Recombinant Human Delta-like protein 4 (DLL4),partial (Active)
In Stock-
货号:CSB-MP878862HU
-
规格:
-
图片:
-
(Tris-Glycine gel) Discontinuous SDS-PAGE (reduced) with 5% enrichment gel and 15% separation gel.
-
Activity
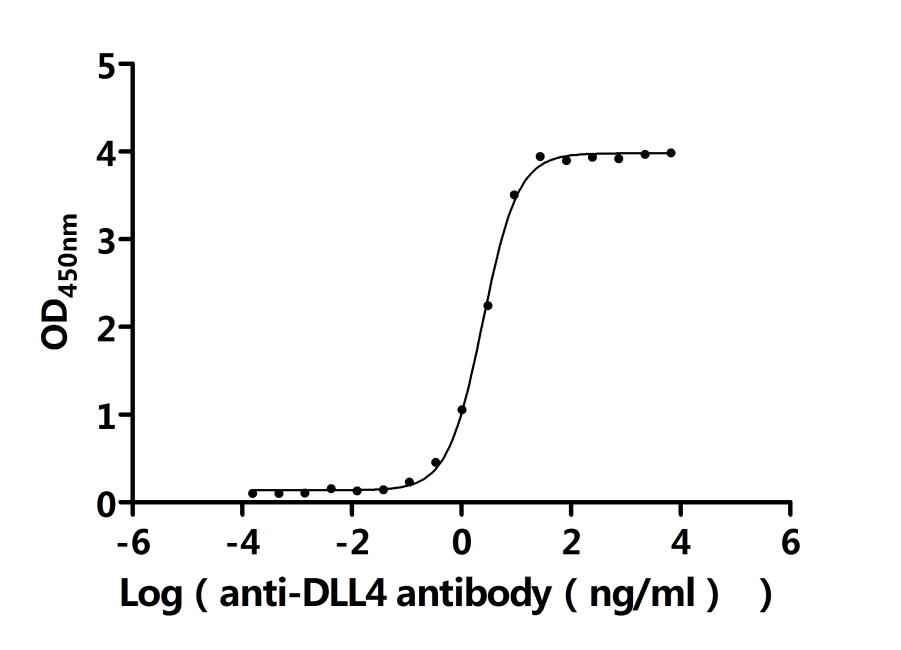
Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized Human DLL4 at 2 μg/ml can bind Anti-DLL4 recombinant antibody (CSB-RA878862MA1HU). The EC50 is 2.322-2.607 ng/mL. Biological Activity Assay
-
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:Greater than 95% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
内毒素:Less than 1.0 EU/ug as determined by LAL method.
-
生物活性:Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized Human DLL4 at 2 μg/mL can bind Anti-DLL4 recombinant antibody (CSB-RA878862MA1HU). The EC50 is 2.322-2.607 ng/mL.
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Delta-like protein 4; Drosophila Delta homolog 4 (Delta4); DLL4; UNQ1895/PRO4341
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
分子量:55.7 kDa
-
表达区域:27-524aa
-
氨基酸序列SGVFQLQLQEFINERGVLASGRPCEPGCRTFFRVCLKHFQAVVSPGPCTFGTVSTPVLGTNSFAVRDDSSGGGRNPLQLPFNFTWPGTFSLIIEAWHAPGDDLRPEALPPDALISKIAIQGSLAVGQNWLLDEQTSTLTRLRYSYRVICSDNYYGDNCSRLCKKRNDHFGHYVCQPDGNLSCLPGWTGEYCQQPICLSGCHEQNGYCSKPAECLCRPGWQGRLCNECIPHNGCRHGTCSTPWQCTCDEGWGGLFCDQDLNYCTHHSPCKNGATCSNSGQRSYTCTCRPGYTGVDCELELSECDSNPCRNGGSCKDQEDGYHCLCPPGYYGLHCEHSTLSCADSPCFNGGSCRERNQGANYACECPPNFTGSNCEKKVDRCTSNPCANGGQCLNRGPSRMCRCRPGFTGTYCELHVSDCARNPCAHGGTCHDLENGLMCTCPAGFSGRRCEVRTSIDACASSPCFNRATCYTDLSTDTFVCNCPYGFVGSRCEFPVGLP
-
蛋白标签:C-terminal 10xHis-tagged
-
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
缓冲液:Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered PBS, 6% Trehalose, pH 7.4
-
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20°C/-80°C. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 3-7 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Involved in the Notch signaling pathway as Notch ligand. Activates NOTCH1 and NOTCH4. Involved in angiogenesis; negatively regulates endothelial cell proliferation and migration and angiogenic sprouting. Essential for retinal progenitor proliferation. Required for suppressing rod fates in late retinal progenitors as well as for proper generation of other retinal cell types. During spinal cord neurogenesis, inhibits V2a interneuron fate.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- These data indicate that DLL4 represents a new prognostic biomarker for nonsmall cell lung cancer , and DLL4 overexpression inhibits cell proliferation and metastasis in vitro. PMID: 30226615
- Study demonstrates that DLL4 is important in regulating the tumour growth of hepatitis B virus (HBV)-associated hepatocellular carcinoma as well as the neovascularization and suppression of HBV replication. PMID: 30228780
- this study revealed that DLL4 has pathophysiological roles on the progression of esophagus cancer cells, including migration, invasion and apoptosis, which indicated that DLL4 may be considered as a potent therapeutic target for the treatment of malignant esophageal cancer. PMID: 29749499
- The regulation of DLL4 by the LDB2 complex provides a novel mechanism of DLL4 transcriptional control that may be exploited to develop therapeutics for aberrant vascular remodeling. PMID: 28946938
- Data show that Delta-like 4 (DLL4) and Jagged1 (JAG1) displayed equal potency in stimulating Notch target genes in HMEC-1 dermal microvascular endothelial cells but had opposing effects on sprouting angiogenesis in vitro. PMID: 28445154
- epigenetic silencing and TP53 mutation have an effect on the expression of DLL4 in human cancer stem disorder PMID: 27542210
- the Notch signaling and atherosclerosis relevant markers in lesions from femoral arteries of symptomatic peripheral artery disease patients, were characterized. PMID: 28472949
