Recombinant Human DNA repair protein REV1 (REV1), partial
-
中文名称:人REV1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP883372HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人REV1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP883372HU
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人REV1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP883372HU-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人REV1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP883372HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人REV1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP883372HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:REV1
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:AIBP 80; AIBP80; Alpha integrin binding protein 80; Alpha integrin-binding protein 80; DNA repair protein REV 1; DNA repair protein REV1; FLJ21523; MGC163283; MGC26225; REV 1 (yeast homolog) like; REV 1; REV 1 homolog; REV 1 like; REV 1 protein; REV 1L; REV1 (yeast homolog) like; REV1; REV1 homolog (S. cerevisiae); REV1 homolog; REV1 like (yeast); REV1 like; Rev1 like terminal deoxycytidyl transferase; REV1 protein; Rev1-like terminal deoxycytidyl transferase; REV1_HUMAN; REV1L
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Deoxycytidyl transferase involved in DNA repair. Transfers a dCMP residue from dCTP to the 3'-end of a DNA primer in a template-dependent reaction. May assist in the first step in the bypass of abasic lesions by the insertion of a nucleotide opposite the lesion. Required for normal induction of mutations by physical and chemical agents.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- These data indicate that dysregulation of cellular Rev1 levels leads to the accumulation of mutations and suppression of cell death, which accelerates the tumorigenic activities of DNA-damaging agents. PMID: 28498946
- The data directly show that, in the human genome, DNA Pol-eta and Rev1 bypass cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers and 6-4PP at replication forks, while only 6-4PP are also tolerated by a Rev3L-dependent gap-filling mechanism, independent of S phase. PMID: 27095204
- the catalytic function of REV1 is moderately or slightly altered by at least nine genetic variations, and the G4 DNA processing function of REV1 is slightly enhanced by the N373S variation, which might provide the possibility that certain germline missense REV1 variations affect the individual susceptibility to carcinogenesis by modifying the capability of REV1 for replicative bypass past DNA lesions and G4 motifs derived PMID: 26914252
- REV1 can promote PCNA monoubiquitylation after UV radiation through interacting with ubiquitylated RAD18. PMID: 26795561
- Saccharomyces cerevisiae PMID: 26903512
