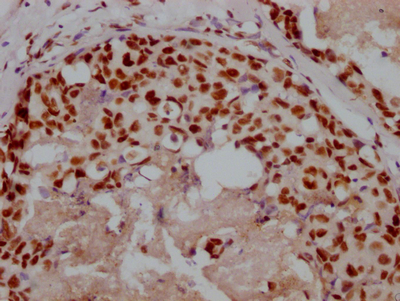
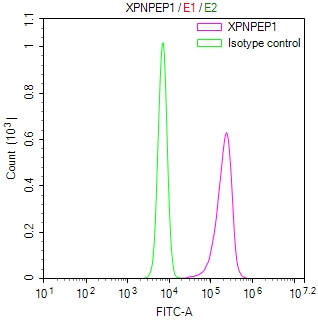
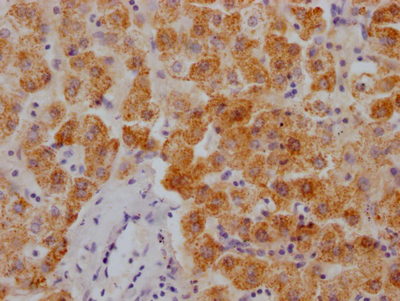
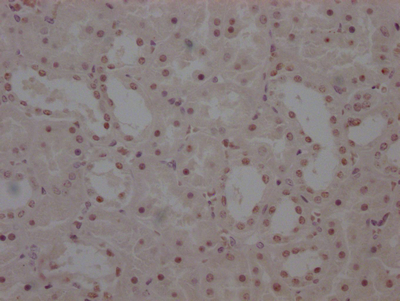
IFNL4 Antibody
-
中文名称:IFNL4兔多克隆抗体
-
货号:CSB-PA20629A0Rb
-
规格:¥440
-
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品名称:Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) IFNL4 Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:
-
基因名:IFNL4
-
别名:IFN-lambda-4 antibody; IFNAN antibody; IFNL4 antibody; IFNL4_HUMAN antibody; Interferon lambda-4 antibody
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human
-
免疫原:Recombinant Human Interferon lambda-4 protein (34-76AA)
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
标记方式:Non-conjugated
本页面中的产品,IFNL4 Antibody (CSB-PA20629A0Rb),的标记方式是Non-conjugated。对于IFNL4 Antibody,我们还提供其他标记。见下表:
-
克隆类型:Polyclonal
-
抗体亚型:IgG
-
纯化方式:>95%, Protein G purified
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存缓冲液:Preservative: 0.03% Proclin 300
Constituents: 50% Glycerol, 0.01M PBS, PH 7.4 -
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
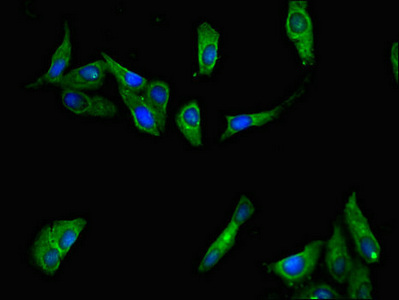
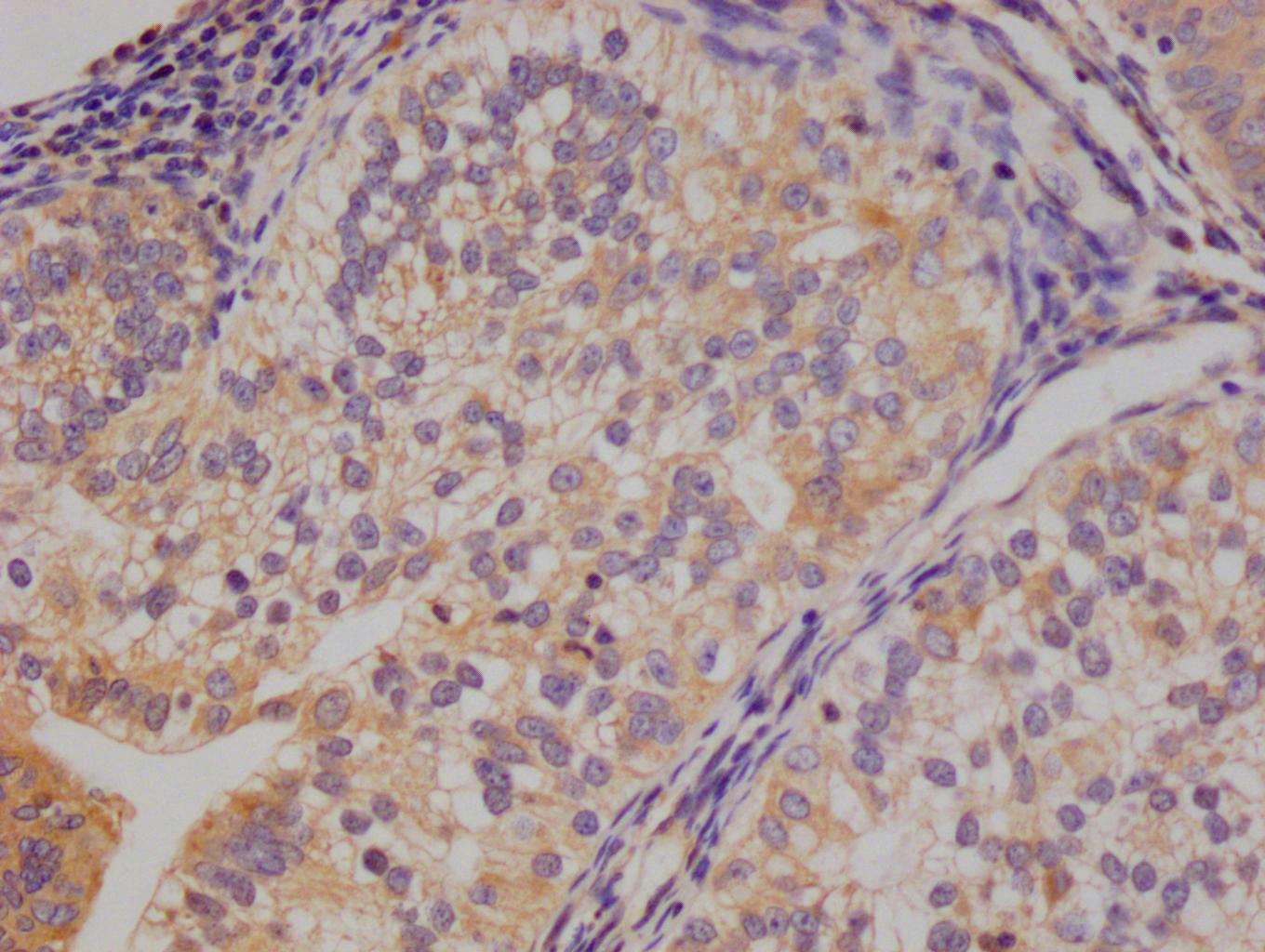
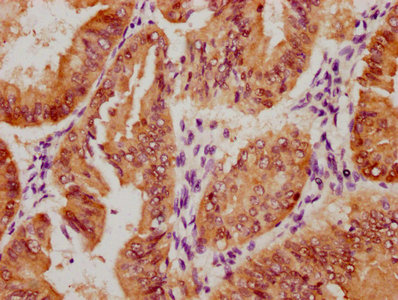
应用范围:ELISA, IF
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution IF 1:50-1:200 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
-
用途:For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Cytokine that may trigger an antiviral response activating the JAK-STAT pathway and up-regulating specifically some interferon-stimulated genes.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- These results demonstrate that virus-induced IFN-lambda4 potently blocks IFN-alpha signalling by inducing high protein levels of ISG15 and USP18. Moreover, the data clearly demonstrate that DAA therapy restores IFN-alpha responsiveness in HCV-infected cells. PMID: 28630501
- The results show that IFNL4 ss469415590 DeltaG/DeltaG genotype was associated with poor virological response to anti-hepatitis C combination therapy. PMID: 30480920
- Studied the association of interferon-lambda 4 (IFNL4)-related polymorphisms and human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-B haplotypes within long-term nonprogressor HIV-1 controllers (LTNP-Cs); HLA-B*57 was independently associated with the LTNP-C phenotype, while IFNL4 genotypes represented independent factors for becoming non-LTNP-C. PMID: 27986689
- IFNL4 genotype might predict DAA-response. PMID: 29866411
- our study validated that IFNL4 ss469415590 was also strongly associated with HCV clearance in Chinese Han population. PMID: 28186161
- IFN-lambda4 suppressed HIV infection of macrophages. This IFN-lambda4-mediated HIV inhibition was compromised by the antibodies against IFN-lambda receptor complex, IFN-lambdaR1/IL-10R2. PMID: 30247785
