-
中文名称:人胆囊收缩素/肠促胰酶肽(CCK)酶联免疫试剂盒
-
货号:CSB-E08116h
-
规格:96T/48T
-
价格:¥3600/¥2500
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品描述:人胆囊收缩素/肠促胰酶肽(CCK)酶联免疫试剂盒(CSB-E08116h)为双抗夹心法ELISA试剂盒,定量检测血清、血浆、组织匀浆样本中的CCK含量。CCK即胆囊收缩素,在生理上可调节胆囊收缩、胃肠运动等。研究机制方面,它通过与相关受体结合发挥作用,在神经系统和消化系统中参与多种生理功能调节,其信号通路的研究对理解神经胃肠病等疾病发病机制有重要意义。试剂盒检测范围为56 pg/mL-800 pg/mL,该产品可应用于胃肠功能研究、摄食行为神经机制探索、代谢综合征模型评估等科研领域,特别适合需要精确测定生物体液或组织样本中CCK动态变化的实验设计,其宽检测范围可满足基础研究中正常生理水平到病理状态下的浓度检测需求。本品仅用于科研,不用于临床诊断,产品具体参数及操作步骤详见产品说明书。
-
别名:(1-49)-CCK58 ELISA Kit; CCK ELISA Kit; CCK12 ELISA Kit; CCK18 ELISA Kit; CCK25 ELISA Kit; CCK33 ELISA Kit; CCK39 ELISA Kit; CCK5 ELISA Kit; CCK58 ELISA Kit; CCK7 ELISA Kit; CCK8 ELISA Kit; CCKN_HUMAN ELISA Kit; Cholecystokinin-5 ELISA Kit
-
缩写:CCK
-
Uniprot No.:
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
样本类型:serum, plasma, tissue homogenates
-
检测范围:56 pg/mL-800 pg/mL
-
灵敏度:20 pg/mL
-
反应时间:1-5h
-
样本体积:50-100ul
-
检测波长:450 nm
-
研究领域:Metabolism
-
测定原理:quantitative
-
测定方法:Sandwich
-
精密度:
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): CV%<15%
Three samples of known concentration were tested twenty times on one plate to assess.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): CV%<15%
Three samples of known concentration were tested in twenty assays to assess.
-
线性度:
To assess the linearity of the assay, samples were spiked with high concentrations of human CCK in various matrices and diluted with the Sample Diluent to produce samples with values within the dynamic range of the assay.
Sample
Serum(n=4)
1:1
Average %
94
Range %
80-98
1:2
Average %
95
Range %
91-105
1:4
Average %
87
Range %
82-94
1:8
Average %
93
Range %
86-98
-
回收率:
The recovery of human CCK spiked to levels throughout the range of the assay in various matrices was evaluated. Samples were diluted prior to assay as directed in the Sample Preparation section.
Sample Type
Average % Recovery
Range
Serum (n=5)
95
89-98
EDTA plasma (n=4)
93
90-100
-
标准曲线:
These standard curves are provided for demonstration only. A standard curve should be generated for each set of samples assayed.
