Recombinant Human A-kinase anchor protein 9 (AKAP9), partial
-
中文名称:Recombinant Human A-kinase anchor protein 9(AKAP9) ,partial
-
货号:CSB-YP857882HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Human A-kinase anchor protein 9(AKAP9) ,partial
-
货号:CSB-EP857882HU
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Human A-kinase anchor protein 9(AKAP9) ,partial
-
货号:CSB-EP857882HU-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Human A-kinase anchor protein 9(AKAP9) ,partial
-
货号:CSB-BP857882HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Human A-kinase anchor protein 9(AKAP9) ,partial
-
货号:CSB-MP857882HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:A kinase (PRKA) anchor protein (yotiao) 9; A kinase (PRKA) anchor protein 9; A kinase anchor protein 350kDa; A kinase anchor protein 450 kDa; A kinase anchor protein 9; A kinase anchoring protein 350; A kinase anchoring protein 450; A-kinase anchor protein 350 kDa; A-kinase anchor protein 450 kDa; A-kinase anchor protein 9; AKAP 120-like protein; AKAP 350; AKAP 450; AKAP 9; AKAP-9; AKAP120 like protein; AKAP350; AKAP450; AKAP9; AKAP9_HUMAN; Centrosome and Golgi localized PKN associated protein; Centrosome and golgi localized protein; Centrosome- and Golgi-localized PKN-associated protein; CG NAP; CG-NAP; hgAKAP 350; hgAKAP350; Hyperion; KIAA0803; Kinase N associated protein; MU RMS 40.16A; PRKA 9; PRKA9; Protein hyperion; Protein kinase A anchoring protein 9; Protein kinase A-anchoring protein 9; Protein yotiao; Yotiao
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Scaffolding protein that assembles several protein kinases and phosphatases on the centrosome and Golgi apparatus. Required to maintain the integrity of the Golgi apparatus. Required for microtubule nucleation at the cis-side of the Golgi apparatus. Required for association of the centrosomes with the poles of the bipolar mitotic spindle during metaphase. In complex with PDE4DIP isoform 13/MMG8/SMYLE, recruits CAMSAP2 to the Golgi apparatus and tethers non-centrosomal minus-end microtubules to the Golgi, an important step for polarized cell movement. In complex with PDE4DIP isoform 13/MMG8/SMYLE, EB1/MAPRE1 and CDK5RAP2, contributes to microtubules nucleation and extension also from the centrosome to the cell periphery.; Associated with the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor and is specifically found in the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) as well as in neuronal synapses, suggesting a role in the organization of postsynaptic specializations.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- RNA sequencing identified in both an AKAP9-BRAF gene fusion PMID: 29464327
- Data suggest that CDK5RAP2 and CEP170 both interact with microtubule nucleation-promoting region of AKAP350A; CEP68 interacts with distal C-terminal region of AKAP350A; AKAP350A spans the bridge between centrioles. (CDK5RAP2 = CDK5 regulatory subunit associated protein 2; CEP170 = centrosomal protein 170kDa; AKAP350A = A kinase (PRKA) anchor protein (yotiao) 9; CEP68 = centrosomal protein 68kDa) PMID: 29054927
- Data suggest that AKAP350A utilizes organelle-specific targeting domains to promote spatially distinct microtubule nucleation pathways. [REVIEW] PMID: 29247130
- Findings suggest MALAT1 increases AKAP-9 expression by promoting SRPK1-catalyzed SRSF1 phosphorylation in CRC cells. These results reveal a novel molecular mechanism by which MALAT1 regulates AKAP-9 expression in CRC cells. PMID: 26887056
- AKAP9 gene harbors not only somatic frameshift mutations but also mutational ITH. PMID: 26786868
- results support a model in which AKAP350 recruits CIP4 to the centrosome, providing a centrosomal scaffold to integrate microtubule and actin dynamics, thus enabling centrosome polarization and ensuring cell migration directionality. PMID: 26208639
- Study suggests a role of rare missense variants at NRXN1 and AKAP9 in schizophrenia susceptibility, probably related to alteration of the excitatory/inhibitory synaptic balance, deserving further investigation PMID: 25943950
- This study demonstrated that two rare AKAP9 variants( rs144662445 and rs149979685) are associated with Alzheimer's disease in African Americans. PMID: 25172201
- AKAP9 has been identified as a Long QT Syndrome Type 1 modifying gene PMID: 25087618
- data indicate that MALAT1 may promote CRC tumor development via its target protein AKAP-9 PMID: 25446987
