressed exclusively by osteoblasts whereas DSPP and LOXL2 are expressed exclusively by odontoblasts. (Review) PMID: 27784228
- A novel pathogenic splicing-mutation c.52-1G>A of DSPP is associated with dentinogenesis imperfecta shields type II. PMID: 26829730
- Adhesive and migratory effects of phosphophoryn are modulated by flanking peptides of the integrin binding motif. PMID: 25396425
- expression of MMP-20 and co-expression and potential interaction with DSPP in human major salivary gland tissues PMID: 25805840
- mutations of the DSP-PP P4 to P4' cleavage site can block, impair or accelerate dentin sialoprotein phosphophoryn cleavage, and suggest that its Bone morphogenic protein 1 cleavage site is conserved in order to regulate its cleavage efficiency PMID: 25158199
- Domain of dentine sialoprotein mediates proliferation and differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells. PMID: 24400037
- analysis of a mutation in DSPP causing dentinogenesis imperfecta and characterization of the mutational effect PMID: 23509818
- DSS domain of DPP functions as a novel cell-penetrating peptide, and these findings demonstrate new opportunities for intracellular delivery of therapeutic proteins and cell tracking in vivo. PMID: 23589294
- efficiency of dentin sialoprotein-phosphophoryn processing is affected by mutations both flanking and distant from the cleavage site PMID: 23297400
- A review of hereditary dentine diseases resulting from mutations in DSPP gene suggests that the localization of mutation in the sequence of the DSPP gene might result in a different phenotype due to the diverse cellular fate of the mutated protein. PMID: 22521702
- This study presents evidence of a shared underlying mechanism of capturing of normal DSPP by two different classes of DSPP mutations. PMID: 22392858
- DSPP, OPN, or MMP-9 expressions at histologically-negative surgical margins predict Oral squamous cell carcinoma recurrence with MMP-9 being the preferred predictor. PMID: 22410369
- The P17 residue of DSPP is a mutational hotspot in a Chinese family with Dentinogenesis Imperfecta type II. PMID: 22310900
- study concludes that enamel defects can be part of the dental phenotype caused by DSPP mutations, although DSPP is not critical for dental enamel formation PMID: 22243242
- Data shows all known DSPP mutations (except Y6D) cause nonsyndromic dentin dysplasia,DD-II, and dentinogenesis imperfecta, DGI II & III, by retention of mutant proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum with associated decreased secretion of normal DSPP. PMID: 22392858
- Data show that the novel dentin sialophosphoprotein (DSPP) mutation was considered as the causation of dentinogenesis imperfecta type II (DGI-II). PMID: 22125647
- predictions of exon 3 skipping in specific DSPP mutations have been validated; cryptic splicing donor site has been identified. possible insight into DSPP mutations in the pathogenesis and genotype-phenotype correlations of hereditary dentin defects. PMID: 21736673
- Results suggest that DSPP is regulated post-transcriptionally by mir32, mir885-5p and mir586 during odontoblast differentiation. PMID: 21687927
- Frameshift mutations in the part of the DSPP gene coding for DPP explain a significant part of inherited and isolated dentin diseases, i.e., dentin dysplasia type II and dentinogenesis imperfecta variants. PMID: 20949630
- DSPP gene mutation not only influences dentinogenesis but also affects early stage amelogenesis. PMID: 21029264
- Data identified novel single bp deletional DSPP mutations in three Korean families with DGI type II. PMID: 20618350
- This review of genetic studies demonstrates that mutations in, or knockout of the Dspp gene result in mineralization defects in dentin and/or bone. PMID: 20367116
- Data show there was a direct correlation between the degree of DSPP-silencing and suppression of MMP-2, MMP-3 and MMP-9. PMID: 21103065