- Data suggest that Numb acts as a Notch antagonist by controlling intracellular destination and stability of the Notch ligand Delta-like 4 (DLL4) through a post-endocytic sorting process; Numb negatively controls DLL4 plasma membrane recycling through well-documented recycling regulator protein AP1. PMID: 29042443
- Results show that DLL4 is involved in SYNJ2BP-induced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) development though activating its pathway. PMID: 27440153
- Positive Jagged1 and DLL4 expression is closely correlated with severe clinicopathological characteristics and poor prognosis in patients with gallbladder cancers. PMID: 27174628
- We show that GIT1, which also contains an ANK domain, inhibits the Notch1-Dll4 signaling pathway by competing with Notch1 ANK domain for binding to RBP-J in stalk cells PMID: 27926858
- Results provide evidence that DLL4 is associated with gastric cancer stem/progenitor cells (GCSPCs), and its expression impacts CSPC stemness characteristics associated with the Notch-1 pathway including self-renewal, differentiation, proliferation, and tumor formation. PMID: 27891816
- The authors present novel structures of human ligands Jagged2 and Delta-like4 and human Notch2, together with functional assays, which suggest that ligand-mediated coupling of membrane recognition and Notch binding is likely to be critical in establishing the optimal context for Notch signalling. PMID: 28572448
- Overexpression of DLL4 could significantly attenuate the cytotoxic effects of docetaxel in MCF-7 cells by increasing Bcl-2 expression, while decreasing Bax expression, apoptosis rate and DNA damage PMID: 27334972
- In gastric epithelial cells co-cultured with Helicobacter pylori, the expression level of the ligand DLL4 was found to be significantly increased. PMID: 27073072
- Low DLL4 abundance in tumour cells may predict the benefit from adjuvant gemcitabine therapy after PDAC resection. PMID: 27755532
- Angiogenesis in Infantile haemangioma (IH) appears to be controlled by DLL4 within the endothelium in a VEGF-A isoform-dependent manner, and in perivascular cells in a VEGF-independent manner. The contribution of VEGF-A isoforms to disease progression also indicates that IH may be associated with altered splicing. PMID: 26957058
- Dll4 modulates liver inflammatory response by down-regulating chemokine expression PMID: 27171900
- Positive Jagged1 and DLL4 expression is closely correlated with severe clinicopathological characteristics and poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic ductal carcinoma. PMID: 27919854
- Data show that the IgA/delta-like protein 4 (Delta-4)/Notch receptor (Notch) axis is not observed in IgG-dendritic cells (DCs). PMID: 27117596
- Data suggest that the vascular DLL4-Notch4 signaling and VEGF signaling complementing each other plays an important role in the progression of tumor angiogenesis in primary glioblastoma. PMID: 26472724
- our data indicate that high DLL4 expression predicts pelvic lymph node metastasis and poor survival in cervical cancer. Therefore, DLL4 may be a potential clinical diagnostic marker for patients with early-stage cervical cancer. PMID: 26546434
- Cyclic AMP Response Element Binding Protein Mediates Pathological Retinal Neovascularization via Modulating DLL4-NOTCH1 Signaling PMID: 26870802
- DLL4 and JAG1 may have opposing effects on tumor angiogenesis in glioblastoma. PMID: 26546995
- Expression of D114 in the vessels of dermal microvasculature was shown to increase from 20 weeks of gestation to 20 years. PMID: 27487663
- Data indicate the role for altered forkhead box C2 (FoxC2)-Delta-like ligand 4 (Dll4)signaling in structural alterations of saphenous veins in patients with varicose veins. PMID: 26808710
- Antagonism of the DLL4-Notch signaling pathway might provide a potential therapeutic approach for breast cancer treatment by preventing angiogenesis. PMID: 26739060