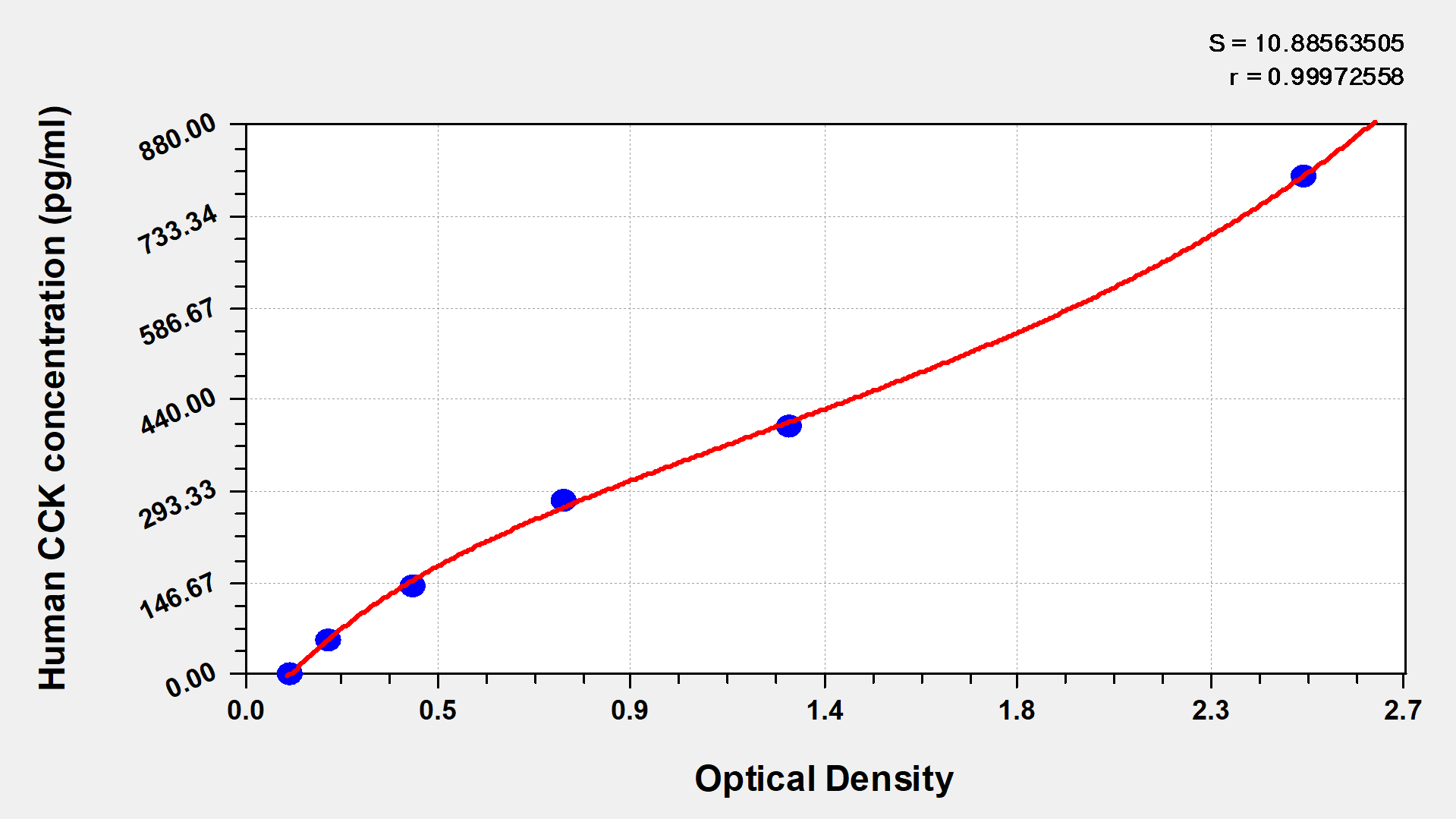
pg/ml
OD1
OD2
Average
Corrected
800
2.453
2.504
2.478
2.478
400
1.275
1.287
1.281
1.281
280
0.756
0.748
0.752
0.752
144
0.395
0.410
0.402
0.402
56
0.200
0.205
0.203
0.203
0
0.112
0.113
0.113
0.113
-
数据处理:
-
货期:3-5 working days
引用文献
- Increased energy intake after pregnancy determines postpartum weight retention in women with obesity Most J,J Clin Endocrinol Metab,2020
- Appetite Suppression and Altered Food Preferences Coincide with Changes in Appetite-Mediating Hormones During Energy Deficit at High Altitude Karl J. Philip.et al,High Altitude Medicine & Biology,2018
- Acute effect of smoking and smoking abstinence on energy intake and appetite-related hormones blood concentrations Yannakoulia M.et al,Physiol Behav,2017
相关产品
相关问答
I would like to ask you if you know what is the most common sample dilution in human CCK elisa kit?
CSB-E08116h, generally there is no need to dilute when detecting.
And if you arrange the preliminary test and find the sample needs dilution, pls consider to use the PBS.