- A590T mutation in KCNQ1 C-terminal helix D decreases KCNE1 channel trafficking and function but not Yotiao interaction. PMID: 24713462
- AKAP proteins, most likely AKAP9, maintain the bronchial epithelial barrier by regulating the E-cadherin expression at the cell membrane. PMID: 24452374
- in heart, Yotiao brings together PKA, PP1, PDE4D3, AC9, and the I(Ks) channel to achieve localized temporal regulation of beta-adrenergic stimulation. PMID: 22778270
- Protein kinase A-phosphodiesterase (PDE)4D3-A kinase anchor protein (AKAP)9 complex generates spatial compartmentalization of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) signaling at the centrosome. PMID: 22908311
- Genotyped 14,843 invasive breast cancer case patients and 19,852 control subjects with white European ancestry and 2595 invasive case patients and 2192 control subjects with Asian ancestry for single nucleotide polymorphism 7q21-rs6964587 (AKAP9-M463I). PMID: 21931171
- AKAP350 participates in mechanisms which determine the development of canalicular structures as well as accurate canalicular expression of distinct proteins and actin organization PMID: 21374596
- identification of AKAP450 as a key determinant of pericentrosomal Golgi ribbon integrity, positioning, and function in mammalian cells PMID: 21606206
- We describe a pathway that integrates Epac-mediated signals with AKAP9-dependent microtubule dynamics to coordinate integrins at lateral borders PMID: 20952690
- Suppression of AKAP450 by overexpression of a dominant-negative form or siRNA knockdown disrupted the positioning and conformational activation of lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 at the immune synapse. PMID: 20231423
- included in a macromolecular complex with PKA and PP1 which is required for the regulation of hKCNQ1 by PKA-dependent phosphorylation PMID: 11799244
- CG-NAP and kendrin provide sites for microtubule nucleation in the mammalian centrosome by anchoring gamma-TuRC PMID: 12221128
- findings support a model in which sub-cellular localization at the centrosome is mediated, at least in part, through the action of CG-NAP/AKAP450 PMID: 12270714
- InsP(3)R1-PKA association is mediated by AKAP9; InsP(3)R1-AKAP9 binding promotes association of neuronal InsP(3)R1 with the NR1 NMDA receptor; and neuronal InsP(3)R1 associate with PP1 directly via carboxy-terminus and indirectly via AKAP9 PMID: 14982933
- AKAP9-BRAF fusion was preferentially found in radiation-induced papillary carcinomas developing after a short latency, whereas BRAF point mutations were absent in this group PMID: 15630448
- These results suggest that CG-NAP/D causes centrosome amplification by anchoring excess amount of cyclin E-cdk2 to centrosomes and, possibly, CG-NAP participates in centrosome duplication by recruiting cyclin E-cdk2 to centrosomes in normal cell cycle. PMID: 15670215
- expression of the intact CG-NAP/AKAP450 and its recruitment to the LFA-1-associated multimolecular complex is critically important for polarization and migration of T cells induced by this integrin. PMID: 16339516
- AKAP350 has a role in the remodeling of the microtubule cytoskeleton. PMID: 16356588
- CG-NAP is recruited to the minus ends of microtubules by interacting with cytoplasmic dynein, thereby localizes to the Golgi apparatus in a microtubule-dependent manner and possibly involved in the formation of the Golgi near the centrosomes. PMID: 17352745
- genetic perturbations in AKAP9 disrupt its binding to KCNQ1 and have a role in long-QT syndrome PMID: 18093912
- Polymorphisms in AKAP9 M4631 were associated with increased risks for familial and nonfamilial breast cancer. The functional consequence of the AKAP9 M4631 polymorphism may involve the PKA pathway. PMID: 18334708
- These results provide the first evidence for the microtubule dependent association of AKAP350A and CCAR1 with RNA stress granules. PMID: 19073175
- Data suggest that recruitment of AKAP450 on Golgi membranes through GM130 allows centrosome-associated nucleating activity to extend to the Golgi, to control the assembly of subsets of microtubules. PMID: 19242490
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Long QT syndrome 11 (LQT11)
-
亚细胞定位:Golgi apparatus. Cytoplasm. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome.
-
组织特异性:Widely expressed. Isoform 4: Highly expressed in skeletal muscle and in pancreas.
