Recombinant Human DBIRD complex subunit KIAA1967 (KIAA1967), partial
-
中文名称:Recombinant Human DBIRD complex subunit KIAA1967(KIAA1967) ,partial
-
货号:CSB-YP822681HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Human DBIRD complex subunit KIAA1967(KIAA1967) ,partial
-
货号:CSB-EP822681HU
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Human DBIRD complex subunit KIAA1967(KIAA1967) ,partial
-
货号:CSB-EP822681HU-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Human DBIRD complex subunit KIAA1967(KIAA1967) ,partial
-
货号:CSB-BP822681HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Human DBIRD complex subunit KIAA1967(KIAA1967) ,partial
-
货号:CSB-MP822681HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
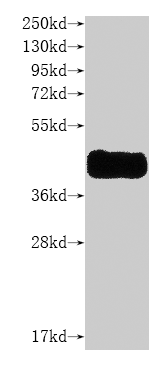
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:CCAR2
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:CCAR2; DBC1; KIAA1967Cell cycle and apoptosis regulator protein 2; Cell division cycle and apoptosis regulator protein 2; DBIRD complex subunit KIAA1967; Deleted in breast cancer gene 1 protein; DBC-1; DBC.1; NET35; p30 DBC
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Core component of the DBIRD complex, a multiprotein complex that acts at the interface between core mRNP particles and RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) and integrates transcript elongation with the regulation of alternative splicing: the DBIRD complex affects local transcript elongation rates and alternative splicing of a large set of exons embedded in (A + T)-rich DNA regions. Inhibits SIRT1 deacetylase activity leading to increasing levels of p53/TP53 acetylation and p53-mediated apoptosis. Inhibits SUV39H1 methyltransferase activity. Mediates ligand-dependent transcriptional activation by nuclear hormone receptors. Plays a critical role in maintaining genomic stability and cellular integrity following UV-induced genotoxic stress. Regulates the circadian expression of the core clock components NR1D1 and ARNTL/BMAL1. Enhances the transcriptional repressor activity of NR1D1 through stabilization of NR1D1 protein levels by preventing its ubiquitination and subsequent degradation. Represses the ligand-dependent transcriptional activation function of ESR2. Acts as a regulator of PCK1 expression and gluconeogenesis by a mechanism that involves, at least in part, both NR1D1 and SIRT1. Negatively regulates the deacetylase activity of HDAC3 and can alter its subcellular localization. Positively regulates the beta-catenin pathway (canonical Wnt signaling pathway) and is required for MCC-mediated repression of the beta-catenin pathway. Represses ligand-dependent transcriptional activation function of NR1H2 and NR1H3 and inhibits the interaction of SIRT1 with NR1H3. Plays an important role in tumor suppression through p53/TP53 regulation; stabilizes p53/TP53 by affecting its interaction with ubiquitin ligase MDM2. Represses the transcriptional activator activity of BRCA1. Inhibits SIRT1 in a CHEK2 and PSEM3-dependent manner and inhibits the activity of CHEK2 in vitro.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Since its up-regulation in cancer patients is usually associated with poor prognosis and its depletion reduces cancer cell growth in vitro, CCAR2 was suggested to act as a tumor promoter. However, there is also evidence that CCAR2 functions as a tumor suppressor and therefore its role in cancer formation and progression is still unclear. Review. PMID: 29807573
- CCAR2/DBC1 inhibits recombination by limiting the initiation and the extent of DNA end resection, thereby acting as an antagonist of CtIP. PMID: 27503537
- conclude, these findings demonstrated that DBC1 was essential in tumorigenesis and proliferation. Moreover, it was identified as a potential therapeutic target for HCC. PMID: 29106957
- Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 interacts with DBC1 to regulate p53 acetylation. PMID: 28973437
- Data suggest that DBC1 has a dual function in regulating beta-catenin-PROX1 signaling axis: as a coactivator for both beta-catenin and PROX1. PMID: 26477307