靶点详情
-
功能:This peptide hormone induces gall bladder contraction and the release of pancreatic enzymes in the gut. Its function in the brain is not clear. Binding to CCK-A receptors stimulates amylase release from the pancreas, binding to CCK-B receptors stimulates gastric acid secretion.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- We found the suicide-associated gene coexpression network. The reconstructed network consisted of 104 genes. Topological analysis showed that in total, CCK, INPP1, DDC, and NPY genes are the most fundamental hubs in the network PMID: 29381655
- L-trp is a luminal regulator of CCK release with effects on gastric emptying, an effect that could be mediated by CCK. L-trp's effect on GLP-1 secretion is only minor. At the doses given, the two amino acids did not affect subjective appetite feelings. PMID: 27875537
- The CCK polymorphism have reported significant association of -45C>T polymorphism with the presence of hallucinations. PMID: 27084212
- CCK does not appear to play a unique independent role in satiety/satiation. PMID: 26429068
- CCK release has been found to be halved in pregnant women with hyperemesis gravidarium, which supports the hypothesis that gastrointestinal motility is increased in pregnant women with hyperemesis gravidarium. PMID: 25331205
- CCK in plasma is an independent marker of cardiovascular mortality in elderly female patients. PMID: 26878472
- These data offer preliminary evidence supporting an association between the rs1799923 polymorphism in the CCK gene and PTSD PMID: 26454231
- Data suggest that endocrine responses differ between jejunal and gastric enteral feeding, with higher peak plasma CCK (cholecystokinin), PYY (peptide YY), and GLP-1/2 (glucagon-like peptides 1/2) concentrations being attained after jejunal feeding. PMID: 26762368
- active GLP-1 produced in the islet stimulates cholecystokinin production and secretion in a paracrine manner via cyclic AMP and CREB. PMID: 25984632
- Cardiac expression of pro-cholecystokinin is cell-specific, which differentiates the expression from that of intestinal endocrine cells and cerebral neurons. Plasma Pro-CCK is a prognostic marker in patients with stable heart failure. PMID: 25627687
- CCK binding modulates the contractile function of the lower esophageal sphincter through differential binding to the CCK-A receptor on the sling and clasp fibers PMID: 24914377
- Data suggest that up-regulation of plasma CCK levels is 50% higher following breakfast of meal replacement beverage containing fat emulsion of rapeseed oil with droplet size of 0.1 um (versus 0.3 um); satiety response and food intake are unaffected. PMID: 23975326
- These studies identify a key role for Cck in the development and treatment of mania. PMID: 23399917
- Results suggest excessive local release of CCK in response to duodenal lipid in functional dyspepsia. PMID: 24252886
- CCK enhances cholesterol absorption by activation of a pathway involving CCK1R/CCK2R, Gbetagamma, PI3K, Akt, Rab11a, and NPC1L. PMID: 24692543
- This review will summarize what is known regarding CCK, its receptors, and pancreatic--{REVIEW} PMID: 24177032
- We aimed to determine whether fasting or meal-stimulated ghrelin, PYY, CCK, and satiety responses are different between lean PCOS patients and healthy women. PMID: 24001751
- hnRNP-K regulates extracellular matrix, cell motility, and angiogenesis pathways. Involvement of the selected genes (Cck, Mmp-3, Ptgs2, and Ctgf) and pathways was validated by gene-specific expression analysis PMID: 23564449
- Normal CCK profiles in AN at admission indicates hormonal responses adapted to low food intake while change of eating habits and weight gain PMID: 23349895
- CD36 is a major mediator of FA-induced release of CCK and secretin. These peptides contribute to the role of CD36 in fat absorption and to its pleiotropic metabolic effects. PMID: 23233532
- a lineage of mature enteroendocrine cells have the ability to coexpress members of a group of functionally related peptides: CCK, secretin, GIP, GLP-1, PYY, and neurotensin PMID: 23064014
- CCK remarkably increases the firing frequency of action potentials of layer III pyramidal neurons in the entorhinal cortex. PMID: 21753024
- CCK gene -45C/T locus T allele was positively associated with schizophrenia in female Han population in northern China. PMID: 21542221
- it is likely that unsulfated CCK peptides constitute a separate hormone system that acts via CCK-B receptors. [review] PMID: 21985915
