Recombinant Arabidopsis thaliana Auxin efflux carrier component 2 (PIN2), partial
-
中文名称:拟南芥PIN2重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP881818DOA
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:拟南芥PIN2重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP881818DOA
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:拟南芥PIN2重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP881818DOA-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:拟南芥PIN2重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP881818DOA
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:拟南芥PIN2重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP881818DOA
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:PIN2
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:PIN2; AGR; AGR1; EIR1; WAV6; At5g57090; MUL3.3; Auxin efflux carrier component 2; AtPIN2; Auxin efflux carrier AGR; Ethylene-insensitive root 1; AtEIR1; Polar-auxin-transport efflux component AGR1; Protein AGRAVITROPIC 1; AtAGR1; Protein WAVY 6
-
种属:Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Acts as a component of the auxin efflux carrier. Seems to be involved in the root-specific auxin transport, and mediates the root gravitropism. Its particular localization suggest a role in the translocation of auxin towards the elongation zone.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Mutation in PIN2 conservative cysteine domain leads to increased intracellular accumulation and altered protein distribution within plasma membrane micro-domains. PMID: 29109378
- The results suggest a peroxisomal ROS-based auxin signaling pathway involving spatiotemporal-dependent CuAOzeta functional regulation of PIN2 homeostasis, auxin distribution, and LR development. PMID: 28992128
- Data indicate that neither the naturally occurring auxins indole-3-acetic acid and indole-3-butyric acid, nor the synthetic auxin analogs were able to inhibit endocytosis of the putative auxin transporter PIN-FORMED2 (PIN2) in root epidermis cells. PMID: 27506239
- Brief treatment with indole-3-carbinol led to a reduction in the amount of PIN1 and to mislocalization of PIN2. PMID: 26252364
- PIN2 auxin efflux carriers are differentially controlled in tricho- and atrichoblast cells. PIN2 proteins show lower abundance at the plasma membrane of trichoblast cells, despite showing higher rates of intracellular trafficking in these cells. PMID: 26041320
- under low-B conditions PIN1 is down-regulated and PIN2 plays an important role in root meristem maintenance. PMID: 25814435
- Reduction in PIN2 intensity, polarization, and endocytosis under low phosphate conditions is MAX2 dependent. PMID: 25609825
- Functional interplay between protein kinase CK2 and salicylic acid sustains PIN2 transcriptional expression. PMID: 24547808
- By using solubilized membrane protein immunoprecipitation assays, we established quantitative approaches, suitable for analysis of PIN2 ubiquitylation and variations therein PMID: 25117288
- Strigolactones (SLs) increase PIN2 polar localization, PIN2 endocytosis, endosomal trafficking, actin debundling and actin dynamics in a MAX2-dependent fashion. PMID: 24571327
- we quantified directly and simultaneously the rate of PIN2 delivery of the newly synthesized protein into the plasma membrane as well as the disappearance of the protein from the plasma membrane due to degradation. PMID: 23637828
- The exocyst is involved in PIN1 and PIN2 recycling, and thus in polar auxin transport regulation. PMID: 23163883
- Consistent with SNX1's role in trafficking of the auxin efflux carrier PIN2, clasp-1 mutant plants have enhanced PIN2 degradation, and PIN2 movement to lytic vacuoles is rapidly induced by depolymerization of microtubules. PMID: 23477787
- Dynamic adjustments in PIN2 ubiquitylation in gravity-stimulated roots, a response that coincides with establishment of a lateral PIN2 expression gradient. PMID: 22902683
- PIN2 is involved in the PKS5-mediated signalling cascade under alkaline-stres and PIN2 is required for the maintenance of primary root growth in its adaptation to alkaline stress by modulating proton secretion in root tips. PMID: 23002434
- Methyl jasmonate effects on PIN2 endocytosis and plasma membrane residence. PMID: 21466556
