-
中文名称:大鼠肺表面活性物质相关蛋白D(SP-D)酶联免疫试剂盒
-
货号:CSB-E12632r
-
规格:96T/48T
-
价格:¥3600/¥2500
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品描述:CUSABIO专为大鼠样本设计的肺表面活性物质相关蛋白D(SP-D)定量检测试剂盒(货号:CSB-E12632r),采用双抗体夹心酶联免疫吸附法原理,可精准检测血清、血浆及组织匀浆中的SP-D含量。SP-D属于胶原凝集素家族蛋白,主要由肺泡Ⅱ型上皮细胞分泌,在肺部免疫防御中发挥重要作用,通过调节炎症反应和病原体清除参与呼吸系统疾病病理机制。试剂盒线性检测范围为0.312-20 ng/mL,最低检测限达0.078 ng/mL,实验流程仅需3.5小时即可完成。所有组分经预包被处理,包含标准品、检测抗体及显色底物,开盒即用,配套提供详细操作指南。适用于科研领域探究肺部疾病模型(如肺纤维化、急性肺损伤或感染性疾病)中SP-D的动态变化,也可用于评估药物干预对肺表面活性物质代谢的影响。试剂盒组分需保存在-20°C环境下,开封后建议6个月内使用完毕,避免反复冻融以保证检测稳定性。
-
别名:Sftpd ELISA Kit; Sftp4 ELISA Kit; Pulmonary surfactant-associated protein D ELISA Kit; PSP-D ELISA Kit; SP-D ELISA Kit; CP4 ELISA Kit; Lung surfactant protein D ELISA Kit
-
缩写:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
种属:Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
样本类型:serum, plasma, tissue homogenates
-
检测范围:0.312 ng/mL-20 ng/mL
-
灵敏度:0.078 ng/mL
-
反应时间:1-5h
-
样本体积:50-100ul
-
检测波长:450 nm
-
研究领域:Signal Transduction
-
测定原理:quantitative
-
测定方法:Sandwich
-
精密度:
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): CV%<8% Three samples of known concentration were tested twenty times on one plate to assess. Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): CV%<10% Three samples of known concentration were tested in twenty assays to assess. -
线性度:
To assess the linearity of the assay, samples were spiked with high concentrations of rat SP-D in various matrices and diluted with the Sample Diluent to produce samples with values within the dynamic range of the assay. Sample Serum(n=4) 1:5 Average % 88 Range % 82-92 1:10 Average % 94 Range % 90-99 1:20 Average % 95 Range % 91-101 1:40 Average % 94 Range % 90-98 -
回收率:
The recovery of rat SP-D spiked to levels throughout the range of the assay in various matrices was evaluated. Samples were diluted prior to assay as directed in the Sample Preparation section. Sample Type Average % Recovery Range Serum (n=5) 89 85-96 EDTA plasma (n=4) 92 87-98 -
标准曲线:
These standard curves are provided for demonstration only. A standard curve should be generated for each set of samples assayed. 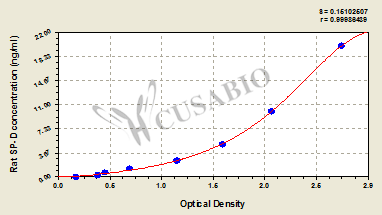
ng/ml OD1 OD2 Average Corrected 20 2.689 2.697 2.693 2.508 10 2.001 2.054 2.028 1.843 5 1.555 1.579 1.567 1.382 2.5 1.112 1.165 1.139 0.954 1.25 0.687 0.697 0.692 0.507 0.625 0.442 0.475 0.459 0.274 0.312 0.382 0.396 0.389 0.204 0 0.184 0.186 0.185 -
数据处理:
-
货期:3-5 working days
引用文献
- Assessment of Biochemical and Molecular Biomarkers for Diagnosis\Prognosis of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia in Iraqi Patients Seiffert J.et al,Respir Res.,2016
- Infliximab attenuates activated charcoal and polyethylene glycol aspiration-induced lung injury in rats /,Experimental Lung Research,2012
- The effect of curcumin on lung injuries in a rat model induced by aspirating gastrointestinal decontamination agents Gunaydin M et al,J Pediatr Surg,2012
- The role of iNOS inhibitors on lung injury induced by gastrointestinal decontamination agents aspiration /,Journal of Molecular Histology,2012
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Contributes to the lung's defense against inhaled microorganisms, organic antigens and toxins. Interacts with compounds such as bacterial lipopolysaccharides, oligosaccharides and fatty acids and modulates leukocyte action in immune response. May participate in the extracellular reorganization or turnover of pulmonary surfactant. Binds strongly maltose residues and to a lesser extent other alpha-glucosyl moieties.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- in acute lung injury, serum level increased from day 5, peaked on day 10, and then gradually decreased until day 28 PMID: 27541374
- SPA binds dipalmitoyl-phosphatidylcholine, the major surfactant lipid component, but not phosphatidylinositol; SPD exhibits the opposite preference. Data suggest flexibility in a key surface loop supports distinctive lipid binding of SPA; quadruple mutant SPA (E171D/P175E/R197N/K203D) that introduces SPD-like loop-stabilizing Ca2+ binding site in carbohydrate recognition domain exhibits ligand-binding preferences of SPD. PMID: 28719181