- Rev1 is indispensable for Translesion synthesis mediated by Poleta, Poliota, and Polkappa but is not required for TLS by Polzeta. PMID: 26680302
- Data suggest Rev1 protein recognition mechanism by Fanconi anemia-associated protein 20 (FAAP20). PMID: 26318859
- show that REV1 is a novel binding partner of the tumor suppressor p53 and regulates its activity PMID: 25614517
- Our results suggest for the first time that REV1 and REV3L SNPs might serve as potential predictive markers of outcome of cisplatin-based chemotherapy PMID: 24956248
- Structural studies suggest the possible involvement of XRCC1 and its associated repair factors, REV1 in post replication repair. PMID: 24409475
- The results show that human Rev1 disrupts G4 DNA structures and prevents refolding in vitro. PMID: 24366879
- the first structural insights into the regulation of human Rev1 for TLS polymerases. PMID: 23220741
- Rev1 but not Poleta depletion is epistatic to the lack of PCNA ubiquitination. PMID: 23761444
- a structural basis for understanding the recognition of the Rev1-CT by Y-family DNA polymerases PMID: 22691049
- Findings indicate that miR-96 regulates DNA repair and chemosensitivity by repressing RAD51 and REV1. PMID: 22761336
- Results suggest that abasic sites might be bypassed by single B- and Y-family pols or combinations, possibly by REV1 and pols iota, eta, and delta/PCNA at the insertion step opposite the lesion and by pols eta and delta/PCNA at the subsequent extension step. PMID: 20888339
- REV7 subunit of pol zeta mediated the interaction between REV3 and the REV1 C terminus. PMID: 22303021
- FAAP20 binding stabilizes Rev1 nuclear foci and promotes interaction of the Fanconi anemia core with PCNA-Rev1 DNA damage bypass complexes. PMID: 22266823
- Hsp90 promotes folding of REV1 into a stable and/or functional form(s) to bind to monoubiquitinated proliferating cell nuclear antigen in the regulation of translesion DNA synthesis-mediated mutagenesis PMID: 21690293
- WRN facilitates REV1-dependent translesion synthesis. PMID: 20691646
- the interaction between REV7 and REV3 creates a structural interface for REV1 binding PMID: 20164194
- REV1 and Polzeta facilitate repair of interstrand cross-links independently of PCNA monoubiquitination and Poleta, whereas RAD18 plus Poleta, REV1, and Polzeta are all necessary for replicative bypass of cisplatin intrastrand DNA cross-links. PMID: 20028736
- The results suggest that the positive charge on R357 could prevent interaction of REV1 with dGTP. PMID: 20059978
- UV-induced mutant frequencies at the HPRT locus were reduced up to 75% in cells with reduced levels of REV1 mRNA and data support that targeting the mutagenic translesion DNA replication pathway can greatly reduce the frequency of induced mutations. PMID: 12930947
- REV1 interacts with three Y-family DNA polymerases. PMID: 15189446