- High dentin expression is associated with dental caries. PMID: 20802180
- Mutation analysis revealed mutation (c.53T>A, p.V18D, g.1192T>A) involving 2nd nucleotide of 1st codon within exon 3 of DSPP gene. This is 7th mutation in DSPP V18 residue. Only 1 other was shown as de novo mutation; it also affected V18 AA residue. PMID: 20121932
- Direct DNA sequencing identified a novel A-->G transition mutation adjacent to the donor splicing site within intron 3 in all affected individuals. PMID: 20146806
- A novel mutation in the first exon of the DSPP gene were found in all dentinogenesis imperfecta patients in a Chinese family. PMID: 19806576
- Transient DSPP expression was seen in the presecretory ameloblasts with continuous expression in the odontoblasts. PMID: 11856645
- there is a novel signaling function for phosphophoryn in cell differentiation beyond the hypothesized role of PP in biomineralization PMID: 15371433
- Dentin sialophosphoprotein expressed by transgenic presecretory ameloblasts contributes to the unique properties of the dentino-enamel junction. PMID: 16014627
- study shows for the first time that DSPP is ectopically expressed in human prostate cancer; expression of this SIBLING protein strongly correlates with conventional histopathological prognostic indicators of prostate cancer progression PMID: 16108038
- Mutational analyses identified no coding or intron junction sequence variations associated with affection status in DMP1, MEPE, or the DSP portion of DSPP. The defects in the permanent dentition were typically mild and consistent with DD-II. PMID: 16567553
- 2 mutation hotspots may be causative for multiple unrelated dentinogenesis imperfecta families with different clinical phenotypes PMID: 16920545
- mutation p.Pro17Ser causes type II dentinogenesis imperfecta in the Chinese family PMID: 17686168
- The results show high expression levels of DSPP in human tooth germs indicating that it may play an essential role for physiological and pathological events in tooth development. PMID: 18211748
- Data provide the first evidence that DPP mutations can cause hereditary dentin disorders and suggest that in-frame length variations and missense SNPs in DPP have no obvious pathogenetic effects on dentin formation. PMID: 18456718
- Within 9 dentin dysplasia (type II) and dentinogenesis imperfecta (type II and III) patient/families, 7 have 1 of 4 net -1 deletions within the a 2-kb coding repeat domain of the DSPP gene while the remaining 2 patients have splice-site mutations. PMID: 18521831
- The aim of this study was to perform phenotype analysis and dentin sialophosphoprotein (DSPP) mutational analysis on 3 Brazilian families diagnosed with dentinogenesis imperfecta type II. PMID: 18797159
- Identification of DSPP splice junction mutation (IVS2-6T>G) in a family with dentin dysplasia type II. Mutation is in 6th nucleotide from the end of intron 2, perfectly segregates with the disease phenotype. PMID: 19026876
- A novel -1 bp frameshift (c.3141delC) falls within the portion of the DSPP repeat domain previously associated solely with the DGI phenotype. This new frameshift mutation shows that overlapping DSPP mutations can give rise to either DGI or DD phenotypes. PMID: 19029076
- The heterozygous deletion mutation in DSPP contributed to the pathogenesis of dentinogenesis imperfecta type II. PMID: 19103209
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Deafness, autosomal dominant, 39, with dentinogenesis imperfecta 1 (DFNA39/DGI1); Dentinogenesis imperfecta, Shields type 2 (DGI2); Dentinogenesis imperfecta, Shields type 3 (DGI3); Dentin dysplasia 2 (DTDP2)
-
亚细胞定位:Secreted, extracellular space, extracellular matrix.
-
组织特异性:Expressed in teeth. DPP is synthesized by odontoblast and transiently expressed by pre-ameloblasts.