- These results establish an important role for CCAR2 in cancer cells proliferation and could shed new light on novel therapeutic strategies against cancer, devoid of detrimental side effects. PMID: 27809307
- important role for CCAR2 in maintaining cell cycle progression and promoting squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) tumorigenesis. PMID: 27725203
- Data show that the interaction between cell cycle and apoptosis regulator 2 (CCAR2) and heat shock protein 60 (Hsp60) increases in the presence of rotenone. PMID: 28254432
- Results found transcriptional levels of DBC1,a negative regulator of HDAC3 significantly reduced in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. PMID: 27904654
- DBC1 protein could be a prognostic marker of shorter recurrence-free survival in hepatocellular carcinoma patients after hepatectomy and human hepatocarcinogenesis was a multistep process accompanied by a stepwise increase in high DBC1 expression from low-grade dysplastic nodules, through high-grade dysplastic nodules, to hepatocellular carcinoma. PMID: 27083241
- Results suggest that DBC1 is integral to the maintenance of the circadian molecular clock. PMID: 26657080
- loss of DBC1 expression plays a role in tumorigenesis and tumor progression in gallbladder carcinoma. PMID: 26617872
- Proteosome-mediated degradation and poly-ubiquitination of AR were increased with the knock-down of DBC1. PMID: 26249023
- These studies further extend and confirm the role of CCAR2 in the DNA damage response and DNA repair PMID: 26158765
- The results suggest that the PP4-mediated dephosphorylation of DBC1 is necessary for efficient damage responses in cells. PMID: 26194823
- These results indicate that the expression of DBC1 and BRCA1 are closely related with in the progression of ovarian carcinomas PMID: 25823848
- the results indicated that DBC1 promotes anoikis resistance in gastric cancer cells by regulating NF-kappaB activity and may thus be a new therapeutic target for preventing potential metastasis PMID: 26035299
- DBC1 modification by Small Ubiquitin-like Modifier 2/3 is crucial for p53 transactivation under genotoxic stress. PMID: 25406032
- molecular mechanism underlying DBC1 function in PEA3-mediated transcription involves inhibition of SIRT1 interaction with PEA3 and of SIRT1-mediated deacetylation of PEA3 PMID: 25417701
- DBC1 might promote adipose tissue inflammation and senescence in obese subjects PMID: 25682741
- Although DBC1 gene expression was reduced in adipose tissue from obese subjects, it was negatively associated with ADIPOQ gene expression in VAT, suggesting that DBC1 might promote visceral adipose tissue dysfunction. PMID: 25648830
- These results clearly indicate a novel mechanism in which CCAR2 may regulate the transcriptional activation function of LXRalpha due to its specific inhibition of SIRT1 and serve to regulate cellular proliferation. PMID: 25661920
- We propose that DBC1 is part of the molecular machinery that regulates fat storage capacity in adipocytes and participates in the "turn-off" switch that limits adipocyte fat accumulation. PMID: 25053585
- CK2 alpha is an independent prognostic indicator for gastric carcinoma patients and is involved in tumorigenesis by regulating the phosphorylation of DBC1. PMID: 24962073
- The results link Chk2 and REGgamma to the mechanism underlying the DBC1-dependent SIRT1 inhibition. PMID: 25361978
- cytoplasmic MCC-DBC1 interaction sequesters DBC1 away from the nucleus, thereby removing a brake on DBC1 nuclear targets, such as SIRT1 PMID: 24824780
- These results suggest that DBC1 is over-expressed in colorectal cancer and that it might serve as a predictor for selecting patients at high risk of poor prognosis. PMID: 23299276
- demonstrates that SIRT1- and DBC1-related pathways may be involved in the progression of soft-tissue sarcomas and can be used as clinically significant prognostic indicators for sarcoma patients PMID: 24019980
- Results reveal novel mechanisms by which TFII-I and DBC1 can modulate cellular fate by affecting cell-cycle control as well as the homologous recombination pathway. PMID: 24231951
- DBC1 as a novel regulator of gluconeogenesis. PMID: 24415752