- Analysis of the IFNL4 polymorphism rs368234815 in association with human papillomavirus (HPV) results, does not suggest its possible role during low or high-risk with HPV infection or in determining HPV outcome (clearance/reinfection or persistence/high-grade lesion). PMID: 29243064
- Significant associations were observed for 4 variants in IFNAR2, IFNLR1 with hepatitis B virus infection, and IFNLR1-rs4649203 was associated with hepatitis B recovery. Moreover, the authors demonstrated the clear relevance of 5 polymorphisms in IFNA1, IFNA2, IFNL4 with hepatocellular carcinoma. PMID: 29080269
- It has been shown that age, spontaneous lymphocyte proliferation, and an IFNL4 polymorphism were associated with progression to HTLV-I-associated myelopathy-tropical spastic paraparesis. PMID: 29129607
- IFNL locus SNPs are subject to either a positive or a negative confounding effect by rs117648444. PMID: 28727946
- Intrahepatic expression of IFNL4 was associated with increased antiviral interferon-stimulated gene (ISG) expression and decreased suppressive ISG expression at baseline, resulting in poor responsiveness to IFNalpha-based therapy in HCV infection. PMID: 28036111
- The association between IFNL3/4 genotypes with elevated HCV VL observed in HCV g6-infected individuals may have implications for the progression of liver disease in Southeast Asian countries where this viral genotype predominates and therefore warrants further studies. PMID: 29022122
- Interferon lambda polymorphisms influence regulatory pathways of cellular response to interferon and affect body iron balance in chronic hepatitis C virus infection. PMID: 27125837
- Studied involvement of two interferon lambda 4 (IFNL4) single nucleotide polymorphisms in predicting sustained virologic response (SVR) following antiviral therapy in patients with inherited bleeding disorder and chronic hepatitis C. PMID: 27735085
- these results suggest unique functional properties of IFN-lambda4 that can be important in viral clearance and other clinical conditions PMID: 29070670
- rs368234815 TT/TT genotype associated with severity of fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease patients of European ancestry PMID: 28741298
- Data show that the genotype distributions of IFNL3 and IFNL4 variants (rs4803217, rs368234815, rs117648444, and rs12979860) were in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. PMID: 28394349
- Data show that interferon lambda 4 (IFNL4) genotypes determine hepatitis C virus (HCV) viral load through a mechanism dependent on a specific amino acid residue in the HCV NS5A protein. PMID: 28394351
- This study provides mechanistic evidence that humans suppress IFNlambda4 expression, suggesting that immune function is dependent on other IFNL family members. PMID: 27799623
- Donor IFNL4 TT/TT genotype, a favorable predictor of spontaneous HCV clearance pre-transplant, is associated with increased early post-transplant fibrosis and decreased survival. PMID: 27875564