-
数据库链接:
Most popular with customers
-
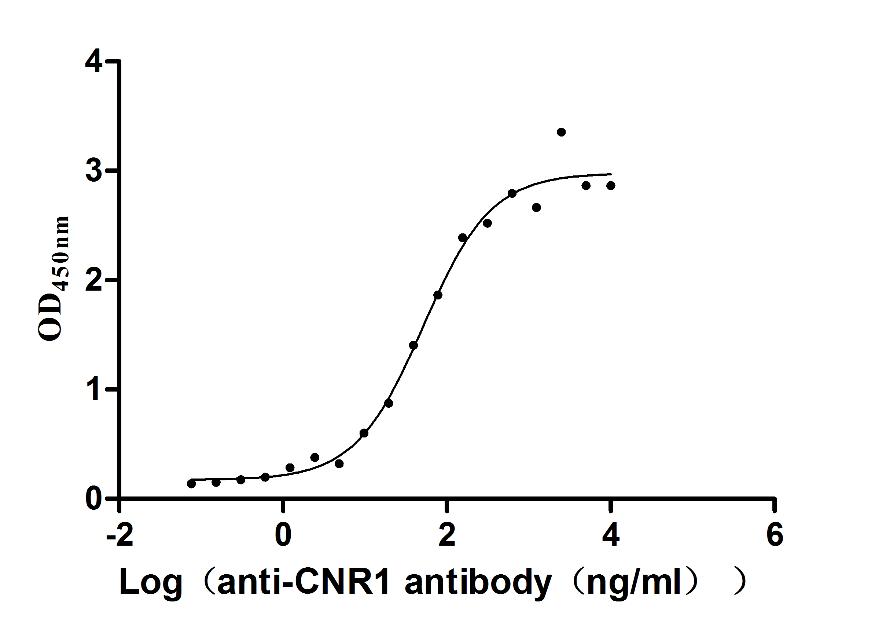
Recombinant Human Cannabinoid receptor 1 (CNR1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
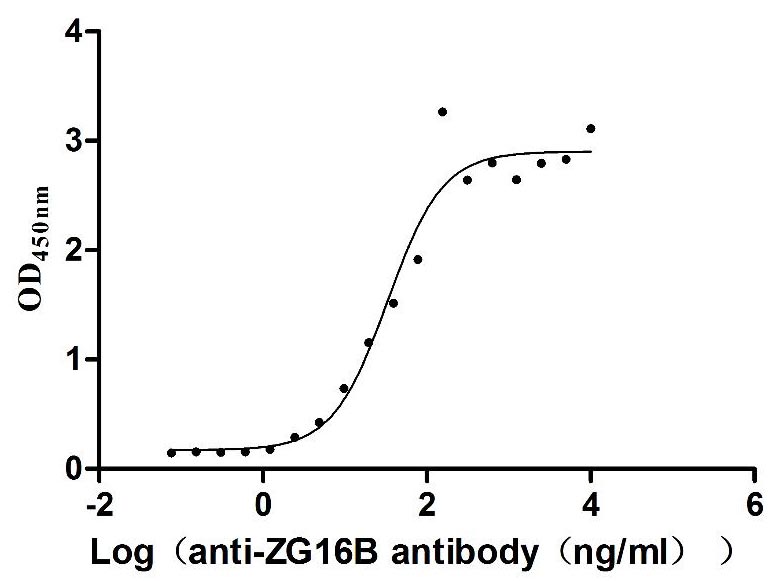
Recombinant Human Pancreatic adenocarcinoma up-regulated factor (ZG16B) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
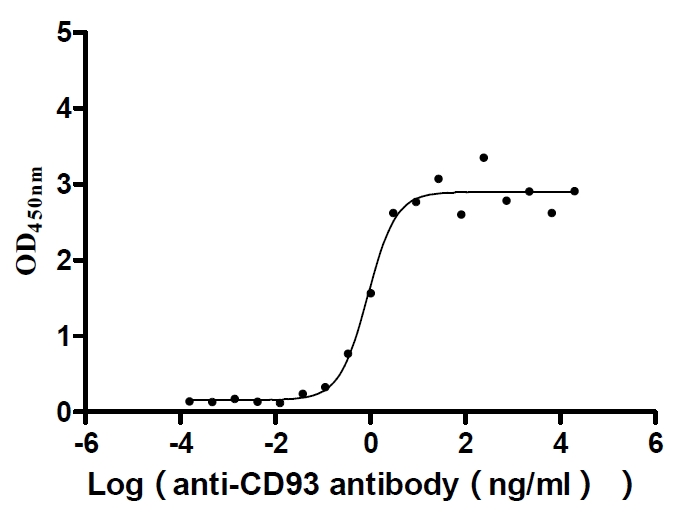
Recombinant Human Complement component C1q receptor (CD93), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
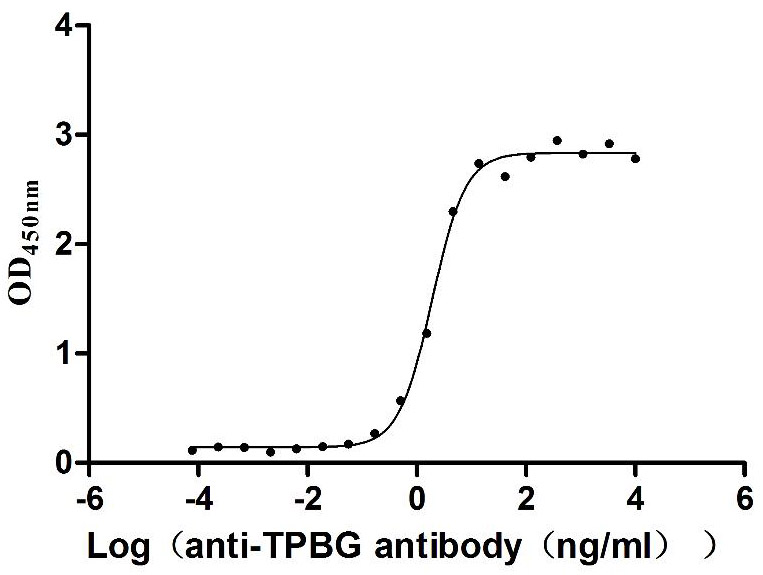