- This article reviews the role of cholecystokinin (CCK), a satiety-producing hormone, in the regulation of binge eating in those who suffer from bulimia nervosa [review] PMID: 22188045
- The results of this study demonistrated that the cholecystokinin polymorphisms is related toin Parkinson's disease hallucinations in asian group. PMID: 21506165
- CCK modulates intrinsic neuronal excitability and synaptic transmission in a surprisingly cell-type specific manner, acting as a key molecular switch to regulate the functional output of neuronal circuits. PMID: 21154912
- Cholecystokinin gene polymorphisms are not associated with antipsychotic induced weight gain in schizophrenia patients. PMID: 20732371
- Neither treatment of pancreatic cancer cells with CCK antibodies nor the down-regulation of CCK mRNA and peptide by shRNAs altered growth in vitro or in vivo. PMID: 21186400
- These results point to a potential route of action by which components of Hoodia might influence appetite control; the natural taste receptor antagonist was identified for further studies as an appetite suppressant. PMID: 20930049
- Study compared CCK-like immunoreactivity (CCK-LI) in plasma from 25 subjects in the late luteal phase (LLP) and the follicular phase (FP) and found that there was no difference during the menstrual cycle PMID: 20457200
- results suggest that the CCK system may play a role in the pathogenesis of panic disorder, with susceptibility alleles both protecting and contributing to the disease PMID: 20023595
- REVIEW: role in thermoregulation and other aspects of energetics PMID: 20036221
- Cefaclor, when given before a meal in the form of a capsule, does not stimulate CCK release or slow gastric emptying in healthy humans. PMID: 19914303
- This article reviews the corpus of work supporting the role of CCK in anxiety and suggests three research approaches which can further enhance our understanding of the CCK-2 system in panic disorder. PMID: 11713976
- This review describes the signaling pathways and transcription factors involved in neuronal CCK gene transcription. PMID: 11713982
- Endoproteolytic processing events of heterologously expressed cholecystokinin are studied in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PMID: 11713985
- mapping of the CCK1R binding site by identifying residues that interact with the methionine and phenylalanine residues of the C-terminal moiety of CCK PMID: 11724786
- Deteriorating gallbladder contractions, possibly induced by alterations in the CCK-AR gene, as well as CCK-AR gene polymorphism, promoted gallstone formation. PMID: 12572876
- Results suggest that the L-(-188G) haplotype may act as a protective factor against panic by reducing the expression of anxiogenic cholecystokinin (CCK). PMID: 12627463
- in Chinese, visual hallucinations in Parkinson's disease are associated with cholecystokinin -45C>T polymorphism, and this association was still observed in the presence of the cholecystokinin-A receptor TC/CC genotype PMID: 12777967
- reduced basal hunger, rather than increased meal-induced satiety, contributes to the anorexia of aging and that changes in cholecystokinin are unlikely to be responsible PMID: 12915664
- CCK's suppression of food intake is enhanced when the stomach is distended. PMID: 12920059
- Ingestion of a CCK-releasing fatty acid reduces the tolerated volume of liquid delivered into the stomach, primarily via a CCK(1) receptor-mediated delay in gastric emptying. PMID: 14764444
- Review summarizes the physiological role of CCK not only in the stimulation of pancreatic and biliary secretions but also in the regulation of gastrointestinal motility. PMID: 15100163
- Study based on a small, well-characterized matched case-control group of patients with Parkinson disease (PD) suggests that the cholecystokinin system may influence the development of hallucinations in PD subjects. PMID: 15313848
- Ewing sarcomas synthesize and secrete proCCK that can be identified in plasma as circulating tumor marker. PMID: 15328192
- CCK regulates pancreatic enzyme secretion and growth, intestinal motility, satiety signalling and the inhibition of gastric acid secretion--REVIEW PMID: 15533776
- conclude that women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) have reduced postprandial cholecystokinin(CCK) secretion and deranged appetite regulation associated with increased levels of testosterone PMID: 15624269
- Gastrin and CCK exert a trophic action on some of the biliary tract cancers. PMID: 15682471
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Secreted.