-
数据库链接:
Most popular with customers
-
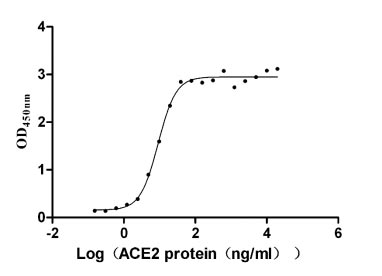
Recombinant Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus Spike glycoprotein (S), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Human SARS coronavirus (SARS-CoV) (Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus)
-
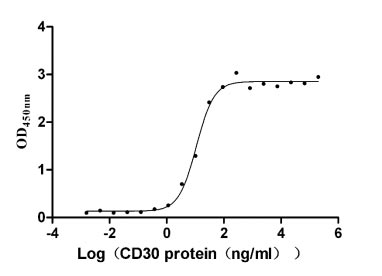
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 8 (TNFSF8), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
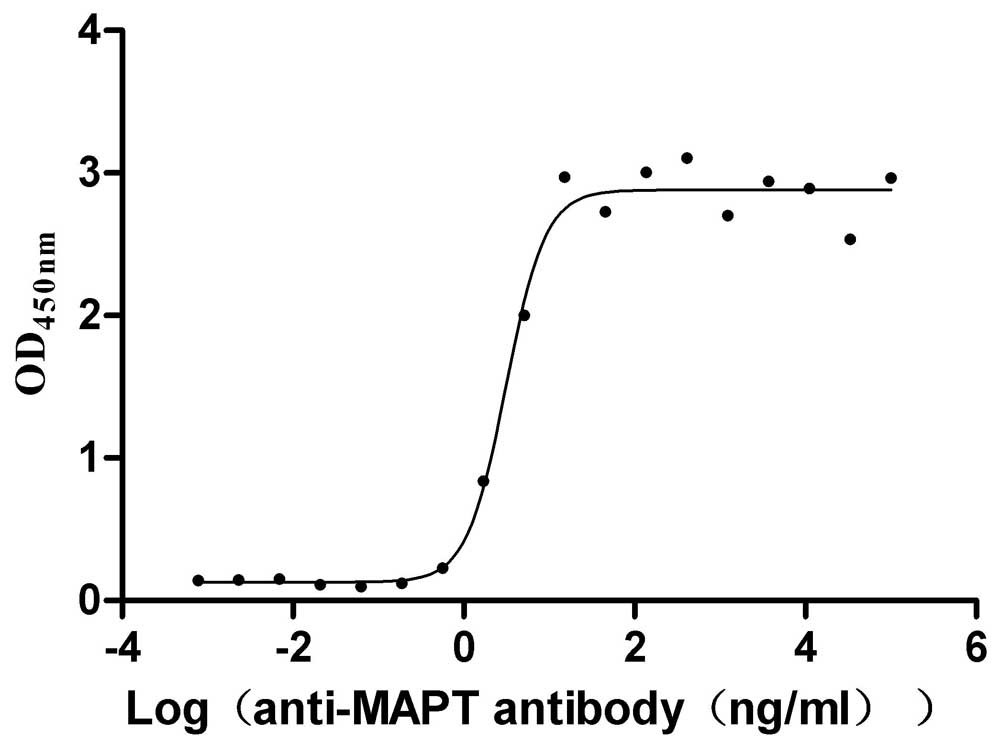
Recombinant Macaca mulatta Microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca mulatta (Rhesus macaque)
-
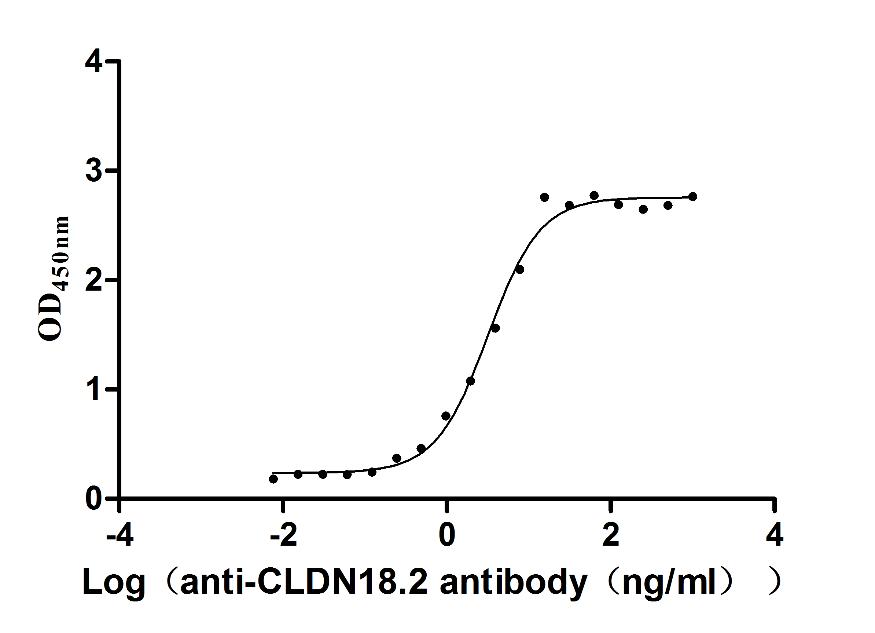
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Claudin 18.2 (CLDN18.2)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
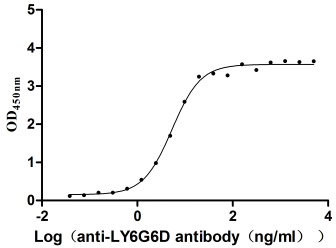
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis lymphocyte antigen 6 family member G6D (LY6G6D) (Active)