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Trophoblast glycoprotein (TPBG), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
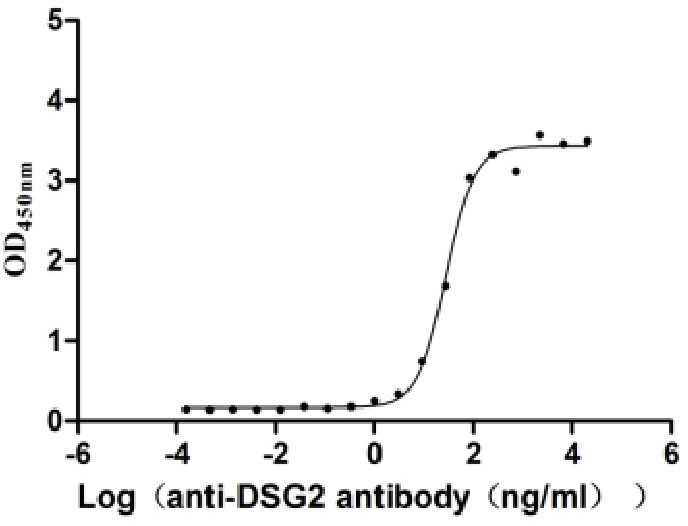
Recombinant Human Desmoglein-2 (DSG2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
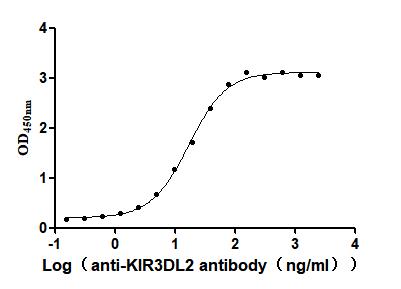
Recombinant Human Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 3DL2 (KIR3DL2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 9 (CCR9)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
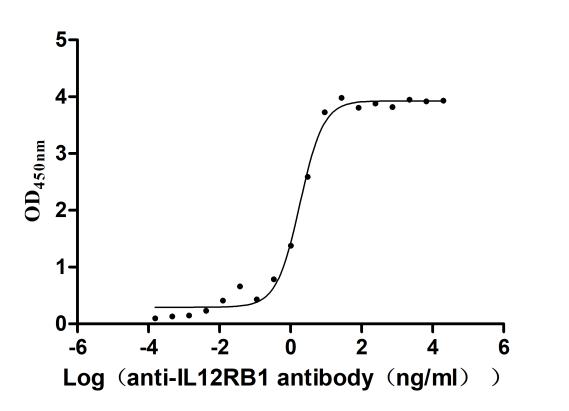
Recombinant Human Interleukin-12 receptor subunit beta-1(IL12RB1),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)