-
蛋白家族:Gastrin/cholecystokinin family
-
数据库链接:
Most popular with customers
-
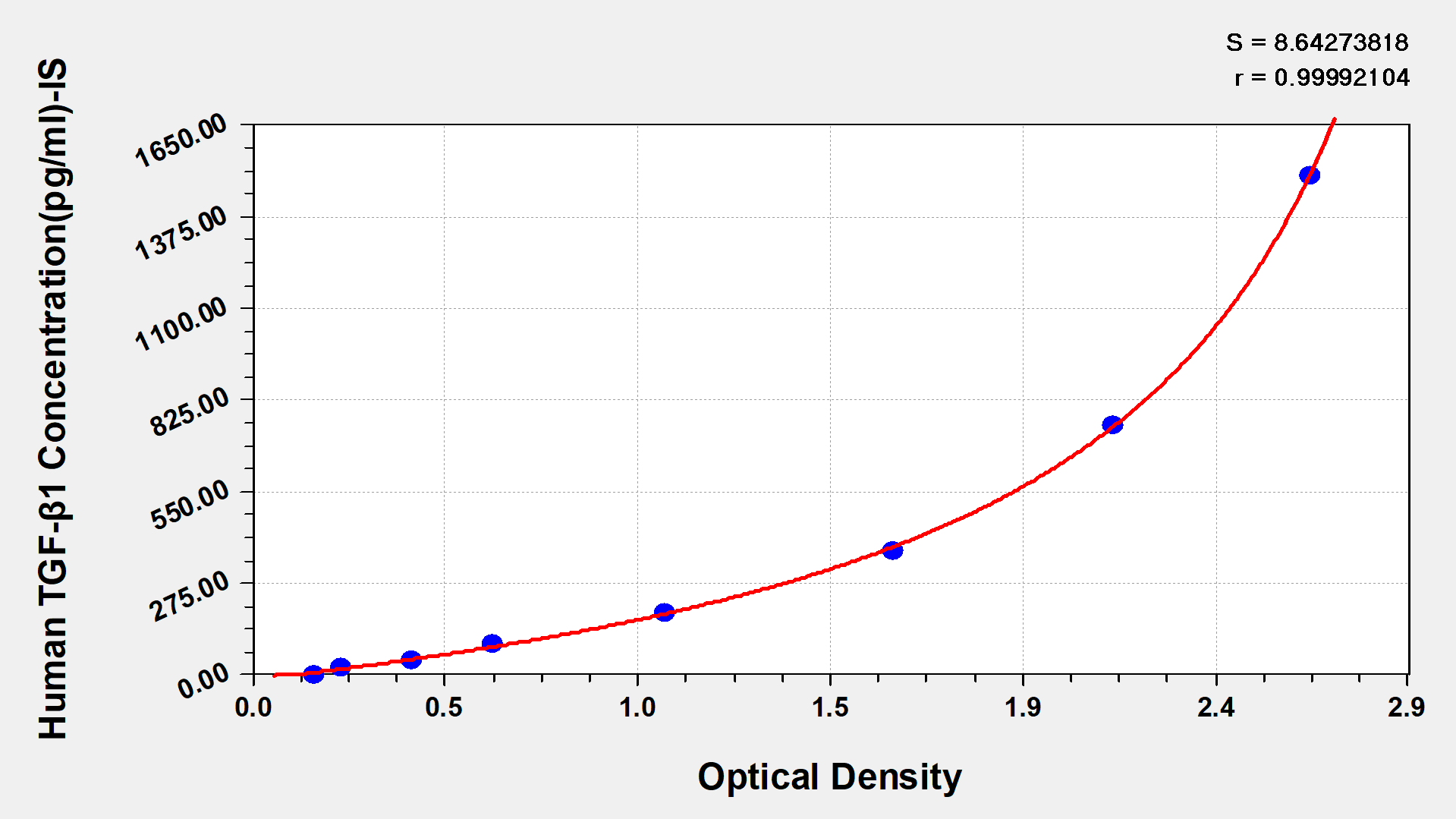
Human Transforming Growth factor β1,TGF-β1 ELISA kit
Detect Range: 23.5 pg/ml-1500 pg/ml