- DBC1 may be implicated in the regulation of cancer cell energy metabolism. [Review] PMID: 23841676
- This study demonstrates that the acetylation status of P53 and the expression of SIRT1, DBC1, and AR could be new prognostic indicators for clear cell renal cell carcinoma PMID: 24018803
- Protein acetylation serves as an endogenous regulatory mechanism for SIRT1-DBC1 binding. PMID: 23892437
- MOF acetylation of DBC1 inhibits binding to SirT1 and serves as a mechanism that connects DNA damage signaling to SirT1 and cell fate determination. PMID: 24126058
- Our findings integrate KSR1 into a network involving DBC1 and SIRT1, which results in the regulation of p53 acetylation and its transcriptional activity. PMID: 24129246
- DBC1 is an important co-factor for the control of the IKK-beta-NF-kappaB signaling pathway that regulates anoikis. PMID: 23588592
- DBC1 enhances cell survival against UV irradiation.Therefore, DBC1 plays a critical role in maintaining genomic stability and cellular integrity following UV-induced genotoxic stress. PMID: 23352644
- DBC1 phosphorylation by ATM/ATR inhibits SIRT1 deacetylase in response to DNA damage. PMID: 22735644
- Data indicate that an increase in cAMP/PKA activity resulted in the dissociation of SIRT1 and DBC1 in an AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)-dependent manner. PMID: 22553202
- data indicate that the DBIRD complex (consisting of DBC1 and ZNF326) acts at the interface between mRNP particles and RNAPII, integrating transcript elongation with the regulation of alternative splicing PMID: 22446626
- Suggest that DBC1 may promote tumor progression, and DBC1 could be a prognostic biomarker in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. PMID: 22127596
- results implicate the principal role of DBC1 in regulating ERbeta-dependent gene expressions PMID: 20074560
- HDAC3 is negatively regulated by the nuclear protein DBC1 PMID: 21030595
- DBC1 may modulate the cellular functions of BRCA1 and have important implications in the understanding of carcinogenesis in breast tissue. PMID: 20160719
- New role for DBC1 as an in vivo regulator of SIRT1 activity and liver steatosis, in which interaction with SIRT1 may serve as a new target for therapies aimed at nonalcoholic liver steatosis. PMID: 20071779
- Expression of DBC1 and SIRT1 is a significant prognostic indicator for gastric carcinoma patients. PMID: 19509139
- Results identify DBC1 as a novel cellular inhibitor of SUV39H1 activity, and suggest that DBC1 may be an important regulator of heterochromatin formation and genomic stability by disrupting the SUV39H1-SirT1 complex and inactivating both enzymes. PMID: 19218236
- Caspase-dependent processing of DBC-1 may act as a feed-forward mechanism to promote apoptosis and possibly also tumor suppression. PMID: 15824730
- biological function for DBC-1 in the modulation of ERalpha expression and hormone-independent breast cancer cell survival PMID: 17473282
- DBC1 directly interacts with SIRT1 and inhibits SIRT1 activity in vitro and in vivo PMID: 18235501
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, spindle.
-
组织特异性:Expressed in gastric carcinoma tissue and the expression gradually increases with the progression of the carcinoma (at protein level). Expressed ubiquitously in normal tissues. Expressed in 84 to 100% of neoplastic breast, lung, and colon tissues.
-
数据库链接:
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Lymphotoxin-alpha (LTA) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Delta-like protein 3 (DLL3), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Macaca mulatta Microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca mulatta (Rhesus macaque)
-
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 8 (CCR8)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis CUB domain containing protein 1 (CDCP1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Human Myosin regulatory light chain 12B(MYL12B) (Active)
Express system: E.coli
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 6(CCR6)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Cadherin-6(CDH6),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)