Express system: Yeast
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
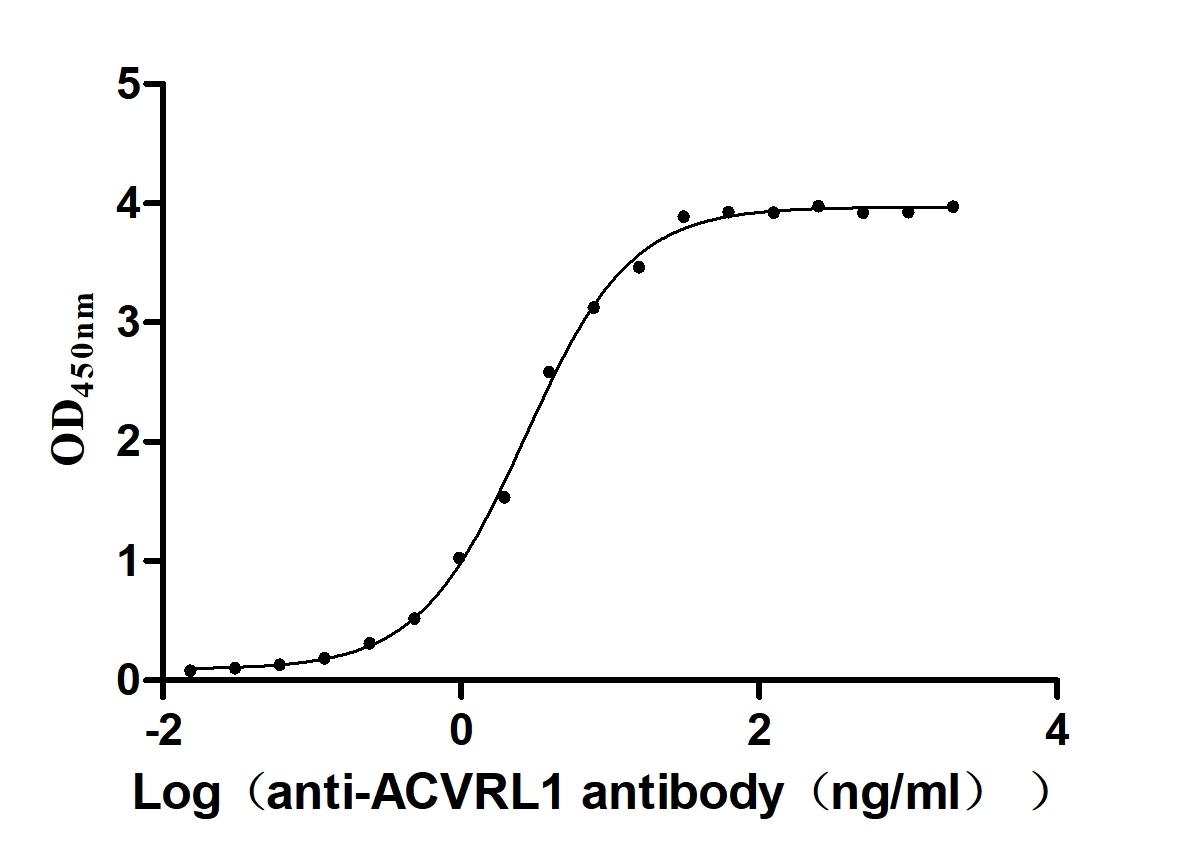
Recombinant Human Serine/threonine-protein kinase receptor R3 (ACVRL1), partial (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
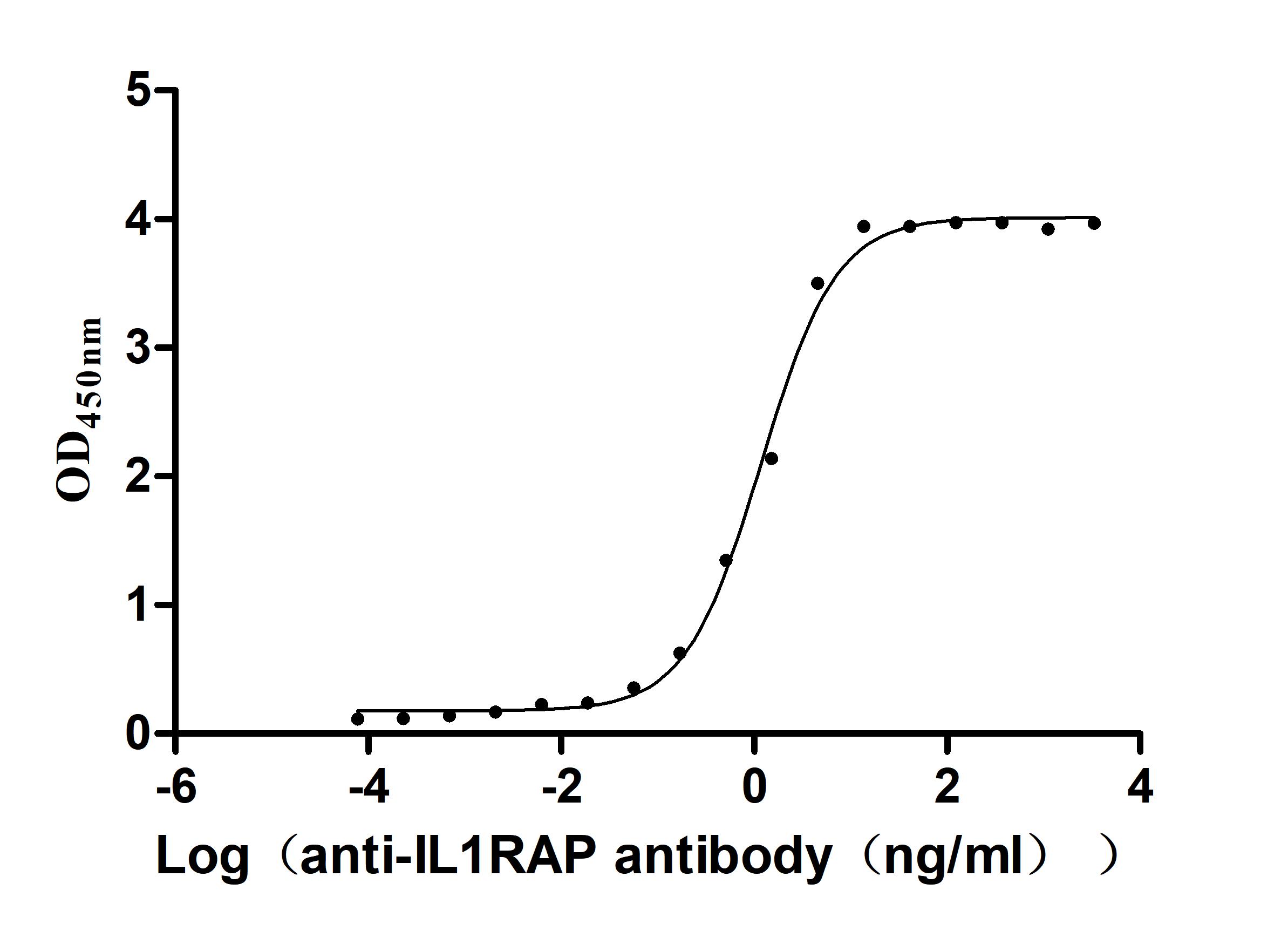
Recombinant Human Interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein (IL1RAP), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)