- PIP5K2 is involved in regulating lateral root formation and root gravity response, and reveal a critical role of PIP5K2/PtdIns(4,5)P(2) in root development through regulation of PIN proteins, providing direct evidence of crosstalk between the phosphatidylinositol signaling pathway and auxin response, and new insights into the control of polar auxin transport PMID: 21894193
- PIN2 is essential for robust root phototropism. Blue light-induced auxin flux in the root apex transition zone is dependent on PIN2, phot1, and NPH3 PMID: 22374399
- PIN2 vacuolar sorting depends on modification specifically by lysine(63)-linked ubiquitin chains. PMID: 22556266
- findings show that polar-competent PIN transporters for auxin are delivered to the center of polar domains by super-polar recycling; within the plasma membrane, PINs are recruited into non-mobile membrane clusters and their lateral diffusion is reduced PMID: 22027551
- Data propose that MM31/EIR1 modulates lateral root formation by regulating the IAA polar transport system, and that auxin transport from the shoot to the root regulates lateral root formation. PMID: 21494100
- Data suggest a role of gibberellic acid (GA) in Arabidopsis growth responses and for a GA-dependent modulation of PIN1, -2, and -3 turnover that may be causative for these differential growth responses. PMID: 21642547
- Narciclasine modulates auxin transport gene expression and PIN2 localization. PMID: 21511360
- These results reveal a plant-specific mechanism for cell polarity maintenance and provide a conceptual framework for modulating cell polarity and plant development. PMID: 21315597
- data show that by directing polar PIN localization and PIN-mediated polar auxin transport, the three AGC3 kinases redundantly regulate cotyledon development, root meristem size and gravitropic response PMID: 20823065
- PIN2 deployment in the cortex represents a mechanism for fine-tuning the flow of auxin as required for optimal responses within the zone of root elongation. PMID: 20562236
- Cold stress inhibits the intracellular trafficking of auxin efflux carrier PIN2. PMID: 20040541
- NOV is required for PIN2 polarity in the root cortex. PMID: 19880797
- Alternative recruitment of PIN proteins by distinct pathways can account for cell type- and cargo-specific aspects of polar targeting, as well as for polarity changes in response to different signals. PMID: 19825603
- Our data suggest that protein phosphatases, sensitive to cantharidin and okadaic acid, are likely involved in regulating AGR1/PIN2-mediated root basipetal auxin transport and gravitropism. [AGR1] [PIN2] PMID: 15807782
- Redistribution of auxin during the gravitropic response may be involved in the regulation of PIN2 protein. PMID: 16489343
- results demonstrate that PIN polarity is a primary factor in determining the direction of auxin flow in meristematic tissues PMID: 16601151
- flavonoids promote asymmetric PIN shifts during gravity stimulation, thus redirecting basipetal auxin streams necessary for root bending. PMID: 18718912
- The vacuolar targeting pathway is used by multiple cargos including PIN-FORMED (PIN) efflux carriers for the phytohormone auxin. PMID: 19004783
- Plasma membrane accumulation of the auxin efflux transporter PIN2 requires the E3 ubiquitin ligase SCF(TIR1/AFB). PMID: 19218398
- The loss of EIR1/AGR1/PIN2 function abolishes root curling of mlo4, mlo11, and wild-type seedlings. PMID: 19602625
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:Auxin efflux carrier (TC 2.A.69.1) family
-
组织特异性:Root-specific. Localized to the cortex, epidermis and lateral root cap, predominantly at the upper side of cells.
-
数据库链接:
Most popular with customers
-
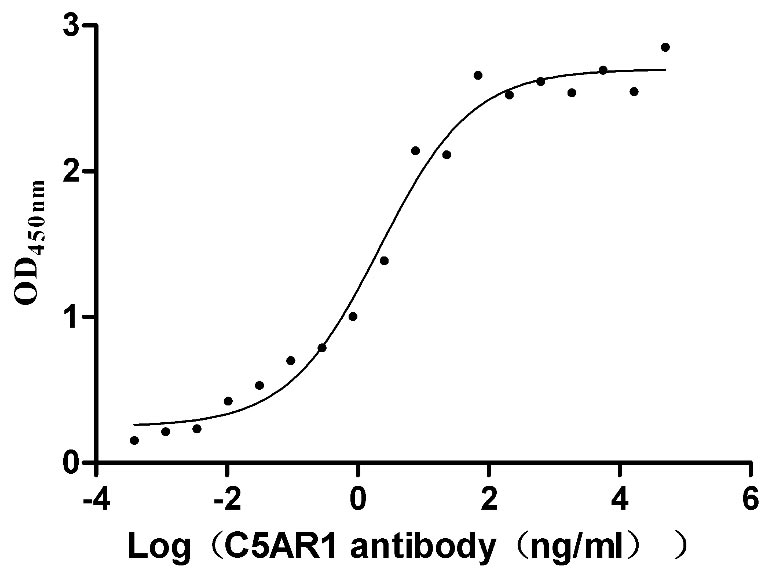
Recombinant Human C5a anaphylatoxin chemotactic receptor 1 (C5AR1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Claudin-6 (CLDN6)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
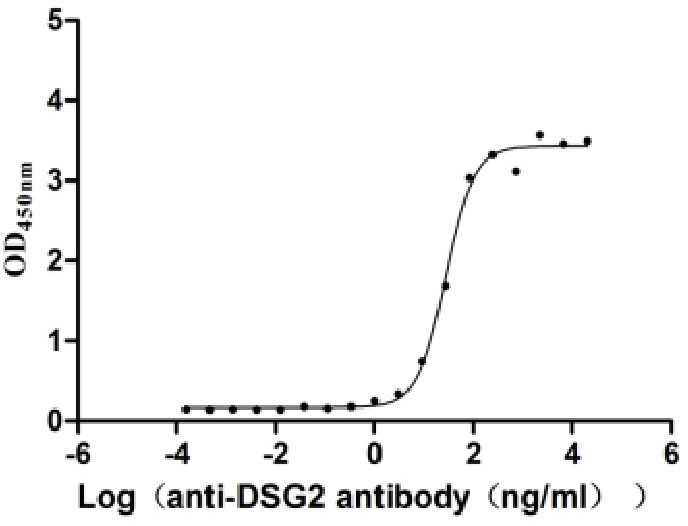
Recombinant Human Desmoglein-2 (DSG2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
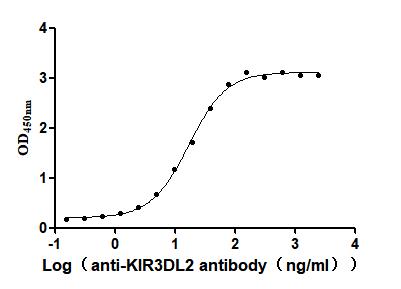
Recombinant Human Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 3DL2 (KIR3DL2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)