- the association of amino acid substitutions in the HCV core protein and the IFNL3 and IFNL4 polymorphisms with the severity of liver disease, particularly in hepatocellular carcinoma development PMID: 27035616
- Population Polymorphism of IFNL3 and IFNL4 Genes of Type 3 Interferon Associated with Spontaneous Clearance of Hepatitis C Virus in Representatives of Caucasian and Mongoloid Races PMID: 27492404
- There was no association between IFNL4 polymorphism and HBV susceptibility or natural clearance. PMID: 27236152
- this meta-analysis suggests that IFNL4 genetic polymorphism may be a predictor of sustained virological response in chronic hepatitis C patients PMID: 27180197
- In this study, there was association of the three isolated polymorphisms (rs8099917, rs12979860 and rs368234815) with both clinical outcome and response to treatment with PEG-IFN and RBV in chronic hepatitis C. PMID: 26973228
- There were no statistically significant differences in endogenous interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs) mRNA levels among HIV-1-positive patients bearing different IFNL4 genotypes, suggesting that ISG expression is independent of the IFNL4 genotype in HIV-1 infection. PMID: 27558125
- Single-nucleotide polymorphisms (rs12979860) in the intronic region of the interferon-lambda4 (IFNL4) gene modulate liver inflammation and fibrosis, in an etiology independent manner. PMID: 26592354
- IFNL4-DeltaG/TT is the primary IFN-lambda region polymorphism for impaired HCV clearance PMID: 26186989
- this report shows that NF-kappa B, IRF3, IRF7, and the GC-rich DNA-binding transcription factor, Sp1, have key roles in stimulating transcription from the IFNL4 promoter. PMID: 26684959
- Despite differences in protein sequences, functional properties of the recombinant human and nonhuman IFN-l4 proteins are comparable-they are all biologically active for induction of interferon signaling. PMID: 26308395
- suggest that IFN-lambda4 protein expression associated with the IL28B-T/T variant preactivates the Janus kinase-Stat signaling PMID: 26896692
- HCV infection is proposed to induce a more efficient antiviral response in individuals with the IFNL4 TT/TT genotype that results either in viral clearance or selection for viral adaptations. PMID: 25849245
- IFN-l4 may have at least 3 functions in human hepatic cells-activation of interferon signaling, inhibition of cell proliferation, and induction of cell death PMID: 26134097
- data on ex vivo derived liver tissue samples argue against an attenuating impact of IFNL3 rs4803217 or IFNL4 rs368234815 minor alleles on hepatic IFNL3 gene expression in vivo. PMID: 26606750
- The described is the association with spontaneous hepatitis C viral clearance and genetic differentiation of IL28B/IFNL4 haplotypes in populations from Mexico. PMID: 26741362