- In rat SP-D overexpressed mice, the lipopolysaccharide-induced levels of TNF-alpha and IL-10 in amniotic fluid and fetal serum and the expression of IL-10 in placenta and fetal membranes were significantly different from wild-type mice. PMID: 22892325
- Surfactant protein D modulated subpollen particle uptake in a cell type specific way (e.g. greater number of macrophages and epithelial cells, which participated in allergen particle uptake) and led to a decreased secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines. PMID: 22296755
- Silica exposure causes dynamic changes of SP-D and CC16 protein expression in lung tissue and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. PMID: 19080379
- An extended binding site for influenza A virus; calcium-dependent antiviral activity involves residues flanking the primary carbohydrate binding site as well as more remote residues displayed on the carbohydrate recognition domain surface. PMID: 20601494
- SP-D promotes attachment of allergen-containing subpollen particles to epithelial cells and may thus be involved in the inflammatory response to inhaled allergen. PMID: 20569420
- analysis of myeloperoxidase-dependent inactivation of surfactant protein D in vitro and in vivo PMID: 20228064
- Results suggest that SP-D-dependent processes regulating surfactant lipid homeostasis were disassociated from those mediating emphysema. PMID: 12163500
- Heterogeneous allele expression of SP-D mRNA in large intestine and other tissues. PMID: 12464693
- SP-A and SP-D are antimicrobial proteins that directly inhibit the proliferation of Gram-negative bacteria in a macrophage- and aggregation-independent manner by increasing the permeability of the microbial cell membrane PMID: 12750409
- SP-A and SP-D are antimicrobial proteins that directly inhibit the growth of Histoplasma capsulatum by increasing permeability of the organism PMID: 12857753
- SP-D interacts with chlamydial pathogens and enhance their phagocytosis into macrophages PMID: 15075250
- Degradation of pulmonary surfactant protein D by Pseudomonas aeruginosa elastase abrogates innate immune function PMID: 15123664
- SP-A and SP-D enhance mannose receptor-mediated phagocytosis of M. avium by macrophages PMID: 15187139
- results indicated SP-A & SP-D have distinct functions in lung homeostasis & the function of the neck domain & carbohydrate recognition domain of SP-D is dependent on its own NH2-terminal & collagenous domains that cannot be complemented by those of SP-A PMID: 16500946
- The ligand binding of homologous human, rat, and mouse trimeric trimeric neck plus carbohydrate recognition domain (neck+CRD) fusion proteins, each with identical N-terminal tags remote from the ligand-binding surface, was compared. PMID: 16514117
- VEGF increased expression of SP-D mRNA in preterm rat lung. PMID: 17267143
- Interactions with the side chain of inner core heptoses provide a potential mechanism for the recognition of diverse types of lipopolysaccharides by SP-D. PMID: 18092821
- These results show that antiviral activities of surfactant protein-D can be reproduced without the N-terminal and collagen domains and that cross-linking of these domains is essential for anti-influenza A virus activity. PMID: 18302538
- After OVA challenge alveolar epithelial cells Type II (AEII) show a significantly higher expression of SP-A and SP-D leading also to higher amounts of both SPs in BALF, and macrophages gather predominantly SP-A. PMID: 18802356
- S-nitrosylation of SP-D causes quaternary structural alterations and a swtich to its inflammatory signaling role. PMID: 19007302
- Multimerization of surfactant protein D, but not its collagen domain, is required for antiviral and opsonic activities related to influenza virus. PMID: 19017984
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Secreted, extracellular space, extracellular matrix. Secreted, extracellular space, surface film.
-
蛋白家族:SFTPD family
-
数据库链接:
Most popular with customers
-
Human Transforming Growth factor β1,TGF-β1 ELISA kit
Detect Range: 23.5 pg/ml-1500 pg/ml
Sensitivity: 5.8 pg/ml
-
-
-
Mouse Tumor necrosis factor α,TNF-α ELISA Kit
Detect Range: 7.8 pg/ml-500 pg/ml
Sensitivity: 1.95 pg/ml
-
-
-
-