- REV1 interacts with pol eta in translesion synthesis of damaged DNA PMID: 15380106
- REV1-dependent processes are important determinants of cisplatin-induced genomic instability and the development of resistance. PMID: 16495473
- a novel biochemical activity of human REV1 protein, due to higher affinity for single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) than the primer terminus PMID: 16803901
- Rev1 is a polypeptide associated with Poleta. The study results suggest that arrested replication forks strengthen interactions among Poleta, Rad18/Rad6 and Rev1, consistent with the requirement for effective TLS by Poleta at sites of DNA lesions. PMID: 16824193
- Results support Phe257Ser and Ser257Ser genotypes are associated with a decreased risk for cervical carcinoma, while Asn373Ser and Ser373Ser genotypes increased the risk. PMID: 18470628
- Data show that PCNA ubiquitination and REV1 play distinct roles in the coordination of DNA damage bypass that are temporally separated relative to replication fork arrest. PMID: 18498753
- human REV1, apparently the slowest Y family polymerase, is kinetically highly tolerant to N(2)-adduct at G but not to O(6)-adducts. PMID: 18591245
- plays a role in mutagenesis and translesin DNA synthesis. (review) PMID: 18975621
- Poleta-REV1 interactions prevent spontaneous mutations, probably by promoting accurate translesion DNA synthesis past endogenous DNA lesions PMID: 19157994
- Novel structural features are important for providing Rev1 greater latitude in promoting efficient and error-free translesion DNA synthesis through the diverse array of bulky and potentially carcinogenic N(2)-deoxyguanosine DNA adducts in human cells. PMID: 19464298
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus.
-
蛋白家族:DNA polymerase type-Y family
-
组织特异性:Ubiquitous.
-
数据库链接:
Most popular with customers
-
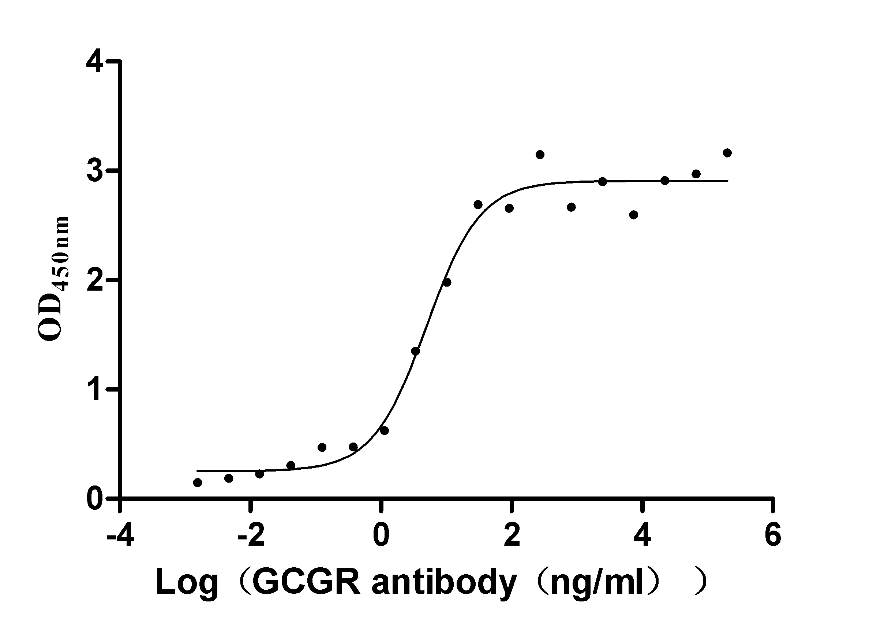
Recombinant Human Glucagon receptor (GCGR), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Mouse Transthyretin (Ttr) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Mouse Complement component C1q receptor (Cd93), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human Claudin-6 (CLDN6)-VLPs, Fluorescent (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
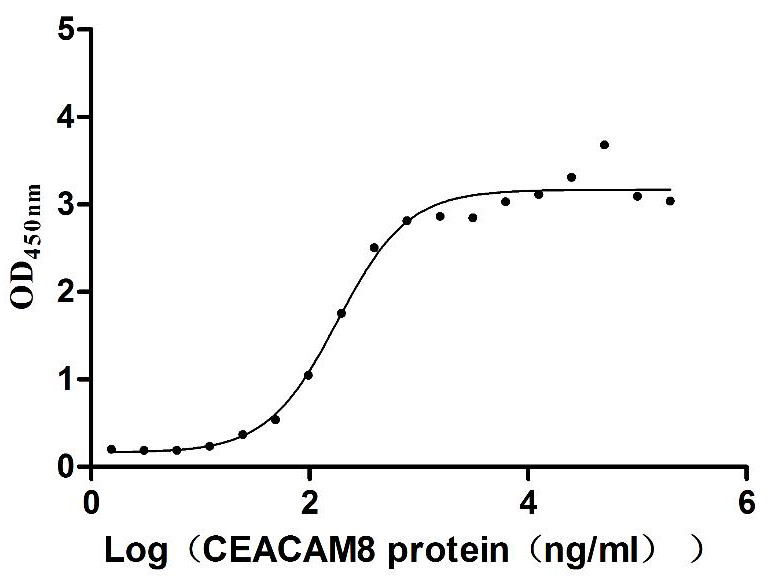
Recombinant Human Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
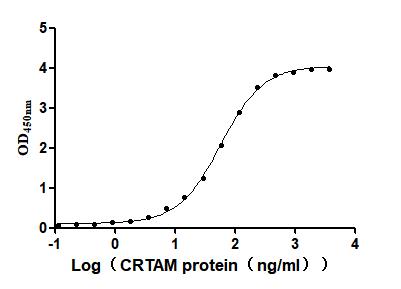
Recombinant Mouse Cytotoxic and regulatory T-cell molecule (Crtam), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
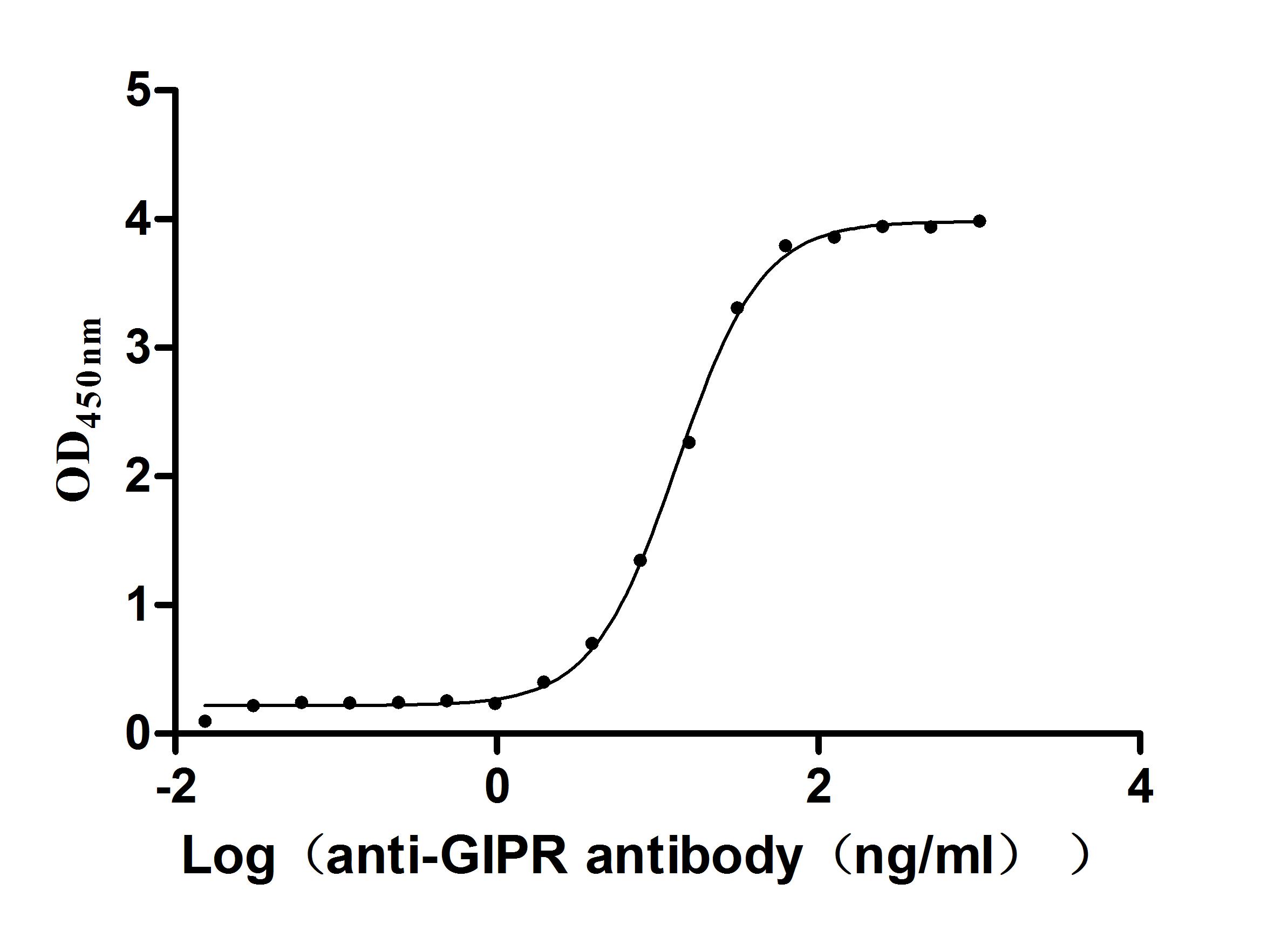
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor (GIPR), partial (Active)
Express system: yeast
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Mouse Cadherin-6(Cdh6),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)


f4-AC1.jpg)