- The hepatitis C protective allele TT was associated with decreased likelihood of HIV-1 infection in male intravenous drug users [odds ratio (OR): 0.3; P = 0.006], and this association was not modified by the genotype of CCR5. PMID: 26372394
- IFNL3 and IFNL4 genotyping could identify those likely to clear naturally and in whom treatment could be delayed, or help prioritize Directly-acting antivirals treatment to those less likely to respond to interferon-containing regimens. PMID: 26150150
- IFNL4-DeltaG/TT genotype was not associated with HSV-related outcomes, including episodes of oral or genital herpes PMID: 26431156
- Transcriptome analysis reveals a classical interferon signature induced by IFNlambda4 in human primary cells PMID: 26066369
- The current study is the first to investigate the effect of IFNL3 and IFNL4 polymorphisms on liver-related mortality. The lower risk of death among African American HIV/HCV-coinfected women is not explained by genetic variation in the IFN-lambda region. PMID: 26115445
- Single Nucleotide Polymorphism of Interferon Lambda-4 Gene is not Associated with Treatment Response to Pegylated Interferon in Chronic Hepatitis B. PMID: 26225703
- Single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the interferon lambda 4 (IFNL4) gene are predictors for treatment success in patients with hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection PMID: 26406534
- Natural selection history of IFNL4-inactivating allele has thus shaped present-day heterogeneity across populations not only in genetic variation, but also in relevant phenotypes and susceptibility to hepatitis C. PMID: 25329461
- The IFNL3.rs12979860 and IFNL4.ss469415590 variants have comparable effects on spontaneous resolution of hepatitis C virus infection among Egyptians. PMID: 25788203
- Interferon-lambda rs12979860 genotype is a strong aetiology-independent predictor of tissue inflammation and fibrosis in viral and non-viral chronic liver disease. PMID: 25740255
- IFNL4 polymorphisms were predictive of treatment outcome only for patients infected with HCV-1. PMID: 25938236
- Females with the IFNL4 genotype detected were more likely to have HCV reclearance. PMID: 25883387
- We found an independent association of the IFNL4 ss469415590 polymorphism with higher prevalence of AIDS-defining illnesses and lower CD4 T cell numbers. PMID: 25658540
- Overexpression of IFNlambda4 suppressed IL28B induction and promoter activation. PMID: 25611696
- IFNL4 and IFNL3 associated polymorphisms strongly influence the spontaneous IFN-alpha receptor-1 expression in HCV-infected patients PMID: 25675103
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm. Secreted.
-
蛋白家族:Lambda interferon family
-
数据库链接:
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-