- Activation of Dll4/Notch signaling led to increased expression of ephrin-B2 and subsequent inhibition of endothelial progenitor cells activity. PMID: 26212082
- DLL4 is a unique functional molecule of human circulating dendritic cells critical for directing Th1 and Th17 differentiation PMID: 26712946
- The expression of DLL4 was positively correlated with CD105-labeled MVD. PMID: 25986715
- The detection of Notch1 and Delta-like 4 expression in peripheral blood lymphocytes of renal transplant recipients can serve as a positive indicator for evaluating the diagnosis and treatment efficacy of the AR reaction. PMID: 26070613
- Among all the Notch ligands, Delta-like4 (Dll4) is specifically involved in angiogenesis. hD4R could suppress angiogenesis in vitro as manifested by network formation assay and sprouting assay. PMID: 25833803
- DLL4 and VEGFA expression was closely related to tumour diameter, clinical stage, histological grade and lymph node metastasis. PMID: 26111775
- DLL4/Notch1 and BMP9 interdependent signaling induces endothelial cell quiescence via P27KIP1/thrombospondin pathway. PMID: 26471266
- Overexpression of DLL4 is associated with thyroid tumor invasion and metastasis. PMID: 26241546
- Macrophage Dll4 promotes lesion development in vein grafts via macrophage activation and crosstalk between macrophages and smooth muscle cells. PMID: 26404485
- Heterozygous Loss-of-Function Mutations in DLL4 Cause Adams-Oliver Syndrome. PMID: 26299364
- IL-23 could promote migration of human ESCC cells by activating DLL4/Notch1 signaling pathway PMID: 26062426
- expression of VEGF and Dll4/Notch pathway molecules in ovarian cancer PMID: 24949865
- Dormant Dbf4 mRNA in immature GV oocytes is recruited by cytoplasmic polyadenylation during oocyte maturation and is dependent on MPF activity via its cytoplasmic polyadenylation element (CPE) PMID: 25348865
- High DLL4 expression is associated with T acute lymphoblastic leukemia. PMID: 25355291
- Inhibition of ADAM10/17 or knockdown of DLL4 reduced the proangiogenic effects of fibulin-3 in culture PMID: 25139440
- Dll4 expression is up-regulated in clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients, and predicts poor prognosis. PMID: 24966922
- Dengue virus up-regulates expression of notch ligands Dll1 and Dll4 through interferon-beta signalling pathway. PMID: 25041739
- Our data suggest that renal cell carcinoma progression is caused in part by activated DLL4/Notch signaling, interaction of endothelium and cells PMID: 24931473
- these results suggest that high expression of DLL4 is associated with axillary lymph node metastasis and a poor prognosis in breast cancer, suggesting its value as a diagnostic marker for breast cancer. PMID: 25260720
- These findings indicate a potential role for the Notch-1-Dll4 signaling pathway in foreign body-induced granulomatous reactions PMID: 24394305
- High expression of DLL4 is associated with metastasis in breast cancer. PMID: 24696220
- findings suggest that ADAM10/Dll4 signaling is a major signaling pathway in ECs driving inflammatory events involved in inflammation and immune cell recruitment PMID: 25130545
- Dll4-containing exosomes increase endothelial cell motility while suppressing their proliferation. PMID: 24504253
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Adams-Oliver syndrome 6 (AOS6)
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein.
-
组织特异性:Expressed in vascular endothelium.
-
数据库链接:
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Lymphotoxin-alpha (LTA) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Heat-stable enterotoxin receptor (GUCY2C), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Mouse Cytotoxic and regulatory T-cell molecule (Crtam), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 8(CEACAM8) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)