Sensitivity: 5.8 pg/ml
-
-
-
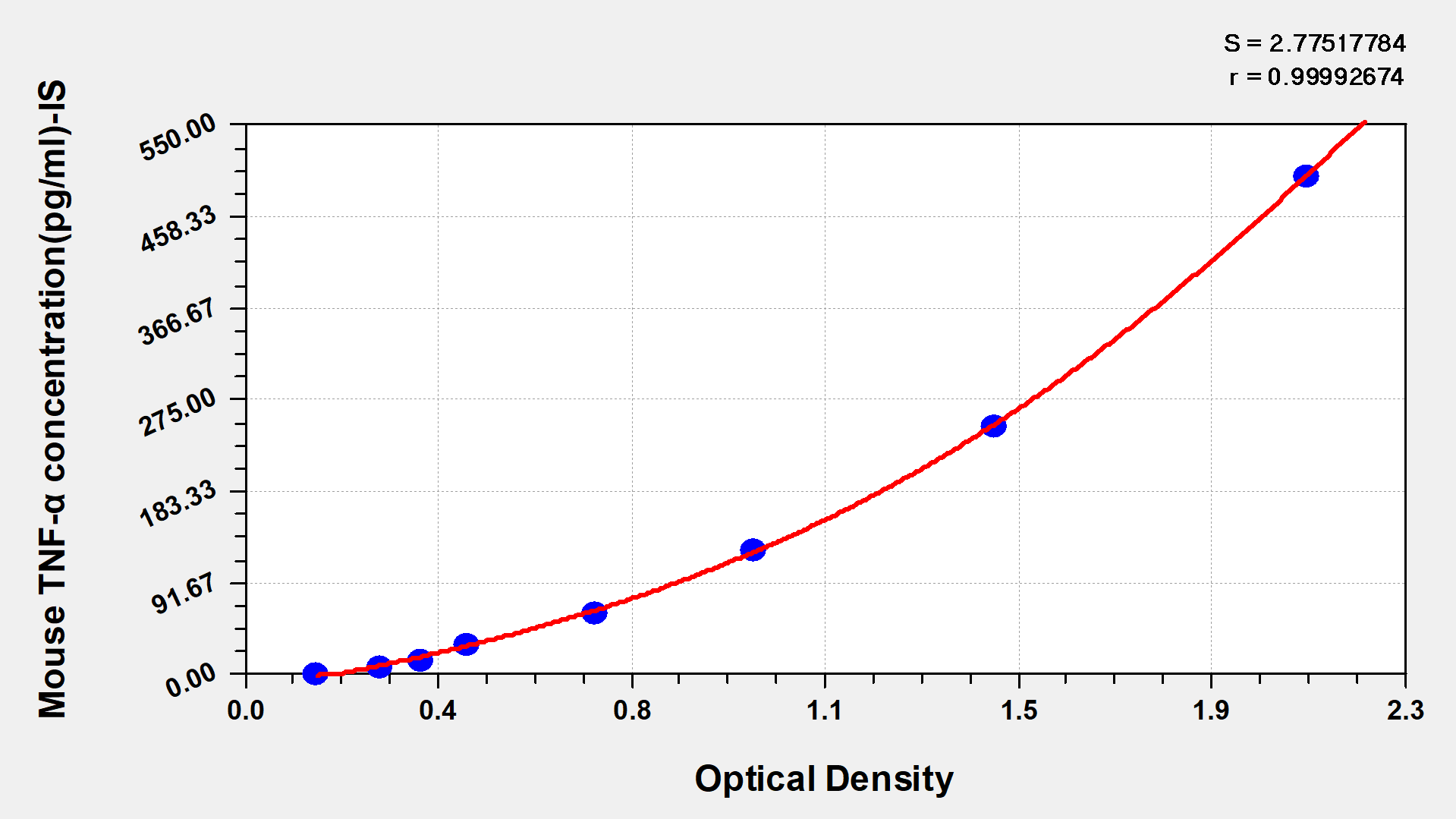
Mouse Tumor necrosis factor α,TNF-α ELISA Kit
Detect Range: 7.8 pg/ml-500 pg/ml
Sensitivity: 1.95 pg/ml
-
-
-
-